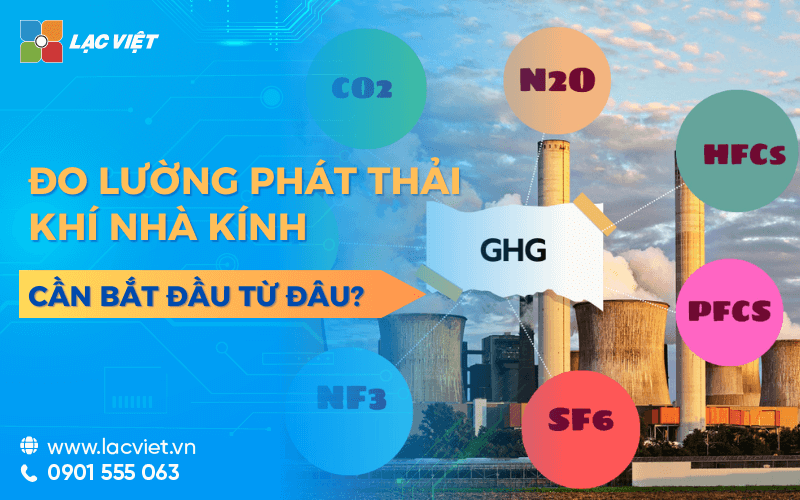
In the context of energy resources increasingly scarce, operating costs increasing, energy audit become an integral solution for the organizations and enterprises. This is not just a measurement tool, efficient energy use, but also is the key to optimize operation and reduce costs, minimize environmental impact.
This article Lac Viet Computing will help you understand more about energy audit, the type of audit common, the implementation process and the actual benefits that it brings.
1. Audit what is energy?
1.1. Definition
Energy audit is a process of analysis, evaluation, and measuring energy use at a manufacturing facility or organization. The main goal of this process is to identify opportunities to improve performance, energy use, reducing waste. This is the first step for enterprises to understand the energy consumption of his, from which the given measure, optimize, energy-saving, effective.

Main characteristics:
- Focus on the identification of source energy consumption is not effective.
- Give specific solutions to reduce energy consumption while maintaining or improving operational efficiency production.
- Data collected in the audit is used as a basis for strategic planning and long-term energy.
1.2. The purpose of the energy audit
Energy audit helps to reduce operating costs and benefits strategy for business:
- Identify the sources of energy consumption main: system analysis energy current to find out the device or process energy consumption biggest. For example, A factory can detect system boiler consumption to 40% of the overall energy, while performance reaches only 70%.
- Given the technical solution: provide specific recommendations as replacement of equipment, improved technology, or apply measures to save energy. For example: Replace old gas compressors by type of energy-saving, can reduce 20% of the cost of power.
- Contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions: The optimization of energy use not only reduce consumption, but also reduce CO2 emissions, help businesses achieve international standards on the environment.
- Save operating costs: Businesses often reduced from 10-30% in energy costs after the implementation of the solution from the energy audit.
2. Types of energy audit
2.1. Energy audit preliminary
This is a form of auditing, fast, focused on identifying basic issues and potential energy savings in a short time.
Characteristics:
- Collects data overview of the energy system.
- Identify opportunities to improve easily and quickly.
- Suitable for new business start deployment of energy solutions.
For example: A manufacturing enterprise discovered that the lighting system using fluorescent lights consume more energy. The replacement by LED lights, saves 50% energy costs for lighting.
Advantages: low Cost, rapid implementation. Helps business identify the big problems without the need for in-depth analysis.
2.2. Energy audit details
This is the form of a comprehensive audit, including in-depth analysis of all the system energy consumption in business.
Characteristics:
- Comprehensive testing from the system boiler, HVAC, production line, to lighting system.
- Use measurement equipment modern to collect accurate data.
- Give detailed report with clear recommendations, including investment costs and benefits of energy savings.
Results: A factory after a detailed audit noticed HVAC systems consumption to 30% of the overall energy performance of low. After improvements, the performance increase by 20%, save 50,000 USD/year.
Advantages: Suitable for businesses that want to optimize the comprehensive energy efficiency. Bring long-term effectiveness and sustainability.
2.3. Energy audit peculiarities
Energy audit special focus on a system or specific areas of business, such as steam oven, production line, or HVAC systems.
Characteristics:
- Just analyze a specific aspect to come up with solutions to save energy, the most optimal.
- Save time, costs more than comprehensive audit.
For example, A company audit boiler and discovered that the old system drain too much energy. The upgrade or maintenance help reduce fuel consumption up to 15%.
Advantages:
- Effective in solving specific problems.
- In accordance with the business have limited resources but want to improve efficiency in a certain field.
3. Implementation process of energy audit
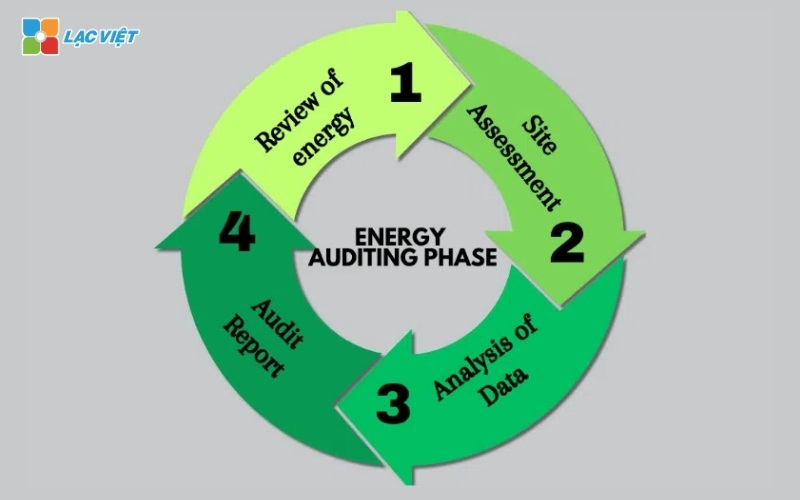
Step 1. Collect initial data
Objective: to Understand the situation of energy consumption current of the business. Determine the source drain of energy.
How to perform:
- Collect energy bills, the measurement data from the device, the report production.
- Record information about the operation of the system energy consumption, such as operating time, fuel consumption.
Step 2. Inspection and analysis of energy systems
Objective: to analyze in detail each system to identify issues, opportunities improve.
How to perform:
- Check the performance of the boiler, air compressor, HVAC systems and production lines.
- Assess the level of energy consumption of each system compared to the standard performance.
Practical examples: A plant discovered that the boiler is operating at 70% efficiency, while the standard is 85%.
Step 3. Proposed solution energy saving
Objective: to Provide specific recommendations to reduce energy consumption, optimize operation.
How to perform:
- Replace the device energy consumption grew by modern technology, save energy.
- Apply measures such as pipe insulation, periodic maintenance, control automation.
Practical example: Replace old gas compressors by types of energy saving helps to reduce 20% cost in power.
Step 4. Reports, energy audit
Objective: synthesis of the results of the audit, the recommended solution, the expected benefit.
Content report:
- The source drain of the energy.
- Investment costs and benefits energy savings of each solution.
- Payback time is expected for each solution.
Practical example: A business get audit report proposed alternative system lighting by LEDS with a total investment cost of $ 50,000, saving $ 25,000/year, payback in 2 years.
4. Benefits of energy audits for business
4.1. Cost savings
Helps business identify areas consumption of energy, given the solution to optimize use. This not only reduces energy consumption, but also significantly reduced operating costs.
- Rate cost savings: businesses apply the solution from the audit can be reduced from 10-30% of the energy cost.
- Practical example: A paper factory in Vietnam savings is $ 50,000/year after replacing the lighting system using LEDS and upgrading HVAC systems.
4.2. Increase production performance
Besides the cost savings, the audit also improve the performance of production systems, increasing the durability of the device.
Optimized operation process:
- Reduce the downtime of equipment due to technical errors related to energy.
- Improve the quality of products thanks to equipment operation more stable.
For example, A textile company after the audit has upgraded production line, increasing performance up to 15%, while reducing electricity consumption.

4.3. Reduce greenhouse gas emissions
Plays an important role in reducing CO2 emissions and greenhouse gases other, help business meet the goal of environmental protection, credits carbon.
Measurement and control of emissions to Help businesses determine the amount of CO2 emissions from each activity and give measures to minimize.
For example: A business cement production cut 20,000 tons CO2/year thanks to optimized systems, furnaces and use alternative fuels.
4.4. Meet international standards
Energy audits help businesses comply with international standards such as ISO 50001 and the GHG Protocol, from which enhance brand reputation, create competitive advantage on the market.
- ISO 50001: international standard on energy management to help businesses optimize performance and minimize energy waste.
- GHG Protocol: business guide measurement and reporting of greenhouse gas emissions according to global standards.
- Specific benefits: Easy to market participants credits carbon international. Attract investor interest in ESG (Environmental, Social and Governance).
5. The tools and standards support
5.1. ISO 50001
ISO 50001 is the international standard for energy management, designed to help businesses improve the performance of energy use and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Application: Evaluation and optimization of the entire energy system. Construction of the monitoring process, continuous improvement.
- Benefits: Increased performance using energy from 10-15% in the first year of application. Reduce CO2 emissions, help businesses achieve their sustainability goals.
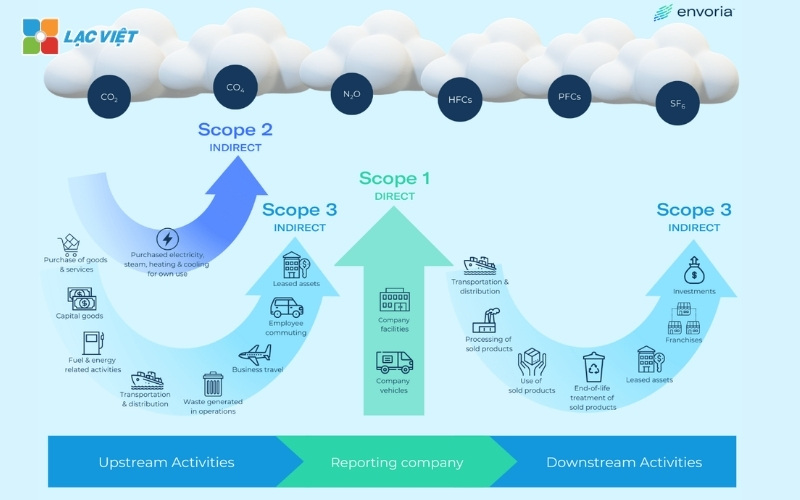
5.2. GHG Protocol
GHG Protocol provides detailed instructions for enterprises to measure, report the amount of greenhouse gas emissions.
- Range: Measuring emissions direct (Scope 1), indirect energy (Scope 2) and other activities in the supply chain (Scope 3).
- Benefits: Increase the transparency and reliability of data emissions. Is the basis for building business strategies for the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
5.3. Tool energy audit
The tool energy audit business support, collecting and analyzing data from which performance optimization of energy use.
- RETScreen: assessment tools, energy efficiency, renewable energy. Support analysis, investment costs, benefits, energy saving.
- EnergyPlus: software, system simulation building energy. Help business optimize your HVAC system and lighting.
- Practical example: A business using RETScreen to analyze the system installation, solar energy, determined that they could reduce 30% energy cost within 5 years.
6. Regulations on energy audit in Vietnam and international
6.1 Regulations in Vietnam
In Vietnam, the energy audit is specified in the Law on energy Use and efficiency savings, 2010, guidelines for implementation. The business use of energy to perform the audit periodically to ensure compliance with legal requirements.
Mandatory subjects made:
- Business, large energy consumption, including: The production facilities consume over 1,000 TOE/year (tons of oil equivalent). Buildings consume over 500 TOE/year.
- The organizations and agencies of public administration under request list.
Frequency of audit: The business subject to mandatory to conduct an audit at least 3 years/times.
Processes, and standards:
- Process audit must comply with the technical standard is Ministry of Industry and Trade regulations.
- The audit report must state the solution energy saving and route taken.
Sanctions: businesses not to comply with regulations can be fined administrative, depending on the severity of the violation.
6.2. The international standard on energy audits
In addition to the regulations in the country, many businesses still apply international standards to ensure they meet global requirements and enhance competitiveness.
- ISO 50001 – energy Management: ISO 50001 is the international standard for energy management, providing specific guidance to optimize the efficient use of energy. Be more business globally applied to achieve energy saving, emission reduction.
- GHG Protocol – protocol greenhouse gases: the ultimate guide to measuring and reporting of greenhouse gas emissions from the active use of energy. The basis for business building strategies to reduce emissions, to meet the requirements for credits carbon.
- Program energy audit of EU (Energy Efficiency Directive): EU requires the large business done periodically to enhance the efficient use of energy in the block.
7. Examples of practices on energy audit success
7.1. Nestlé: Reduce energy consumption and global CO2 emissions
Nestlé, one of the leading corporations in the world of food, drinks, has deployed program energy audit at all his plants around the globe. Their goal is to optimize energy efficiency, reduce greenhouse gas emissions towards sustainable development.
- Strategy: perform detailed audit system produced at each plant. Focus on the system energy consumption as big as the boiler, chain packing, HVAC system.
- Results: Reduction of 15% of energy consumption within 5 years. Cut hundreds of thousands of tons of CO2 emissions per year, contributing significantly to the goal of reducing global emissions of the company.
- Lesson: energy audit not only bring economic benefits, but also helps to improve brand image as a responsible business with the environment.
7.2. Toyota: optimize your HVAC system and save on energy costs
Toyota, the leading corporations in the automotive industry, has applied energy audit at the production facilities of its aims to increase operational efficiency and minimize environmental impact.
- Strategy: evaluate the performance of the HVAC system at the factory in Japan, Usa, Europe. Upgrade technology and improve management temperature to reduce energy consumption.
- Results: saving millions of DOLLARS in energy costs each year. Reduction in CO2 emissions from HVAC systems at a minimum, contribute to the objective of carbon neutral by Toyota in the year 2050.
- Lessons: The simple enhancements, but the right focus can bring economic benefits and environmental.
Energy audit is a tool to save the cost and also the strategic move to help enterprises improve production efficiency, reduce greenhouse gas emissions to meet international standards such as ISO 50001 or GHG Protocol. Practical examples from large corporations such as Nestlé, Toyota, or Unilever shows the audit activities bring huge benefits on the economy, the environment, the whole brand image.
To build a production system operating optimally and sustainably, businesses need to conduct energy audits periodically. This is not only solution to save costs but also the opportunity for businesses to affirm pioneering role in protecting the environment towards sustainable development.
Let's start today by implementing energy audit to optimize operation, and the goal of reducing global emissions!