In the business environment competitive, controlling the cost of production not only help enterprises to reduce the cost of products, but also ensure sustainable growth contribute to improve profitability. However, many enterprises still face difficulties in the establishment report production costs accurate tracking fluctuations in cost, find out solutions to optimize efficiency.
So, expense reports play a role in how to manage business finance? How to business can reduce waste, improve production efficiency and optimize product price?
In this article Lac Viet will in-depth analysis of report production costs, the cost type is important, methods of making accurate reports by applying technology to optimize production costs.
Content of the same theme:
- Detailed instructions report on public debt for business
- Sales reports effective for business
1. Overview of the report the cost of production
1.1 report production costs, what is?
Report production costs is one of the important document to help businesses financial control, performance evaluation and production activities, calculate the accurate price of the product. The establishment cost report not only support managers in decision-making, financial accuracy, but also help enterprises optimize costs, improve productivity, maintaining sustainable profitability.
Report the cost of production is not just a requirement in the accounting profession but also bring many practical value in admin:
- Track control the whole of the expenses incurred in the production process.
- Provide accurate data to calculate the product price, guarantee business with the reasonable price, the optimal profit.
- To help businesses evaluate the performance of production, from which adjust the process to minimize waste.
- Support financial planning and forecasting the cost of future production.
- Decision-making flexibility: Based on fluctuations in cost over time or according to the workshop, the leader can adjust the scale of production, restructuring resources.
- Serve the audit report, appraisal, loan or calling for investment: A cost system clearly create trust for partners and financial institutions.
1.2. When businesses need to report the cost of production?
Reporting the cost of production should not be carried out only under the obligation of accounting that should be viewed as a monitoring tool cost, decision support administrator. Here is the point, businesses should prioritize reporting.
- Reporting periodically: Month – Quarter – Year: Reporting periodically to help ensure regular monitoring of the situation of production, timely, cost control and financial planning correctly. Compare costs across the states, detect trends, growth abnormalities (for example: raw material costs increased steadily in 3 months) to actively renegotiate pricing input or change provider.
- When there's large fluctuations in input costs: For example, the price of raw material suddenly increases (due to market fluctuations); a minimum wage Increase, the costs increase; the Price of electricity, fuel production increased sharply. To measure the degree of influence on the cost of production unit (for example: 20% increase in cost of supplies will make the price increase, how much percent). Help finance calculations back to the norm, the proposed adjustments to the sale price or optimize the production.
- Before the financial reporting period-end: Report the cost of production is the basis for calculating the cost of goods sold, directly affect the profit recorded in the financial statements. If recorded wrong the cost of production, will lead to a false profit, affect reports filed tax authorities or rating from the audit.
- When you need a decision on price, invest to expand or cut back production: Reporting at this help answer questions such as: Cost to create 1 product are beyond the sale price? Products are hole, still selling? Any costs accounted for a large proportion and can optimally be?
2. Report template cost-effective production should have what?
A reported cost effective production't just stop at the “general number”, which should become the tool analysis a decision fast help businesses control the entire manufacturing life cycle, from raw materials to finished products. To do that, the report template will need to meet 3 criteria: full – easy to understand – easy to analyze.
2.1. The composite panel according to orders, products, workshops
A manufacturing enterprises often operate under orders or production runs according to the code of each product at a lot of different workshops. Therefore, the report should clearly elements:
- Product name / product code
- Order code or code production
- Name factory made (if have divided according to the area machining)
- Production time (start date – end date)
- Number of finished product
For example, a garment company should monitor the cost of production of code T-Shirt 2024-SP01, which is cut in the workshop on A sewing machine at factory B, the amount of 2,000 pcs, production time within 7 days.
The split by product – order – workshop help retrieve information quickly detect the points cost overruns at each step instead of only the total figure.
2.2. The columns of data: The rate – actual – Rate difference
This is the core section of the report helps businesses to clearly see the level of cost control in manufacturing practice. The proposed structure for each cost element (material, labor, overheads), including:
- The cost of the level: is the level of cost expected/standard according to the plan (for example: 50.000 đ/raw material/product)
- Actual cost: the actual amount spent in the states (for example: 54.000 dd)
- Rate disparities: is the % difference between fact and norms (for example, +8%)
This form helps businesses know already how much money have cost more than expected't, where, why. This is the facility to check the cause as:
- The price of raw material increase?
- There is waste in the production process?
- Technical errors that cost repair team up?
2.3. Report form dashboard chart visual
A good report is not just for accountants to understand, but also should be easy to understand with the manager. That's why there should be more dashboard visualization production costs by:
- Duration: month, quarter, year
- Type of cost: material, labor, general production
- Compare the workshop or group of products
Chart often used include:
- Column chart: comparison of cost between the month or between fact and norm
- The line chart: track expense trends over time
- Circle graph: analysis of the proportion of costs in total production costs
For example: When looking at the chart columns, managers find that months 4 cost at factory C higher than 18% compared with an average quarter. This is the signal need to check more thoroughly about hours, salary increases, shift or low performance.
In summary: A report template cost-effective production need help businesses answer the following questions:
- I spent how much for each stage of production?
- Are superior to the plan? Why?
- Workshop, active, effective / ineffective?
- Costs are going in the right direction to optimize profitable?
When the report template is designed to be clear, so detailed, the operating business will be easy to make decisions based on data instead of hunches.
3. Download full sample report production costs professional

ACCOUNTING SOLUTIONS ACCNET ERP INTEGRATED AI AUTOMATE ALL BUSINESS
AccNet ERP is a software solution financial accounting integrated in the management system, comprehensive enterprise, which is developed by Lac Viet corporation. Difference highlights of AccNet ERP is the app artificial intelligence (AI) in many accounting process to help businesses:
- Automation of accounting and classified documents.
- Improving the accuracy in data control.
- Shorten processing time business accounting – financial.
Thanks to that, AccNet ERP not only is support tool but also a “smart assistant” with the business in financial management transparent effect.
Feature highlights:
✔️ Automatic accounting vouchers, collate public debt thanks to AI.
✔️ Manage your finance – accounting multi-branch, multi-subsidiary.
✔️ Financial statements consolidated standards of Vietnam & international (VAS, IFRS).
✔️ Cash flow management, budgeting, forecasting the exact cost.
✔️ Connect with the manure management system, hr, production, sales to sync data.
✔️ Integration of AI in data analysis, risk warning and proposed optimal scheme.
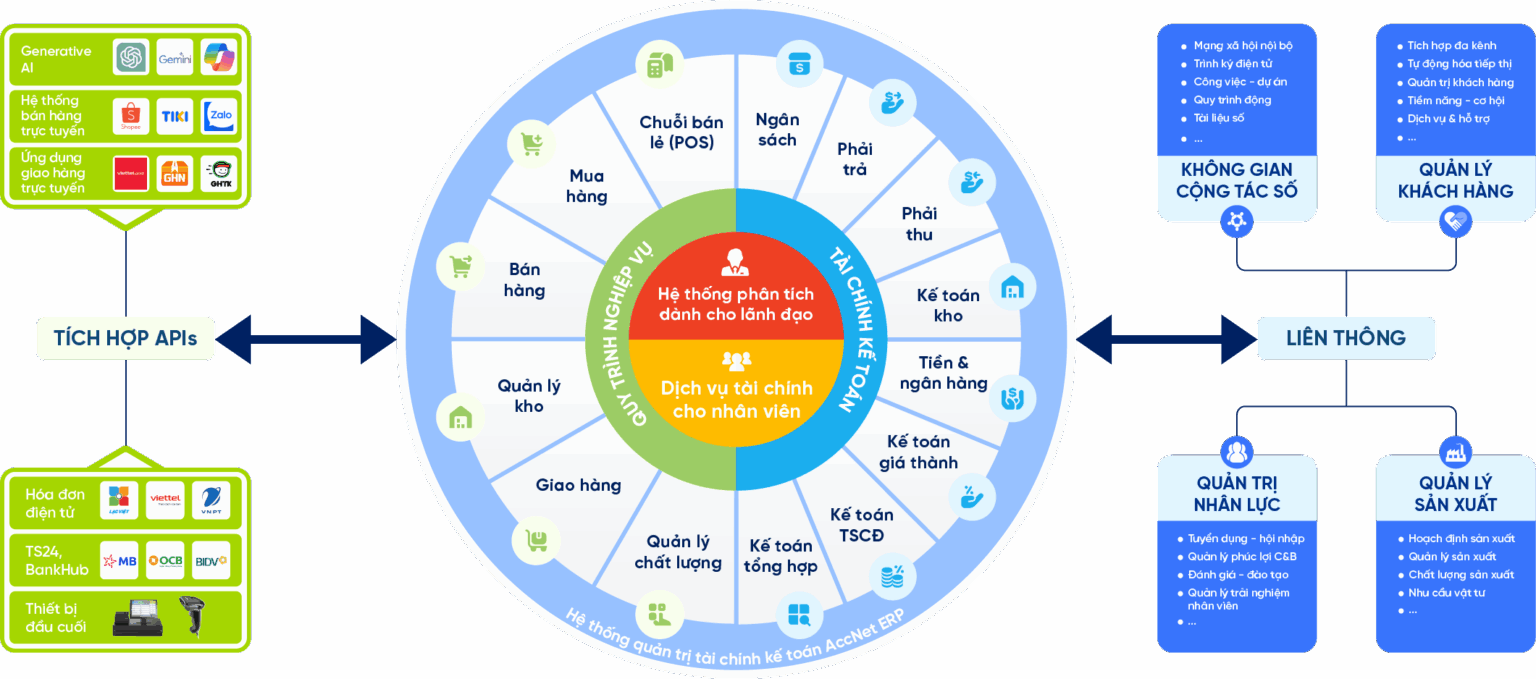
TYPICAL CUSTOMERS ARE DEPLOYING ACCNET ERP
- Nitto Denko – control production costs thanks to the application of accounting costing: Nitto Denko has chosen solution AccNet ERP to deploy the system accounting calculating cost ofhelp business control costs more effectively in the production process. After a period of use, company, highly effective, practical system that brings, as well as the degree of stability superior to other software in the market.
- ANTESCO – restructuring process works with management accounting operation: At ANTESCO, our team of consultants and deployment of AccNetERP has collaborated closely with the business in the first phase, reset the standard process and construction work-flow related departments throughout. The solution has helped ANTESCO significantly improve management capabilities, operating in a synchronized way and versatile
- Khatoco – expansion pack solution AccNetC after the successful implementation of original: Lac Viet has successfully deployed package solution AccNetC for trade co., LTD Khatoco in Nha Trang, according to the agreement signed on 29/07/2014. After the system is first put into operation efficiency, Khatoco intends to continue cooperation and expand the distribution finance – accounting and retail management with AccNetC, expressing the deep trust in implementation capacity and quality of service from Lac Viet.
SIGN UP TO RECEIVE DEMO NOW
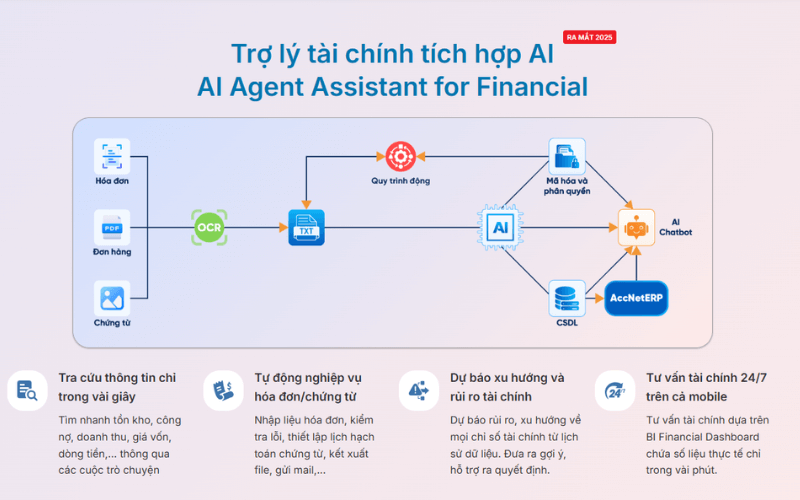
INTEGRATED AI ACCELERATION CONVERTER OF ACCOUNTING
AI in AccNet ERP't just stop at automate data entry, but also:
- Identification & classification certificate from smart: AI scan, read & sort invoice, voucher, receipt, limit errors due to input manually.
- Financial forecasting & budget: the system uses algorithms machine learning to forecast cost, revenue, business support decision fast.
- Warning risk accounting: AI to detect abnormalities in the book, from which timely warning of false or fraud risks.
- Reports assistant smart: AI suggested report template, automatic data aggregation support, leadership, financial analysis instant.
BUSINESS IS WHAT WHEN IMPLEMENTING ACCOUNTING SOFTWARE LAC VIET?
- Experience more than 30 years develop software solutions business management in Vietnam.
- Ecosystem of comprehensive: AccNet ERP easily connect with other solutions of Lac Viet (HRM, Workflow, Portal...).
- Advanced technology: Integrated AI support, cloud & on-premise flexible.
- Services dedicated support: A team of knowledgeable professionals with accounting – finance in Vietnam, companion throughout the deployment.
- Trust from thousands of customers in many areas: finance, banking, manufacturing, trade, services.
See details, feature & get FREE Demo
CONTACT INFORMATION:
- Hotline: 0901 555 063
- Email: accnet@lacviet.com.vn | Website: https://accnet.vn/
- Office address: 23 Nguyen Thi Huynh, Phu Nhuan, ho chi minh CITY.CITY
4. The main ingredient in report production costs
Report the cost of production is the general analysis of the expenses incurred in the process of creating products. To report maximize the role of management support and decision-making, enterprises need to understand the 4 main costs that any accounting system or software administrator would also need to follow up.
4.1. The cost of raw materials directly
This is the biggest cost to fluctuations in production includes the entire main raw materials, auxiliary materials, consumables, direct to create products.
The elements should follow:
- The level of raw materials: is consumption expected for each unit of the product (for example: 0.5 kg fabric/product)
- The actual number used: is the amount of material fact has import export warehouse user
- Unit price real income
- The rate difference between norms and reality: to see the status, wastage, waste or process has not been optimized
Illustrative example: A factory manufacturing aluminum doors are the norm 1.2 m aluminum/door, but this month incurred 1.35 m/store → difference of 12.5%. If not, analysis, business easy to ignore the cost increase due to shrinkage.
Value for business: Help identify fast cause team cost (input prices rise or wasting machining), from which the given solution as control norms, negotiating the purchase price, or process improvement cutting.
4.2. Costs directly
This cost reflects the wages paid to workers directly involved in production. Including salary, allowances, overtime, insurance if available.
The only goal should be:
- Total hours of practice according to shift/crew
- Unit price paid by the hour or by product
- Rate cost/finished product
Illustrative example: A workshop may complete the 5,000 austria with a total cost of 75 million → average 15.000 đ/austria. If the same pattern, months ago as 12,000 vnd/austria it is necessary to check: reduced productivity? increased ca not effective? salary spike?
Value for business: Help manage labor productivity, detect points of congestion in the organization shifts from it staffing and calculate the appropriate human resources.
4.3. The cost of production in common
Is group costs not directly associated with a particular product but still necessary to maintain production activities. Includes:
- Depreciation machinery and equipment
- Electricity, water, fuel, repair costs, maintenance
- Indirect costs other: wage foreman, consumables, shared...
The analysis should go towards:
- The proportion of production overhead in the total price (if exceeding 30-40% is the sign needs analysis)
- Average cost according to the hours of machine operation or according to the product
Illustrative example: A factory in packaging detect the power consumption rises sharply during the night shift that the output does not increase, respectively. Analysis of production costs general shift helps to identify energy waste adjust operation schedule.
Value for business: Reduce fixed costs not cut bush, which by optimizing operating performance enhancement use the property.
4.4. The price of the finished product
This is the norm sum up the whole of the expenses mentioned above to calculate the price of unit product, serving for:
- Valuation ba
- Profitability analysis according to each code, order, workshop
- Efficiently control the production time
The method of calculating the price of popular in Vietnam business:
- Simple: for process, single-step, homogeneous product (for example: ice factory)
- System number: for product, product at the same time (for example, food industry, processing)
- Step stool: used for the process has many stages, and clear (textile engineering)
- The lowdown: business has stabilization technology according to standard norms
Illustrative example: A business processing apply the method of coefficients to allocate costs between the main product (fillet) and by-products (fish bones, fish head fish), from which the true cost of each type of restaurant, avoid the price wrong cause the hole.
Value for business: Help pricing products close to reality is not lower than the cost price or valuation is too high reduce the competition.
A reported production cost want to create real value to reflect the individual link costs, the comparison is between plan and reality from that clarification is effective or inadequacies in the production process. When businesses understand the cost components, the control cost, increase profitability and investment decisions will correct much more flexible.
5. Instruction set table reports the cost of production details professional
The report detailed visual to help businesses evaluate production efficiency, the detection of inconsistencies in the process of using resources to make decisions to improve fit.
Here are the steps to take to report the exact cost effective.
Step 1. Identify the main expense item
Before reporting, businesses need to identify and classify the main expense items, including:
- The cost of raw materials directly
- Costs directly
- The cost of production in common
Determine fixed costs – variable costs
- Fixed costs: Expenses do not vary with the level of production, such as rent factory, depreciation of machinery.
- Variable costs: The costs change according to the number of products produced, like raw materials, wage workers work according to the product.
Determine the range reported production costs
Businesses need to determine:
- Statements according to the accounting period (month, quarter, year).
- Report by project or manufacturing orders.
- Reports according to type of product or production line.
Step 2. Collects data processing, accounting
Recorded aggregate cost data
- Collect data from the accounting department, raw material production.
- Collated with the purchase invoices, warehouse, payroll workers.
- Recorded costs according to each stage of production, to help businesses determine the period incurred cost.
Use accounting software to manage cost data
- Automatic recognition and classification of costs according to each item to minimize errors.
- Synchronize accounting data with the ERP system or software to manage production in order to have accurate reporting.
- Support to generate reports quickly under each accounting period, avoid entering data manually cause mistakes.
For example: A manufacturing enterprise electronic components use ERP software to track each consignment and warehousing of raw materials, automatically calculates the cost of raw materials according to each order.
Check out the collated data, the actual costs with the estimates
- Compare the data collected with the budget had set up previously to detect the difference.
- If there is a deviation, need to check the price of raw materials increase, consumption of raw material is larger than expected, or low labor productivity.
- Check the validity of the cost of joint production, ensure no waste in spending operate.
Step 3. Analysis of performance evaluation cost
Compare actual costs with the budget expected
- Calculate the percentage difference (%) between actual costs and estimates to determine the cost exceeds the budget.
- If the cost is higher than expected, should cause analysis to propose a solution to cut costs.
Analyze the causes of discrepancies costs
- If the cost of raw materials increase, the need to assess the causes from the raw material or consumable in the manufacturing process.
- If labor costs increase, the need to check the level of overtime hours, labor productivity, performance machinery.
- If the cost of joint production increase, the need to consider factors such as maintenance, machinery, electricity and water consumption more than usual.
Performance evaluation using raw materials and labor
- Check the percentage of shrinkage of raw materials in each stage of production.
- Reviews labor productivity based on the number of finished product per hour worked.
- Giving solutions to optimize the efficient use of raw materials and labor to help reduce the cost of production.
Step 4. Optimized production costs to improve financial performance
Technology application to manage the cost of production more efficient
- Integrated AI system to analyze cost data, to help businesses forecast is fluctuating costs in the future.
- Use warehouse management software smart to track raw materials, in real time, avoid the excess or shortage of raw materials.
- Optimize workforce productivity by monitoring system production helps reduce wasted time and increase efficiency for manual labor.
For example, A company produces plastic that can use AI to analyze data consumption of raw materials according to each shipment of production, from that given the local project save cost more efficiently.
Adjust the manufacturing processes to reduce costs
- Re-evaluate the production stage has a high cost, from which the optimization process to reduce costs not necessary.
- Consider adopting automation technology to replace manual labor helps to reduce costs and improve performance.
6. The method of reporting the cost of production
Business can choose one of following three methods to the organization reporting the cost of production, depending on the level of investment for the accounting system, human resource capacity and production scale. Each method has distinct advantages, but the most important is the business need to understand the essence to choose the method that reflects the cost best.
6.1. Method of
Principle of operation: Business recorded continuously every professional import – export raw material, semi-finished products, finished products throughout the production. News is that fluctuations of raw materials, workers, production costs are reflected instant details.
How to perform:
- When importing raw materials, accounting recorded an increase in warehouse
- When used for production, establishment votes. the recorded cost
- Other expenses, such as salaries, production costs, general... also be recorded as soon as they arise
- Periodically or at maturity, accounting gather data on TK 154 to report the cost of production
| Advantages | Restrictions |
|
|
Fit: Businesses have medium and large scale, continuous production, there is the investment for accounting software, ERP software, inventory management as AccNet, MISA, FAST...
6.2. Methods of inventory periodically
Principle of operation: Business no detailed tracking of goods and supplies throughout the production, which to the end of any new inventory to determine the amount of inventory the beginning of the period, enter in the states, cumshot, use and conservation of the end states. From that calculate the energy used to accounting for expenses.
How to perform:
- Not recorded cost of materials immediately upon use
- Final inventory inventory, use the formula:
The raw materials used = the first viable states + Enter in – Survive the end of a. - Then new record to report the cost of production
| Advantages | Restrictions |
|
|
Fit: small Business, startups, business, craft or produce according to orders, simple, no system management software.
6.3. Method coefficient/ratio
Principle of operation: Business use of constant or proportional allocation to split production costs for many products produced the same process, the same raw material.
How to perform:
- Building coefficient of conversion for each type of product (usually according to the consumption of raw material or the machining time)
- The total cost of production in the states will be allocated according to this coefficient to calculate the price of each type of product
For example: Business beverage production there are 3 types: type 330ml, 500ml and 1 liter. Based on consumption of raw materials can be converted into score:
- 330ml = 1 unit
- 500ml = 1.5 units
- 1 liter = 2.5 units
The total cost of production will be allocated according to the number of products multiplied by the coefficient.
| Advantages | Restrictions |
|
|
Fit: Business big production process, stable, homogeneous product of processes such as brewing, beverage, cement, pharmaceutical products.
7. Analysis of data the cost of production: From report to action
In production environments, the modern, the establishment cost report is not enough. True value lies in the ability to read – understand – analysis given timely action from that data. A reported cost-effectiveness need not only lists the numbers that need to be clear on: the cost of any increase, because the stars rise, rise now, businesses need to react. Here are 4 angle of view analysis essential to turn reports into the operating tool, efficient production.
7.1. Cost analysis exceeds the cause from now?
When the cost of raw materials, workers or the general production exceeds the norm, businesses need to clearly identify the root causes, instead of just recorded a number of cross detail. Approach suggestions:
- Compare the norm – in fact according to each product code, each workshop or each order.
- Access according to the time line to see the level crossing occurs at any time: the ca mid-month or end of quarter.
For example, If the cost of raw materials increases abnormally high in the first week, maybe due to the unit price of imported raw materials increase or the rate of loss exceeds the permitted level. When discovered, the business can renegotiate with suppliers, or inventory control input better.
Practical value: cost Reduction, not by cutting the bush, but by understanding the causes, optimal right place.
7.2. Performance evaluation workshop – yield vs. cost
No little business to “think” a workshop is doing well because of the complete quantity. But when confronted with the actual cost, can be unexpected: productivity increase, but the cost doubles. That's when businesses need to evaluate the performance according to the ratio of cost/product instead of just according to the output.
Suggested indicators should analyze:
- Cost / finished product
- Cost of joint production / output
- Total cost / hours of machine operation
For example: the workshop A and B are produced 10,000 units, but the workshop B consumes lots of power, labor, overtime, lead to the total cost higher than 15%. When that priority cornered order for A will be more effective.
Practical value: the optimal allocation of production resources between the workshop to save cost without compromising progress.
7.3. Determine the production cycle is optimized to reduce fixed costs
One of the costs silently “corrosion profit” is the fixed cost is spread not rational, such as depreciation of machinery, cost of rent, electricity, water... When production is irregular, these costs will increase the unit price of products.
Solution: analyze the number of manufactured products by week/month, in conjunction with fixed costs over time, to find out “point effect” (the minimum quantity should reach to the cost of the average does not exceed the limit).
For example, If running under 5,000 products/month, the depreciation expense + operating that price exceeded profit. When that business needs gom order to produce cyclical greater, or coordinate the product code to sustain the load machine.
Practical value: Reduced cost without loss of quality, by operating more reasonable, doesn't necessarily have to cut.
7.4. Application software data analysis to visualization cost
In-depth analysis will not be effective if the business is still “detector numbers in Excel spreadsheet 10,000 lines”. Meanwhile, the application of software visualization data such as Power BI, AccNet BI, or Google Looker Studio is inevitable. Shorten decision-making time from a few days to a few minutes, at the same time reducing dependence on department, general accounting
The features needed are:
- Dashboard production costs in real time
- Comparison chart of the norm – in fact according to each stitch
- Warning exceeding the threshold cost automatic
- Filter by workshops, products, orders, and date easily
For example, On Power BI, the chief accountant can design dashboard synthesis of the entire cost of production in January, with the filter in each workshop and charting express regional “hot” about the cost. The director need only look 1 screen is probably the right decision.
Analyze the cost of production is no longer private job of accountant. When business page is how the look “from data to action”, all levels of management – from the head of the yard to the CEO – can all participate in the process of optimizing costs. Because when you understand the costs come from, where businesses will know how to cut somewhere, investment property and increase profitability in a sustainable way.
8. Accounting report production costs, according to circular 200 and 133
8.1. Specified current accounting of recorded cost of production
According to the regulations of the Ministry of Finance, production costs are recorded in accordance with appropriate principles honesty. Specific:
- Circular no. 200/2014/TT-BTC: applies to business scale, accounting system, complex, requires preparation of financial statements in full compliance with international standards more.
- Circular 133/2016/TT-BTC: Apply for small business and medium textured account is simple, easy to deploy more.
Both circular require business to reflect the full costs incurred in the period, not to survive the cost or recorded at the wrong time. The cost of production must be clear classification, tracking details for each object set costs such as products, orders, works or factory production.
8.2. The accounting accounts often use
To report the cost of production, the accountant should use the account the peculiarities follows:
- TK 621 – the Cost of raw materials, live: Recorded value of raw materials used to produce products.
- TK 622 – Cost, direct labour: Recorded salaries, the account related to workers directly.
- TK 627 – the Cost of joint production: Include the indirect costs such as depreciation, electricity, water, and repair of machinery and salary management workshop.
- TK 154 – Cost production of unfinished business: Is account aggregation, whole set cost from 621, 622, 627 to calculate product price. Final cost from TK 154 will be the switch to TK 155 (Finished products) or 632 (cost of goods sold) if the product has been completed and consumption.
Illustrative examples:
A business furniture manufacturer in month 4:
- Purchased raw materials worth $ 500 million
- Wage workers 120 million
- Cost of joint production: 100 million
Accounting will the account:
- Debt 621: 500 million
- Debt 622: 120 million
- Debt 627: 100 million
- There are 152, 334, 111... depending on the source of the cost
=> Set on 154: Debt 154/ There are 621, 622, 627
8.3. Mistakes common business needs to avoid
Business, especially small and medium enterprises, often suffer from some flaws common following:
- Don't separate clearly the direct costs and the cost of joint production, leading to misleading price.
- No detailed tracking for each order or workshops, which causes difficulties when analyzing production efficiencies.
- Recognition of expenses in the wrong accounting period, distort financial statements.
- Teen record, the record comes (for example: warehouse, timesheet), that cost is not sufficient grounds accounting.
- Do not adjust or provisioning when the uncompleted last long.
The solution is: construction accounting procedures, internal clear, the use of accounting software has the function of automatic synthesis cost, cross-check periodically between accounting – inventory – production.
9. Trend digitized reported production costs in the modern enterprise
In the context of the cost of production increasing volatility, demand control over financial increasingly high, the number of goods to report the cost of production is no longer the trend that has become essential requirements for every business, including small and medium business.
Instead of reporting tools, Excel, collated manually between the accounting – inventory – production, businesses today are turning to use the technology solution integration allows automate the process of collecting, synthesizing, analyzing costs.
Automatically collect data from the operating systemsystem of a modern allows:
- Connect directly with warehouse management software: automatically records the amount of raw materials used, warehousing, inventory end of period.
- Integrate data from workshop production: recognition of the consumption of materials, labor time, power consumption,...
- Connect with accounting software: the System will automatically retrieve information costs, depreciation, cost general to include in your report.
Thanks to that cost data be updated immediately and the sync limit errors manually.
Instead of waiting to the end of the month knows the situation cost, now business can:
- See the report production costs by day, by order or by product
- Analysis of the volatility of each type of cost over time
- Warning when the cost exceeds the helping decision right adjustments in production
This is the core value that digitization brings: decisions faster, based on data more accurate.
Integrated AI technology to support forecasting decisions
Besides tool set reports, a prominent trend is now app artificial intelligence (AI) in the analysis of production costs.
LV Financial AI Agent is an intelligent platform that enables enterprises to:
- Automatic synthesis of data from the accounting system, warehouse, manufacturing and ERP
- Analysis of production costs of the multi-dimensional data: according to products, orders, any accounting or department
- Hints the change of the cost when there are unusual fluctuations
- Detect risks in operating costs (in excess of the budget, exceeding consumable supplies)
- Support reporting analysis according to the model of financial governance, not just in accounting data
This is the right choice for all businesses have accounting software but need a layer of management analysis-intensive manufacturing enterprises want to strictly control cost effective to order – workshop.
Digitization not only help business reporting faster, which also turn reports into decision-making tools. The application solution as LV Financial AI Agent not only is the switch number, which is the upgrade capability financial management and cost control of the business in the era of new competition.
Lac Viet Financial AI Agent to solve the “anxieties” of the business
For the accounting department:
- Reduce workload and handle end report states such as summarizing, tax settlement, budgeting.
- Automatically generate reports, cash flow, debt collection, financial statements, details in short time.
For leaders:
- Provide financial picture comprehensive, real-time, to help a decision quickly.
- Support troubleshooting instant on the financial indicators, providing forecast financial strategy without waiting from the related department.
- Warning of financial risks, suggesting solutions to optimize resources.
Financial AI Agent of Lac Viet is not only a tool of financial analysis that is also a smart assistant, help businesses understand management “health” finance in a comprehensive manner. With the possibility of automation, in-depth analysis, update real-time, this is the ideal solution to the Vietnam business process optimization, financial management, strengthen competitive advantage in the market.
SIGN UP CONSULTATION AND DEMO
Let's start today by upgrading the system report production costs of the business, application and technology to optimize processes, reduce errors and improve financial performance.

![[Trọn bộ] File Excel mẫu báo cáo chi phí sản xuất kèm hướng dẫn lập chi tiết](https://lacviet.vn/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/bao-cao-chi-phi-san-xuat.png)












