Accounting is the set of manipulations recorded, processed and reported economic activities – financial arise in business, creating a “map” reflects the entire cash flow, assets and liabilities. The accounting exactly the service according to the accounting Standards (as TT 200/133) helps businesses ensure data transparency, legal compliance, and provide reliable data to the leader board reviews the business performance and give strategic decisions in a timely manner.
Business accounting is the core foundation in the operation of financial management of the business, determines the accuracy of the recognition, processing, and reporting economic transactions arise. Not only is this the recorded invoices, receipts/expenditures or import warehouse, which is still in process control, cash flow management, liabilities, assets and costs, from which support the strategic decisions on investment, costs, capital and the production plan – business.
In fact, many enterprises still face difficulties when implementing the accounting profession, basic general and the accounting profession businesses due to the diverse nature of the transaction, the payment form different, or the lack of standardized processes. Errors in the accounting of the business, this can lead to financial reporting is not accurate, affect the tax settlement, cash flow management and operational efficiency.
Understand and implement the right accounting the basic accounting master of professional general accounting and the accounting profession business will help the business not only adhere to the law but also enhance transparency, reduce risk and optimize business efficiency. Let's Lac Viet explore detailed article below.
1. Overview of accounting in business
1.1. Accounting what is? Role in business?
Accounting is the set of manipulation, recording, processing and reporting of economic activity – financial arise in the business including the business such as buying and selling goods, debt management, cash, bank accounts, fixed assets, operating costs, revenue, as well as other transactions. In other words, this operation is “map” reflects the entire cash flow, assets and liabilities of the business in a given time period.
Role in the financial system business:
- Provide timely information precisely for business decisions: For example, when a business wants to expand production, data from the operations, general accounting of the debt, inventory and cash flow will help leaders assess the liquidity demand for real capital.
- Ensure compliance with the law on accounting – tax: Business must be recorded as well as proper reporting transactions under the provisions of the Ministry of Finance, such as circular no. 200/2014/TT-BTC (upcoming is circular 99/2025 update replacement revision no. 200) to avoid the risk of penalties, audit.
- Support performance management activities: accounting the basic accounting helps the business to control inventory, reduce the costs incurred are not necessary, optimize cash flow and improve business efficiency.
1.2. Why do accountants need to know?
- Ensure accounting accuracy, reducing legal risks: When accountants understand accounting the basic accounting and master of professional accounting general journal entries are recorded to the right audience, right time right value. For example, sales revenue must be recognized immediately when the invoice of export avoid the status of “accrued revenue” end-states adhere to accounting standards to avoid tax penalties.
- Improve the efficiency synthesis, analysis of data and preparation of financial statements: accounting staff can aggregate data from multiple sources, service from that financial reporting accuracy, profitability analysis, cash flow, debt, inventory... Help leaders take strategic decisions based on real data, for example the decision to increase production, or adjusting the selling price.
- Support other parts of the business: accounting profession not only serve the accounting department that is a source of reliable information for other departments: sales department for monitoring the debt the customer, procurement, inventory control, personnel management, payroll costs.
2. Principles to be followed when accounting
When performing transactions, business accounting, compliance with principles of accounting are important factors to ensure data accuracy, transparency has high value to use for business decisions. These principles are detailed rules in accounting Standards, Vietnamese (VAS) and the guidelines of the Ministry of Finance. Here are the basic principles that every accountant should master:

2.1. Ensure honesty, objectivity, consistency
These principles are emphasized in the Standards, the Vietnamese accounting no. 01 (VAS 01) – general Standards.
- Honest: All accounting information must reflect the true nature business arising. Not allowed to reduced revenue, increased costs or adjust figures for “beauty” report. For example, if business purchased raw materials worth $ 100 million, accounting to record the correct amount of this is not recorded lower or delayed recognition to change the profit.
- Objective: data must be based on documentation such as invoices, receipts, testing, warehouse. Do not use speculations or estimated subjective if there is no legal basis.
- Consistency: Method of accounting must be applied uniformly over the accounting period. For example, if the business is choosing the method of calculating the price of stock FIFO (First In, First Out – first-ago), it should apply throughout, avoiding changes between the states in order to ensure comparability and reliability of financial statements.
2.2. Recorded right time arises
This principle compliance with accrual basis according to VAS 01 detailed instructions in Circular no. 200/2014/TT-BTC about accounting business.
The expenses, revenue, assets and liabilities must be recorded at the time of actual incurred, not when paid or when reporting.
For example: sales Business day 5/11 but money is only paying customers on 20/11. Revenue must still be recorded on 5/11, because this is the time of the transaction.
Similarly, the cost of buying the raw materials used for production year 11 to be recorded in the states 11, even when the bills are paid then.
2.3. Store stock from the full prescribed by law
The stored documents are specified in Article 40, Article 41 of the Law on accounting 88/2015/QH13 details about deadlines, responsibilities in the Decree 174/2016/ND-CP.
All documents relating to the accounting profession must be kept full, systematic and easy to access. Including: invoices, receipts/expenditures, contracts, commissioning records, payroll, stock from the bank.
- Help check and compare as well as verification of data in the process of financial reporting.
- Business support in audit, tax inspectors, as well as explanations when the agency management requirements.
For example: If the business accounting advertising costs of $ 50 million, the storage contract advertising, VAT invoice and payment receipt will help to prove legal costs reasonable, when the tax check.
3. Guide accounting 10 accounting profession the most basic need for business
In business and accounting the business is the foundation to ensure data transparency, accurate, and can be aggregated into financial statements service management to strategic decisions. Here are 10 business most basic, is presented in accordance with the provisions of circular no. 200/2014/TT-BTC (applicable for large COMPANIES) and circular 133/2016/TT-TBC (small and medium ENTERPRISES).
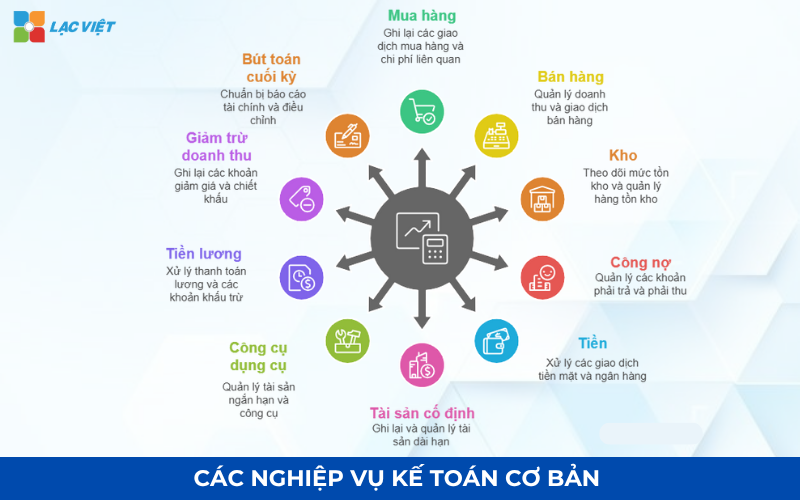
3.1. Accounting Purchase
Accounting Purchasing is the process of recording and tracking transactions, purchase of raw materials, goods, tools, or services from supplier to service production activities of business.
| Name service | How accounting |
| Purchase of Raw materials, goods, CCDC about warehousing | Debt: TK 152, 153, 156 (Price excluding tax), TK 1331 (input VAT)
Have: TK 331, 111, 112 (the Total value of payments on the invoice) |
| Buy used goods now through warehouse (Charged straight at cost) | Debt: TK 621, 623, 641, 642 (Price excluding tax), TK 1331 (VAT deductible)
Have: TK 331, 111, 112 |
| Payment of the debt to the supplier (NCC) | Debt: TK 331
Have: TK 111, 112 |
The purchase is the management of public debt effectively, avoid overdue; providing accurate data for cost analysis, purchasing, estimating the budget, reduce the cost of working capital.
For example: Business-buying 50 million raw materials unpaid. When receiving invoice: Debt 156/1331, There are 331. When payments: Debt 331, There are 112.
3.2. Professional accounting Sales
Professional accounting Sales process is recorded, reflect the transfer of goods, products or services from the business to the customers, which determine the revenues and accounts receivable.
| Name service | How accounting |
| Bill of sale (Not money) | Debt: TK 111, 112, 131 (the Total value of payments)
Have: TK 511 (revenue excluding VAT), TK 3331 (VAT output) |
| Autumn sale amount (debt Collection) |
|
| Recorded cost of goods sold |
|
This helps to predict cash flow, evaluate business performance according to customers ' products at the same time reduce the risk of bad debts.
For example: Sale of goods worth $ 30 million customers who paid after 15 days. Bill: Debt 131, There 511/3331. Upon receipt of money: Debt, 112, 131.
3.3. Business accounting, Stock/inventory
Inventory (HTK) is a short-term assets most important of manufacturing enterprises as well as trade. Includes materials, tools, finished products and goods. Business accounting and Inventory tracking threading import/ export/ backlog of these assets.
| Name service | How accounting |
| Enter stock buy out (Not paid) | Debt: TK 152/156, TK 1331
Have: TK 331 |
| Enter the warehouse of finished products (From the production process) | Debt: TK 155 (Finished products increase)
Have: TK 154 (production Costs unfinished business loss) |
| Stock materials (NVL) directly for production | Debt: TK 621 (MATERIAL Cost, direct)
Have: TK 152 (NVL up) |
| Export warehouse NVL/tools (CCDC) use for management | Debt: TK 642 (Cost management business)
Have: TK 152/153 (HTK up) |
| Sale of goods/products (Recorded Price of capital) | Debt: TK 632 (cost of sales)
Have: TK 155/156 (HTK up) |
| Store excess inventory (Pending) | Debt: TK 152/156 (HTK increase)
Have: TK 3381 (surplus Assets pending) |
| Items to inventory (Pending) | Debt: TK 1381 (lack of Assets awaiting disposal)
Have: TK 152/156 (HTK up) |
| Establishment provision for decline in inventories (End of period) | Debt: TK 632 (cost of sales)
Have: TK 2294 (provision for decline in inventories) |
This aims to reduce losses, optimize cash flow, providing data, calculate the price of capital and profitability analysis.
For example: Import of raw materials 20 million (before tax): Debt 156, There are 331. 10 million used in the production of: Debt 621, 156.
3.4. Accounting liabilities
Business liabilities accounting is the process of tracking, management and accounting of funds that business receivables from customers (when sold on credit) and the sum of money that a business must pay to the supplier (upon buyer).
| Types of public debt | Name service | How accounting |
| Receivable (TK 131) | Sales/service not collect money | Debt: TK 131, TK 3331
Have: TK 511 |
| Collect money from Customers | Debt:TK 111/112
Have: TK 131 |
|
| Provision for doubtful Debts | Debt: TK 642
Have: TK 2293 |
|
| Pay (TK 331) | Purchases/Expenses not yet paid | Debt: TK 156/6xx, TK 133
Have: TK 331 |
| Payment to The seller | Debt: TK 331
Have: TK111/112 |
|
| Advance money to The seller | Debt: TK 331 (Debit)
Have: TK 111/112 |
|
| Other liabilities | Arising pay | Debt: TK 641/642
Have: TK334 |
| Spend money advance | Debt: TK 141
Have: TK 111/112 |
Service public debt to credit control internal, avoid backlog liabilities and weight loss for working capital.
3.5. Accounting Currency – Banking – Capital
This profession focuses on the management of the items have the highest liquidity (Cash, Bank deposits) and the item constitutes long-term resources of the business (Equity).
| Name service | How accounting |
| Cash receipts (cash sales/service) | Debt: TK 111 (Money increases)
Have: TK 511 (Sales tax), TK 3331 (output VAT) |
| Cash expenditures purchase of goods/cost | Debt: TK 156, 642, ... (value of goods/cost excluding tax), TK 133 (input VAT is deductible)
Have: TK 111 (Cash discount) |
| Cash deposit into bank account | Debt: TK 112 (bank deposits increase)
Have: TK 111 (Cash discount) |
| Withdrawal of bank deposits of cash funds | Debt: TK 111 (Money increases)
Have: TK 112 (bank deposits up) |
| Customers pay the debt through the bank | Debt: TK 112 (bank deposits increase)
Have: TK 131 (customer receivables decrease) |
| Transfer payments public debt to suppliers | Debt: TK 331 (To pay the seller loss)
Have: TK 112 (bank deposits up) |
| Receipt of capital contribution in cash/transfer | Debt: TK 111 or 112 (Money increases)
Have: TK 411 (Equity/Capital increase) |
| Use the money to pay back capital to the owners | Debt: TK 411 (Equity decrease)
Have: TK 111 or 112 (Money up) |
| Bank charges (transfer Fee, maintenance fee) | Debt: TK 642 (Cost management business)
Have: TK 112 (bank deposits up) |
Ensure liquidity, optimize cash flow at the same time comply with the rules on capital, support investment decisions.
3.6. Accounting of fixed Assets
Fixed assets (tangible fixed assets) is the property of great value (under current rules) and duration of use, recovery of economic benefit on a year. Accounting fixed assets focused on keeping track of the original value, accumulated depreciation, and the situation fluctuations (increase or decrease) of the property.
| Name service | How accounting |
| Accounting when buying fixed assets | Debt: TK 211 (value of fixed assets excluding tax), TK 133 (Amount of input VAT is deductible)
Have: TK 111, 112, 331 (Total value of fixed assets according to invoice) |
| Depreciation of fixed assets periodically | Debt: TK 154, 641, 642 (Recorded cost respectively)
Have: TK 214 (wear and tear of fixed assets) |
| Delete window fixed assets (liquidation sale) | Debt: TK 214 (Total value of fixed assets have depreciated to the time of liquidation, sale), TK 811 (residual value of fixed assets)
Have: TK 211 (of fixed assets) |
| Revenue recognition liquidation, sale of fixed assets | Debt: TK 111, 112, 131 (the proceeds from the liquidation or sale of fixed assets)
Have: TK 711 (Price sale of fixed assets), TK 3331 (VAT sold out of fixed assets) |
| Repair of fixed assets before liquidation | Debt: TK 811 (Costs of liquidation of fixed assets), TK 1331 (VAT deductible)
Have: TK 111, 112, 331 (amount Of repair of fixed assets) |
Effective management of long-term assets and report accurate property, calculate the depreciation expense, reasonable service, strategic planning, investment.
3.7. Accounting tools (CCDC)
Tools (CCDC) is the property does not qualify to be classified as fixed Assets (fixed assets), but is still used in many states business. According to the current accounting, fixed assets have value from 30 million VND and use time from a year or more; CCDC is that the assets are worth less than this level.
| Name service | How accounting |
| When buying CCDC warehousing | Debt: TK 153 (value CCDC hasn tax), TK 1331 (input VAT)
Have: TK 111, 112, 331 (Total amount paid) |
| CCDC used 1 times (allocated off) | Debt: TK 154 (Used for production), TK 641 (for business), TK 642 (for management)
Have: TK 153 (value tools and supplies used) |
| CCDC used to allocate many times – When user CCDC | Debt: TK 242 (prepaid Expenses) Have: TK 153 (value tools and supplies used) |
| CCDC used to allocate many times – When allocating CCDC (recurring) | Debt: TK 154 (Used for production), TK 641 (for business), TK 642 (for management)
Have: TK 242 (prepaid Expenses decrease) |
Business CCDC is used to control operating costs, avoid losses, support budgeting details.
3.8. Accounting salary/ deductions from wages
Accounting salary is the process of recognition, allocation of the cost of wages, deductions from wages (social insurance, health, unemployment, union funds) and calculate the deduction (Personal income Tax) to determine the number of real wages of workers.
| Name service | How accounting |
| Accounting costs, wages (Wages payable to the employee) | Debt: TK 154, 641, 642 (wage Costs of the parts respectively)
Have: TK 334 (To pay workers) |
| Accounting cost insurance business subject (Approximately 23.5%) | Debt: TK 154, 641, 642 (insurance Costs of the parts respectively)
Have: TK 3383 (SI), TK 3384 (health INSURANCE), TK 3386 (UI), TK 3382 (KPCĐ) |
| Extract the amounts deducted from the salary of the employee (SOCIAL insurance, health INSURANCE, UNEMPLOYMENT insurance, PIT) | Debt: TK 334 (Except employee salary)
Have: TK 3383, TK 3384, TK 3386 (The EMPLOYEES bear), TK 3335 (PIT – circular 200) |
| Payment of wages to employees (food field) | Debt: TK 334 (food field loss)
Have: TK 111, 112 (payment by cash or bank transfer) |
| The payment of insurance, personal income Tax, for The state | Debt: TK 3383, TK 3384, TK 3386, TK 3382 (Total debt BH, KPCĐ), TK 3335 (PIT – Additional)
Have: TK 111, 112 (Money up) |
Management, cost transparency, reporting salary, accuracy, compliance, labor law, support planning, personnel costs.
3.9. Accounting reduced revenue
Reduced revenue is the account adjustment reduces the total sales revenue, and provide services in states. The accounting accurate deductions help determine the net revenue (Net Revenue) to calculate gross profit.
| Name service | How accounting |
| Trade discounts (Reduction in the listed price when customers buy large volume) | Debt: TK 5211 (the discount amount excluding tax), TK 3331 (VAT of account discount)
Have: TK 111, 112, 131 (actual amount discount) |
| Discount sale (Reduced by the poor quality, wrong size) | Debt: TK 5213 (discount amount excluding tax), TK 3331 (VAT of discounts)
Have: TK 111, 112, 131 (actual amount discount) |
| Sales returns (Customer returns goods sold) | Debt: TK 5212 (revenue of the bounce before tax), TK 3331 (VAT of the goods being returned)
Have: TK 111, 112, 131 (actual amount to pay back for guests) |
| The end of the period (transfer the sales deductions) | Debt: TK 511 (Total deductions)
Have: TK 521 (Total 5211 + 5212 + 5213 |
| Accounting price of capital (Recorded cost of sales returns) | Debt: TK 156, 155 (Price real capital of the goods being returned)
Have: TK 632 (cost of sales) |
Reflect the actual revenue, to help assess profit, adjust strategy, sales management, customer efficiency.
3.10. Accounting accounting final
Pen math final is the accounting profession was made on the last day of the accounting period (month, quarter, or year). The main purpose is to ensure the principle of accrual accounting is compliant, adjust the accounts to reflect the actual cost and the transfer of accounts, revenue, cost about 0 to start new. To ensure the principles of this profession need to make the pen to calculate the following:
- Depreciation of Fixed Assets (fixed assets)
- Allocation of Costs prepaid (CCDC, the cost of rent, etc.)
- Recorded accrued Expenses (accruals payroll costs, interest on loans, etc.)
- The shipping cost of Goods sold
- The Net revenue (net reduction of revenue)
- The shipping Cost of Sales
- The shipping Cost Business Management
- Transfer revenue – Cost Financial
- Gay Recorded Cost of Corporate income Tax (CIT)
- Transfer Rate (or loss), net
The accounting period end to ensure data financial reports full, accurate, decision support, strategic planning, capital, expenses and analyze the efficiency of business operations.
4. Implementation process of the accounting profession in business
To ensure financial data is accurate, transparency and comply with the law, businesses need to perform operations according to a standard procedure. This process standardization service, general accounting of the business, from collecting documents to reports, helping to minimize errors and optimize cash flow. In fact, the process includes four main steps:
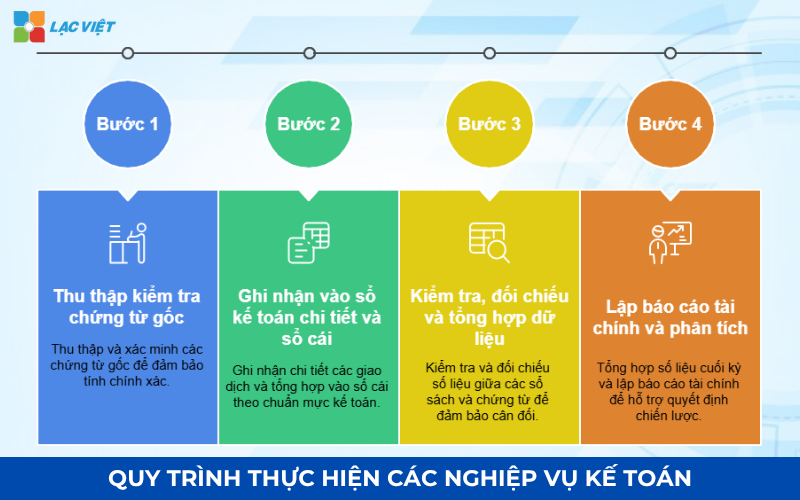
Step 1: collect – check the original documents
This is the platform to ensure all transactions are certified from the legal, valid and responsive full information according to the regulations.
- Check out the bill of sale, receipt/expenditure, contracts, commissioning records, as well as the evidence from other related.
- Collate information between the voucher to confirm accuracy and consistency.
The collect – check stock from tightly helps reduce the risk of errors in accounting, ensure transparency, public debt, and provide full documentation service audit. According to a survey by PwC, the business process test voucher closely can reduce up to 35% risk of accounting errors.
Step 2: Recorded at the ledger Details and ledger
After the voucher is valid claim, accounting proceed noted the business system book.
- Accounting: recognition of the economic (for example: Business warehousing raw materials 20 million unpaid: Debt TK 156, There is TK 331. When payments: Debt TK 331, Have TK 112).
- Data entry into the details window: Records detailing the purchases, sales, debt, cash, inventory, fixed assets (fixed assets)...
- Aggregate the data into the ledger: Collection of journal entries from window detail by account, compliance with accounting Standards in Vietnam (VAS) or IFRS.
The data is standardized, serves for the establishment, financial statements, cost analysis, and tracking cash flow to the leader board can strategic decisions in a timely manner.
Step 3: Check, collate and Aggregate Data
Here is the step of quality control, to ensure the data to balance the books, accounts and dovetail with evidence from the root.
- Reconcile the balance of public debt customers, suppliers, inventory, practical, on the book, bank balances (for projection window bank).
- Detection and timely correction of errors before reporting official.
This step will reduce the risk of false data, optimal cash flow management, and improve operational efficiency overall of the business.
Step 4: Financial reporting and analysis
The final step is to aggregate the data end of the period, provides financial information is reliable for leadership and management agencies.
- Reporting business results, Balance Sheet, statements of Cash flows and notes to Financial statements.
- Analysis of financial ratio important (such as profitability ratios, solvency, capital turnover) to support management decisions.
Provide the basis for strategic decisions, planning, capital, and evaluate the effectiveness of business operations of the business.
5. LV-DX Accounting – optimize the entire process of business accounting
Software, LV-DX Accounting of Vietnam to help businesses automate the entire process of accounting, from data entry to account to the establishment of financial statements, ensuring compliance with norms and international Vietnam.
Outstanding advantages
- Minimize errors, the optimal duration input: auto-account, cross-check vouchers, error warning before recording window.
- Integrated debt management, treasury, payroll and fixed assets: Support accounting the accounting profession, basic synthesis without the need to manipulate craft many steps.
- Support financial reporting according to the latest standards: including report on business results, balance sheet, cash flow, service audit and tax reporting.
Details: LV-DX Accounting
Master of professional accounting basic platform is the core guarantee of accuracy and transparency of financial system business. To be successful accountants need advanced analytical skills, financial reporting, cost control and optimization in finance.
In the digital era, the automation of business processes is essential trend. Therefore, the investment in fostering expertise as well as possessing the certificate according to international standards is solid path to expanded career opportunities, mastering the entire cycle of accounting.














