In the era of data, referred to as the “new gold” of the business, not just resources, but also is a key factor determining competitiveness in the market. However, with the explosion of big data, the extraction of value from data is not easy. This is the time Data Mining become important tools for businesses to find out the valuable information hidden from that support strategic decisions and optimize business processes.
This article Lac Viet will help you understand Data Mining what isrole of it in business, the engineering, data mining, downloads the same challenges, and specific solutions when deploying help your business maximize the power of data to reach on the development process.
1. Overview of Data Mining
1.1 Data Mining what is?
Data Mining, also called data mining, is the process of analyzing a large volume of data to find out the pattern (pattern), trend or relationship potential can bring value to the business. This is not merely a storage or reporting data, which is the journey to “dig deep” into the data to draw insights can direct application to business operations.

If simple comparison, business data like a mine resources not fully exploited. Data Mining is a tool to help businesses “gold-panning”, turning raw data into useful information to help make decisions faster, more accurate, more efficient. In other words, instead of just looking at the numbers in the report, the “explore” to help businesses understand what is happening behind the numbers there and why it happened.
For example, A retail chain, there are millions of transactions per month. Through mining data, businesses can detect that customers who buy diapers often buy with wet towels on the last Friday of the month. This information allows the marketing department up promotions combination right time to increase sales, retain customers.
1.2 distinguish Data Mining and the concepts easy to confuse
To learn about data mining, many businesses often confused with a number of related concepts such as Data Analytics, or Big Data. The clear distinction will help the business determine the right direction application in accordance with actual needs.
Data Mining vs. Data Analytics
- Data Analytics is a broad concept, covering the entire process of collecting, processing, analyzing and presenting data to support decision-making.
- Data Mining is a part of that process, focusing on the stage of the search patterns hidden deep in the data.
For example: In a sales campaigns, Data Analytics help businesses track the number of orders by day, Data Mining goes further by finding out the cause sales to increase in a time frame given.
Data Mining vs. Big Data
- Big Data refers to the data volume is extremely large, diverse changes quickly, requires special technology to handle.
- Data Mining is a technique used to harness the value from Big Data – like the use of the tool for ore mining large.
For example, A storage bank billions of transactions per year (Big Data). When banks want to detect unusual transactions to prevent fraud, they will use data mining to analyze the strange behavior.
Summary:
- Big Data is “big data”
- Data Analytics is “comprehensive analysis”
- Data Mining is “unleash the hidden value in data”
With respect to the business, understand the correct terminology will help to orient invest in the analytical solution fit, from which to tap the maximum value of the data available to cater for strategy development.
2. Process data mining in business
Data mining (Data Mining) does not take place in a single step retail, which is both a process closely linked, from collecting to a specific action based on what data bring. With the perspective of a business, understanding each step in this process will help optimize resources, avoid wasted time and increase efficiency investments in data.
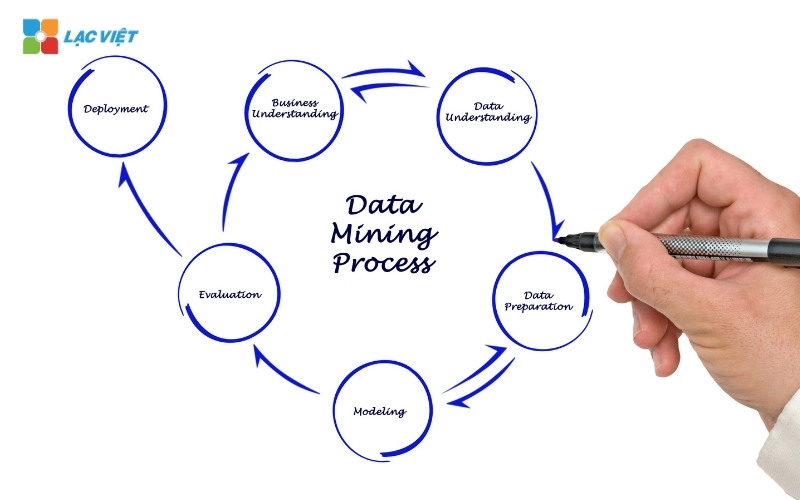
Step 1: collect data – Laying the foundation for analysis
Every day, businesses generate a lot of data: from bill of sale, customer feedback, site visits, to history interactive via email, social network, or software, internal management. The problem is that data are scattered in many places yet to be connected into a coherent mass.
In this first step, businesses should:
- Clearly identify the source of existing data (sales software, accounting, CRM, social networking, website...)
- Choose collection form fit (automatically or manually)
- Data storage in a way that can easily access management
For example, A pharmacy chain, can gather data from software sales (POS), purchase history of customers through the app, accumulate points and feedback on Facebook to build a database consistency service, analyze consumer behavior.
Step 2: data cleaning – Turn raw data into valuable data
Not any data collected also can use right now. Real data is often duplicated, omissions, wrong format or inconsistency between the sources.
The “clean” data, including:
- Remove duplicate records or misleading
- Standardized format (e.g., date, customer name, product code)
- Data processing teen (addition or removal can control)
If you skip this step, the business will see the situation analysis wrong or making decisions based on inaccurate data – thing more dangerous than having no data.
Step 3: analyze the data to find out what business has ever known
This is the most important stage of Data Mining. After the data is cleaned, use business analysis techniques to find out:
- Consumer trends over time
- The group of customers whose behavior similar
- The relationship between the product, the time of purchase
- The factors that affect revenue, expenses, profit
Depending on specific goals, businesses can apply classification techniques (clustering customer), clustering (finding clients has the same behavior), or detect the relationship (buy A regular attachment B). It is important that businesses do not need a thorough understanding of the technique – just need to know the target question to solve.
Step 4: interpret the results to turn data into business story
Data after the analysis can not only shown by the chart or table of data. Business need a step metabolism: from numbers to action.
In this step, data professionals or business managers need to ask the question:
- Results analysis say anything about customer behavior?
- Any trends that are affecting business performance?
- Business should adjust anything from these findings?
If you see group of customer first are the rate of return is very low, businesses can consider improving the experience after purchase, additional customer care or incentive program for next purchase.
Step 5: application to practice
Don't stop at the analysis, result from Data Mining need to be put into operation, in particular:
- Marketing: personalization content, advertising budget allocation more reasonable
- Sales: accurate Forecast seasonal demand service, support sales staff decision
- Administration: optimally operate, predict risk adjusted trading strategy
For example, A retail business noticed orders spike at the end of the week. They regulate ca work of staff and additional inventory separately for Saturday – Sunday, thus reducing 25% shortage of goods, increase the level of customer satisfaction.
In summary, the process of data mining is not just for big businesses with technology system complexity. With the right approach, even the small and medium enterprises can also take advantage of available data to improve operational efficiency, grasp the trend to make decisions smarter every day.
3. The technical methods, data mining, popular
3.1. Classification (Classification)
Goal: classify objects (customers, transactions, products, etc.) into the specific group has been defined, based on the characteristics and historical data.
Imagine your business has a new client. Based on information such as age, living area, purchase history... you want to know this person has high likelihood that customers who buy many times, customers who only buy once, then leave, or risk bad debt? Classification techniques will help you give the answer by learning from the data of the previous customers.
Business will get nothing from this technique?
- Easily detect valued customers to focus care.
- Predict orders have the possibility of fraud to minimize the risks.
- Automate the classification of customers to personalize user experience from that increase conversion rates, customer retention.
Practical application:
- In the bank: Classification of customers loans of the group risk low – medium – high to bring out term interest rates accordingly.
- In electronic commerce: predict which customers are likely to buy more products from that personalization email marketing.
- In insurance: The type of claim reasonable or suspected fraud to the handle for fast, accurate.
3.2. Clustering (Clustering)
Objective: to Find groups of objects have in common in the data, without identifying the group first.
Other with the kind – where you have available the group as “loyal customer”, “new customer”, “customer risk”, then clustering is the process for the system to find out what this group based on the behavior, needs, or habits of customers, whether you have not been defined.
Business will get nothing from this technique?
- Explore the group of potential customers hasn't been identified.
- Design promotions tailored to each specific group.
- Optimization strategies, products/services according to each segment of reality.
Practical application:
- In retail: customer Group based on time of purchase, the order value, product type love.
- In education: students according to the level of interaction and the ability to complete the course to put in place policies to support matching.
- In tourism: customer Group tour-style travel (vacation, explore, save...), from that personalization service package.
Specific example: A restaurant chain use clustering to analyze customer data for 12 months and noticed there are three groups stand out:
- Group online ordering on Friday evening (guests young, single).
- Group lunch on weekdays (office staff).
- Group party booking weekend (family).
Based on this result, they designed the promotions separately for each group: free delivery end of the week, discounts noon and gifts for girls party, – from that increase revenue and reduce advertising costs rambling.
3.3. Regression (Regression)
Regression (Regression) is a technique of Data Mining is used to predict the value (continuous value) based on the relationship between the variables.
Practical application:
- Revenue forecasts: predict revenue based on factors such as trend and shopping advertising budget.
- Finance: analyze market data to forecast stock prices.
Benefits:
- Providing accurate predictions to support planning business.
- To help businesses understand the relationship between the factors that affect business results.
3.4. Association rules (Association Rules)
Objective: to Detect the relationship has regularity between events in the data, for example, the products are often purchased together or this behavior leads to the behavior.
This is the technical foundation of the analysis of cart help answer the question: “If customers buy A, they tend to buy what's next?”. It's like you call coffee will usually call more pastries from there, you give hints or design matching combo.
Business will get nothing from this technique?
- Increase revenue through strategic sales with cross-selling.
- Program design combo-efficient instead of guessing.
- Sort products at reasonable store, stimulating demand to buy more.
Practical application:
- In the supermarket: product Suggestions comes when customers select goods.
- In electronic commerce: Hint “customers also bought” when viewing the product.
- In physical stores: product display group has links to increase the likelihood of purchase.
For example, A supermarket chain, data analysis, hundreds of thousands of orders, and discovered that customers who buy fresh milk on the Monday there is high probability buy more sandwiches. From there, they launched the program a 10% reduction bread for customers who buy milk at the beginning of the week. Results: revenues in this product group increased by 18% within only 2 weeks, at the same time raising the average spend per order.
3.5. Forecast (Prediction / Regression)
Goal: Help businesses predict what events may happen in the future based on historical data, from which actively in the planning, production, business, hr or finance.
Prediction is the business, “read the future” through the numbers in the past. If the business has recorded sales by month for the past 3 years, the system will learn from the trend, seasonal fluctuations... to estimate the sales of the next month or the next quarter.
The actual value for the business:
- Planning production with market demand, avoid inventory or shortage of goods.
- Financial management initiative, prepare cash flow cyclical revenue – cost.
- Estimate the amount of personnel needed for each time point, optimal operation.
- Capture consumer trends to launch new products the right time.
Practical application:
- Commercial business revenue forecast year later to adjust the budget for marketing.
- Factory production forecast amount of orders to plan the purchase of raw materials.
- Business service predicts the number of customers to prepare personnel in high season.
For example, A fashion companies use sales data of 3 years ago to realize that product group jacket spike in early January 12. They actively increase production, additional branch point and push up advertising online 2 weeks ago this time. Thanks to that, sales of the fourth quarter increased 22% compared with the previous year without increasing operating costs.
3.6. Anomaly detection (Anomaly Detection)
Goal: automatically determine the data point “unusual” – can be a sign of fraud, system failure, or behavioral risks in operation.
In a sea of big data, if there is an order too large than normal, or a staff member to access the system at 3 in the morning not in the habit, the system will get out to warn. That's the role of technical anomaly detection.
The actual value for the business:
- Prevent financial fraud, asset protection, corporate reputation.
- Detect product defects or errors in operation earlier than craft.
- Monitoring IT system alerts, visit strange, enhances security.
- Ensure the quality of products and services, thereby improving the customer experience.
Practical application:
- The bank discovered the transaction suspicious based on spending habits.
- Factory alerts when a machine malfunction parameters.
- Floor ecommerce tracking orders cancelled unusual to identify fraud.
Specific example: A sales system automatically detects an order worth $ 200 million from an individual customer – while the purchase history of that person hasn't exceeded 2 million. The transaction is marked “irregular” and may temporarily defer to the customer care department to verify. This helps businesses to avoid the risk of payment fraud, while strengthening the trust of the customers about the safety of the transaction.
3.7. Reduced-dimensional data (Dimensionality Reduction)
Objective: abridged complex data with tens or hundreds of elements on a small set of factors have the greatest influence, from that analysis faster, more accurate, more understandable.
Like when business analysis the reason why customers leave, instead of having to look at 50 different elements, the system will indicate that the 5 factors such as waiting time delivery, price, product support after the sale, return policy and deals for returning customers are the main causes.
Thanks to that, the manager is not “sink” in the data that can still be effective action.
The actual value for the business:
- Reduce complexity when processing data, saving analysis time.
- Focus on the important metrics really avoid wasting resources.
- Support data visualizations more effective in reported decisions.
- Boost system performance when handling large amounts of data.
Practical application:
- In marketing: shortened dozens of indicators of few factors the greatest influence on the conversion rate.
- In the customer management: Find out the main factors that make customers satisfied or leave.
3.8. Time series analysis (Time Series Analysis)
Time series analysis is the technique data mining to forecast trends based on data collected over time.
Practical application:
- Financial planning: predicting sales according to the season.
- Supply chain: demand analysis to optimize inventory.
Practical examples: A fashion companies use time series analysis to predict demand for winter clothing to help increase the accuracy in the production and reduce the amount of excess inventory.
Benefits:
- Help business plan more effective.
- Accurate predictions of market trends in the future.
4. Application of Data Mining in business
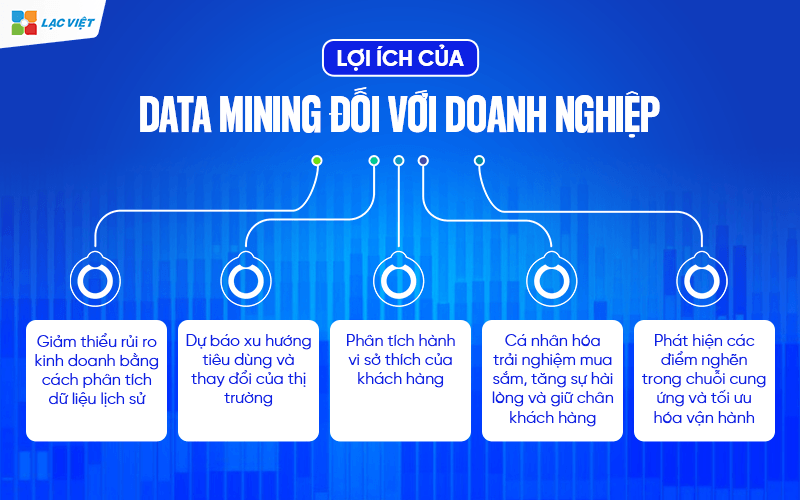
4.1 Increase efficiency Marketing – customer care
In the context of consumers increasingly expect the personalization in each experience, the marketing campaign tradition, the tea is styled “a message for all” was no longer promote efficiency. This is the time for Data Mining to become an “assistant behavior analyst” invaluable for marketing department and customer care.
Specifically, mining data to help businesses do what?
- Build portrait clients accurate: Instead of just based on age or gender, businesses can analyze customer purchase history, frequency of visit website feedback via email, consumption habits according to the time... to paint a full picture of each customer group.
- Predict future demand: For example, if customers often buy gifts on the occasion of the end of the year, the system will suggest suitable products before that time, with preferential personalization to stimulate purchase.
- Marketing automation, according to individual scenarios: Business can set string email, sms or push notifications to be automatically sent when the customer has specific behaviors such as abandoned cart, account registration, but do not buy, buy products time Tuesday...
Practical benefits:
- Increase the conversion rate of messages to suit each customer.
- Optimal marketing costs, do not need to spend money seamless experience for the customer group is not potential.
- Increase the loyalty thanks to customer care right expectations right time.
4.2 decision Support in management and finance
Wrong decisions in management or finance can make business major damage, especially in the period of economic fluctuations or hot growth. Data Mining plays a role as a “strategy map”, to help managers see the trends, early warning and risk-oriented decision-making evidence-based practices.
Business can apply Data Mining to:
- Forecast the revenue, profit and cost over time: analysis of the sales cycle time, increase revenue reduce costs, unusual, to adjust financial plans flexible.
- Optimized operating costs: Identify the suture spending budget, many but not effective. For example, an advertising campaign online inexpensive but does not create switch as expected.
- Strategic decisions from data: Instead of decisions based on perceived or subjective experience, business leaders can rely on pattern analysis to select the direction of investments, market expansion or cut product.
Practical benefits:
- Minimize waste budgeting and hidden costs in operation.
- Improve the accuracy of business planning, from budgeting to planning personnel.
- Increase the speed of decision making, from which capture opportunities more quickly than rivals.
4.3 detection of fraud and irregularities in the system
In the business environment digitized increasingly complex, the detection of fraud or other unusual behavior promptly can help businesses avoid big losses on financial, reputation and legal. Data Mining is not only based on process rigid which can learn from the behavior and data in the past to detect “unusual things” right when it happened.
Featured app in practice include:
- Monitoring unusual transactions in real-time: the System automatically detect the transaction exceeds the normal level, made at the time, unreasonable, or come from strange position.
- Warning deviations in financial reporting: When accounting data are the difference abnormalities (for example, marketing costs suddenly increase 3 fold but revenue does not change), the system may give a warning.
- Behavior tracking, internal personnel: staff identification unusual activity on the system, such as copying data access out of hours or change account information important.
Practical benefits:
- Prevent fraud early, asset protection business data.
- Minimize financial losses, time troubleshooting.
- Increase reliability and transparency in internal operations and partners.
5. The software tool supports data mining
5.1 Lac Financial AI Agent
Lac Viet Financial AI Agent to solve the “anxieties” of the business
For the accounting department:
- Reduce workload and handle end report states such as summarizing, tax settlement, budgeting.
- Automatically generate reports, cash flow, debt collection, financial statements, details in short time.
For leaders:
- Provide financial picture comprehensive, real-time, to help a decision quickly.
- Support troubleshooting instant on the financial indicators, providing forecast financial strategy without waiting from the related department.
- Warning of financial risks, suggesting solutions to optimize resources.
Financial AI Agent of Lac Viet is not only a tool of financial analysis that is also a smart assistant, help businesses understand management “health” finance in a comprehensive manner. With the possibility of automation, in-depth analysis, update real-time, this is the ideal solution to the Vietnam business process optimization, financial management, strengthen competitive advantage in the market.
SIGN UP CONSULTATION AND DEMO
5.2 RapidMiner: visualization tool and data analysis strong
RapidMiner is one of the software data analysisdata mining today's top is designed to support users at all skill levels, from beginners to experts of the analytical data.
Feature highlights:
- Interface drag-and-drop, easy to use without the need to write code.
- Integrated learning algorithm machine (machine learning) to analyze and predict the data.
- Ability to handle big data with fast speed.
Practical application: A company e-commerce use RapidMiner to analyze buying behavior and predict product demand, thereby increasing sales up 20%.
5.3 WEKA: Support data mining with multiple algorithms, machine learning integration
WEKA is an open source software popular in the field of Data Mining with multiple algorithms, machine learning, powerful for professionals to analyze data.
Feature highlights:
- Support diverse algorithms such as clustering (clustering), sorting (classification), regression (regression).
- User interface simple, easy to learn and use.
- The ability to integrate with programming languages such as Python or Java.
Practical application: WEKA is used in medical field to analyze patient records, support, doctor, given the more accurate diagnosis.
5.4 Python and R: a programming language popular for data analysis
Python and R are the two programming languages are the most popular in the community data science thanks to the ability to customize high ecosystem rich library.
Python:
- Popular visualization libraries: Pandas, NumPy, Scikit-learn, TensorFlow.
- Pros: versatile, easy to learn, can be used both for data analysis, basic and complex.
R:
- Library downloads: ggplot2, caret, dplyr.
- Advantages: Specialized in statistical analysis, data visualizations.
Practical application: The financial companies often use Python and R to build models to predict stock prices or analysis of credit risk.

5.5 Tableau and Power BI: Integrated, data mining, visualization results
Tableau and Power BI are the two top tools of data visualizations to help businesses transform the complex numbers into the chart control panel is easy to understand.
Tableau:
- Strong ability to connect multi-source data, create a dashboard to visually.
- Suitable for the data presentation in the meeting.
Power BI:
- Tightly integrated with the Microsoft ecosystem.
- The ability to analyze real-time data and automatically generate reports.
Practical application: A manufacturing company uses Power BI to monitor production performance, detection of bottlenecks, process optimization, help increase productivity up to 15%.
5.6 Google Cloud AI and AWS AI: Support analysis processing big data with AI technology
Google Cloud AI and AWS AI solutions provider, data processing, powerful, integrated technology artificial intelligence to automate the analysis process, the predicted data.
- Google Cloud AI: service AutoML helps to build the machine learning models without the need for in-depth knowledge about programming.
- AWS AI: Support tools such as Amazon SageMaker to train and deploy machine learning models quickly.
Practical application: A large bank use AWS AI to detect fraudulent transactions, reduce financial losses at 20% in the first year of deployment.
6. Challenge when the application data mining in business
Lack of staff expertise
One of the biggest barriers when implementing Data Mining is the shortage of personnel with expertise in the field of data analysis. Businesses often have difficulty in:
- Looking for specialists, data analysis, Data Scientist, or Data Engineer experienced.
- Training staff internally to understand, use tools Data Mining.
- Connect departments to leverage data in a synchronized and effective.
A survey from Gartner (2023) indicates that 63% of business said their lack of hr expertise to successfully implement the project, data mining.
Data heterogeneity or poor quality
Data is the core asset of Data Mining, but not always business also have high-quality data. Common problems include:
- The data is duplicate, outdated, or incomplete.
- Data from multiple sources of heterogeneity (CRM, ERP, social networking, sensors, IoT).
- No data is organization for standardization leads to difficulties in processing and analysis.
Security issues and data privacy
The collected data analysis in the digital age faced with the challenge of security of privacy. Common problems include:
- Data leakage: network Attack or manage loose lead to sensitive data being divulged.
- Violation of privacy: The collection and use personal data does not comply with the legal regulations, such as GDPR in Europe or Decree 13/2023/ND-CP in Vietnam.
- Lack of a mechanism to protect data: the Enterprise does not have measures encryption, data protection, powerful.
A study from Ponemon Institute (2023) said, 45% business join security incident data within the first 2 years of deployment of Data Mining. The violation of privacy not only lose credibility but also lead to fines, extreme, making serious impact on business operations.
7. Business need to do to into practical application?
Internal training and hire expert data
To solve staffing problems, the business can perform:
- Internal training: Organization of the course, data analysis, basic to advanced for employees. Use the tool easy to learn as Tableau or Power BI to build background knowledge solid.
- Hire expert: Search for expert Data Scientist or cooperate with company professional advice to support the deployment, the original guide.
- Team building, professional liability: establishment department specializes in data, combining expert on information technology, statistics, business analysis.
Investing in technology infrastructure and security tools data
To solve the problem of quality and data security, businesses need to:
Technology infrastructure:
- Construction, storage systems, data management concentration (Data Warehouse).
- Use cloud platforms like Google Cloud or AWS ability to expand storage, data processing.
Security tools:
- Deploy the solution data encryption (encryption) to protect sensitive information.
- Use the system detect and prevent network attacks, such as SIEM (Security Information and Event Management).
Compliance with laws:
- Build process collects data processing complying with the legal regulations such as GDPR or CCPA.
- Staff training about the privacy policy and the privacy.
Optimized cleaning process standardized data
To ensure input data are of high quality, business need:
- Use specialized tools: Apply tools like Trifacta or OpenRefine to automatically clean and standardized data.
- Build standardized processes: rule definitions, clear standards for collecting data storage.
- Check data periodically: perform the quality check the data regularly to detect and handle problems soon..
Data Mining not only is a tool, which is the bridge to help businesses explore and transform data into a competitive advantage. From the analysis of customer behavior, forecasts, market trends, to optimize operation, data mining, brings the practical value to help businesses make decisions, strategy correctly and efficiently.
Though the process of deployment Data Mining can face many challenges, but with thorough preparation, investing in technology and building a team of the quality, businesses can fully overcome the barriers to leveraging the maximum potential of data. Let's start the journey of data mining today, so the data is not just numbers that became the impetus take your business far more than the market competition is fierce!
Related questions
1. Why the need for data mining?
Data in business is only worth when mined properly. If only stored without analysis, data will be like “resource not tapping”.
Businesses need data mining to:
- A deeper understanding of customer behavior: Not just stop in the know who bought that know why they buy, what they like, have the ability to go back or not.
- Trend forecasting, prepare for the future: For example, analyze purchase history to help predict seasonal demand, thereby optimizing inventory.
- Optimal operation cost reduction: data Mining can help detect the point of obstruction in the process of commissioning or wasting budget marketing.
- Decisions based on data instead of feeling: Help administrators reduce risk, increase accuracy when making the decision strategy.
2. The main goal of data mining what is digital?
The main goal of data mining number is: transform raw data into valuable information to support decision-making, optimal operation create competitive advantage.
More specifically, data mining, number directed to:
- Discover hidden knowledge hidden in the data: The model behavior, relationship, and trends that people difficult to detect with the naked eye.
- Increase the speed of decision making: Based on the analysis results from the data, managers can react quickly to market fluctuations or internal risk.
- Personalization service/product: Understand each customer group to take out appropriate strategy for each segment, thereby increasing the conversion rate.
- Maximize the performance/profitability: By analyzing performance over time, forecast revenue, identify points for improvement.
3. Role of data mining in business
Data mining (data mining) acts as a “map enlightenment” to help businesses see the opportunities, risks, as well as the trend implicit in the data they possess that can never paid attention to. Specific data mining brings 5 essential role in business:
- Understand more customers: analysis of behavior, habit, and customer feedback to help businesses subtypes, personalization, care more effective.
- Increase revenue – optimal cost: Based on the data of purchase, inventory, performance, channel sales, business development is cross-selling opportunities, product potential, at the same time cut down poor performance.
- Risk prediction: data Mining helps in early detection of unusual signs such as customer about to leave, the debt difficult to collect, or process error.
- Decision support fast accurate: business decisions based on real data instead of feeling help to increase the reliability efficiency in action.
- Create competitive advantage in the long term: Corporate mining, good data will adapt quickly, understand the market early and maintain a firm position than the opponent.
Data in business is only worth when mined properly. If only stored without analysis, data will be like “resource not tapping”.
Businesses need data mining to:
- A deeper understanding of customer behavior: Not just stop in the know who bought that know why they buy, what they like, have the ability to go back or not.
- Trend forecasting, prepare for the future: For example, analyze purchase history to help predict seasonal demand, thereby optimizing inventory.
- Optimal operation cost reduction: data Mining can help detect the point of obstruction in the process of commissioning or wasting budget marketing.
- Decisions based on data instead of feeling: Help administrators reduce risk, increase accuracy when making the decision strategy.
The main goal of data mining number is: transform raw data into valuable information to support decision-making, optimal operation create competitive advantage.
More specifically, data mining, number directed to:
- Discover hidden knowledge hidden in the data: The model behavior, relationship, and trends that people difficult to detect with the naked eye.
- Increase the speed of decision making: Based on the analysis results from the data, managers can react quickly to market fluctuations or internal risk.
- Personalization service/product: Understand each customer group to take out appropriate strategy for each segment, thereby increasing the conversion rate.
- Maximize the performance/profitability: By analyzing performance over time, forecast revenue, identify points for improvement.
Data mining (data mining) acts as a “map enlightenment” to help businesses see the opportunities, risks, as well as the trend implicit in the data they possess that can never paid attention to. Specific data mining brings 5 essential role in business:
- Understand more customers: analysis of behavior, habit, and customer feedback to help businesses subtypes, personalization, care more effective.
- Increase revenue – optimal cost: Based on the data of purchase, inventory, performance, channel sales, business development is cross-selling opportunities, product potential, at the same time cut down poor performance.
- Risk prediction: data Mining helps in early detection of unusual signs such as customer about to leave, the debt difficult to collect, or process error.
- Decision support fast accurate: business decisions based on real data instead of feeling help to increase the reliability efficiency in action.
- Create competitive advantage in the long term: Corporate mining, good data will adapt quickly, understand the market early and maintain a firm position than the opponent.