According to research from McKinsey, 80% of businesses can't maintain sustainable profit if there is no management strategy cost-effective. Spending unreasonable lack of data cost analysis business or just focus cut without optimization can cause the business to fall into the trap of reduced performance.
So how do business not only control costs but also use it as a tool to maximize profit? The answer lies in the in-depth analysis combined with technology to help businesses forecast trends, detect waste and financial decisions smarter.
This article Lac Viet Computing will provide comprehensive information on cost analysis from traditional methods to the application of modern technology to help businesses optimize financial resources in the most efficient way.
1. Overview of business expenses
1.1 Cost what is the business?
Cost of business is the whole amount that businesses have to spend in the process of operation, production, business and management in order to maintain, operate and develop the activities of the organization. In simple words, the cost of business is the input value that a business must pay to create products, provide services, maintain the operating system to generate revenue.

Some concepts cost need to understand prior to analysis:
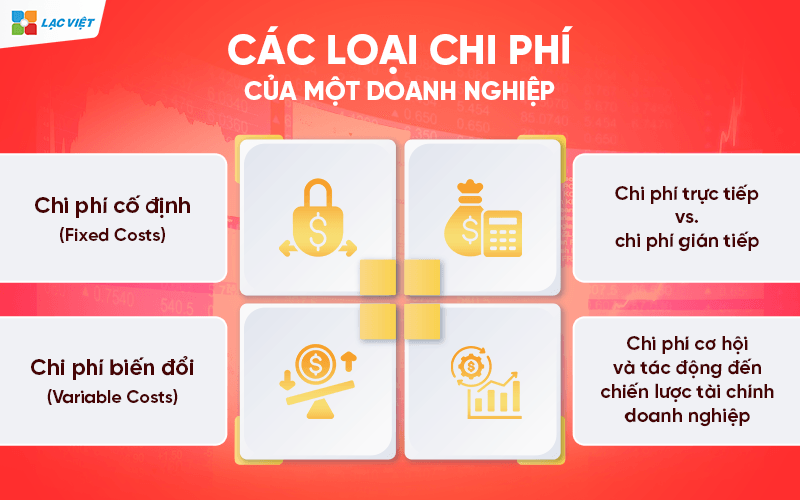
- Fixed costs: Are those costs do not change with output as: rent, salary management, asset depreciation. Though the business of producing more or less then the cost of this remains the same in the short term.
- Variable cost: Is the cost varies with the volume of production or sales, for example, raw materials, shipping costs, sales commissions.
- Direct costs: direct Mounting with creating products and services, for example: raw materials, wages of production.
- Indirect cost: cost Is not tied to a specific product, often used for the entire operation, such as: electricity, payroll accounting, administrative costs.
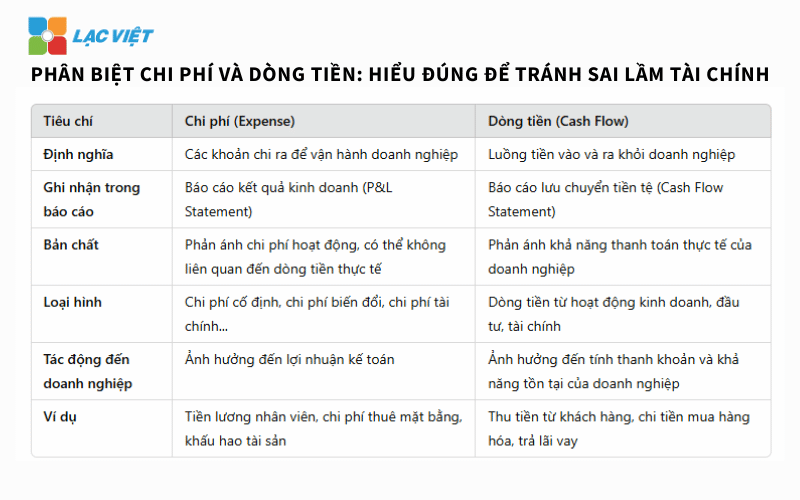
1.2 distinguish costs and cash flow
Many businesses often confuse cost and cash flow, leading to mistakes in financial management.
- Cost: Is all the business account must be spent to operate, including fixed costs – variable costs. Expenses are recognized in the reporting business results (P&L Statement).
- Cash flow (Cash Flow): The cash flows into/out of the business, reflecting the possibility of actual payment. Cash flow appear in the cash flow statement (Cash Flow Statement).
Sai lầm phổ biến: Một doanh nghiệp có thể có lợi nhuận trên sổ sách nhưng vẫn thiếu tiền mặt để thanh toán các khoản chi, do công nợ khách hàng cao hoặc quản lý dòng tiền kém. Vì vậy, phân tích chi phí không chỉ tập trung vào chi tiêu mà còn phải xem xét dòng tiền để đảm bảo doanh nghiệp không gặp rủi ro thanh khoản.
- 10+ ERP Management Accounting Software with AI Compliant with Circular 99/2025 for Vietnamese Businesses
- 9 Accounting Software online cheap cost reduction for small and medium ENTERPRISES
- [Trọn bộ] File Excel report template production costs with the instructions set details
- Types of costs in business: Classification, examples and controlling the efficient
2. Cost analysis what is a business?
Cost analysis business is the process business review, assess and understand the causes fluctuations of the expenditures in manufacturing operations – business. The ultimate goal is the reasonable control each type of costs, avoid waste, at the same time improving the efficiency use of resources that retains the quality of products, service and competitiveness.
Other than the merely keep track of accounting data, cost analysis help businesses answer the very specific question such as:
- Why the cost increase that profit does not increase proportionately?
- Parts which are incurred beyond the level?
- There are expenses which are consuming resources that do not bring value commensurate?
The analysis not only helps businesses control the budget, but also plays an important role in financial strategies long term. A business can have a high turnover, but still in financial trouble if not managed cost effectively. The main benefits of cost analysis include:
- Specify the account details are not needed to optimize profit
- Support financial decisions based on real data
- Help business valuation products/services more accurately
- Increasing competitiveness through cost control efficiency
For example illustrated easy to understand: A workshop for production of bottled water are:
- Fixed cost is 200 million/month (rent warehouse wages technician)
- Variable costs about 2,000 vnd/bottle (plastic bottle, labels, shipping)
If that month producing 50,000 bottles, variable cost will be 100 million → total cost is 300 million. If months later increased to 70,000 bottles, variable costs increase to 140 million, but the fixed cost is still 200 million. The analysis help businesses clearly see that: fixed costs do not increase, as production lot cost units as low → this is the potential to optimize the cost.
3. Cost classification – Step platform to accurate analysis
3.1 fixed Costs and variable costs
This is how the classified according to the rate of change of the cost in comparison with the scale of operations (production volume, sales revenue, number of orders,...).
- Fixed costs are those costs do not change as output, in a certain period of time. For example: rent, office buildings; staff Salaries fixed; Cost of property maintenance, machinery; depreciation of fixed assets; the Cost of insurance, cost management. Fixed costs are often difficult to cut in the short term, but if business can be optimized (for example: negotiate price, rental office, optimize hr) can help improve the profit margin.
- Variable cost is the cost increase or decrease according to the output, such as raw materials, packaging costs, wages according to the product, or commission on sales according to sales, production costs direct (electricity, water, labor, production), transportation costs, logistics costs, advertising, marketing by revenue. Manage variable costs effectively help business control good profit margin.
Why business need to distinguish two types of this cost?
- To calculate the breakeven point, news of the minimum yield to be achieved to no holes.
- To build the scenario cost flexibility to scale growth, help plan financial police more realistic.
To control financial risks: if the proportion of fixed costs too high, business easily affected when reduced output or revenue instability.
3.2. Direct costs and indirect costs
This is classified by the relationship of cost with subject specific costs, such as products, services, projects or departments.
- Direct costs are costs that can be clearly defined and directly tied to a product or specific activities. For example: raw materials used to produce a commodity, wage garment workers in an order specific.
- Indirect costs are those costs can't scale, right for a specific object, it should be allocated. For example: power water general, the cost of software, common salary accounting department, administrative.
Practical value the business receives:
- Distinguish right help calculate the price of the product accurate, avoid the price too low, resulting in holes underground, or too high a loss of competitiveness.
- Help build the system cost allocation fairness transparency between departments and projects.
- Is platform to report profit/loss according to each product line or business channel.
Illustrative example: the Same factory produces two types of products A and B:
- The cost of raw materials for product A is the cost of direct
- The cost of electricity to run the entire plant is indirect costs, need to allocate according to the output of each product line
3.3. The cost of production and cost of production (sales – management)
Classification by function of the cost of operations, here is a comprehensive view of the role of each expense.
- Cost of production: the entire cost to create the product or service, including raw materials, direct labour, operating costs, machinery costs, workshop,...
- Cost of sales Includes costs incurred in the process of bringing products to our customers as the cost of advertising, shipping, promotion, commission sales staff.
- Cost management business: Is the account service of the executive, such as salaries administrative department, legal costs, stationery costs, information technology,...
Why enterprises need to understand the boundaries between groups, this costs?
- Help assess the effectiveness each stage in the value chain from production to sales.
- From that analysis, profit/loss according to each distribution channels, customer groups or product lines.
- Is platform to devise strategy to cut costs, smart – cut right place waste, keep the account value creation.
Illustrative examples: Business manufacturing software:
- Cost programmer salaries: cost of production
- Cost of marketing, running Google ads: cost of sales
- The cost of office rent, salary hr department: cost management business
3.4 opportunity Cost and impact on strategy, corporate finance
The opportunity cost (Opportunity Cost) is the value of the opportunity lost when businesses choose a plan instead of another embodiment.
For example:
- A business has 50 billion and can invest in the expansion of production or invest in AI technology. If you choose to expand production, the opportunity cost is the benefit from the application AI that business can have reach.
- If a company uses cash to pay dividends instead of investing in research, new product, opportunity cost is the ability to growth in revenue from that product.
The consideration of opportunity costs help businesses make financial decisions more optimal, especially in the stage of expansion or restructuring.
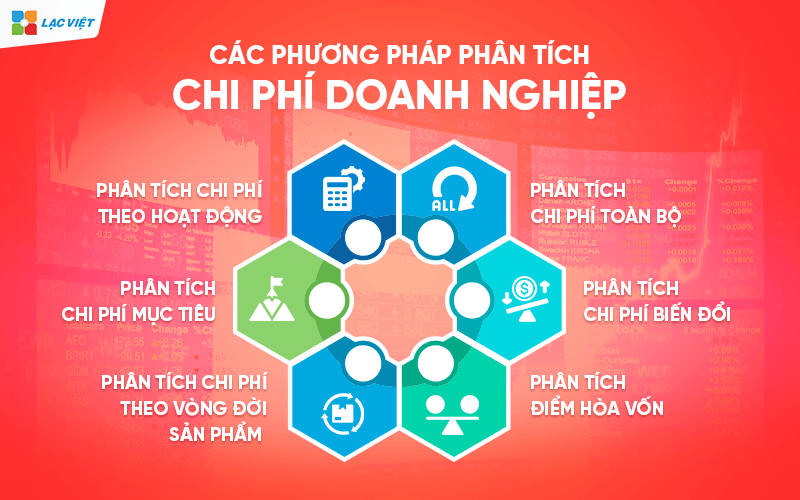
4. The method of analysis cost-effective business
The cost analysis business should not stop at the track costs rise or fall, but need to according to different angles to find out the causes, trends, and optimization opportunities. Here are 4 methods of analysis are widely used in practical financial management business.
4.1. Cost analysis by states (compare the cost over time)
This is method to help businesses compare the level of expenditure between the different periods to recognize the increase and decrease irregularity of each expense. The comparison can be made by month, quarter, year or seasonal, depending on the particular operation.
How to perform:
- Select an item specific costs (e.g. cost of sales, operating costs, cost of raw materials...)
- Comparison between two or more periods next
- Analysis of the level of fluctuations in the value (increase/decrease how much percent)
- Question: this change are located in the plan? Have commensurate with revenue growth or yield?
Practical example:
The cost of electricity months 3 is 40 million, to January 4 increase to 70 million, while the output without change. Possible causes come from:
- Systems, machines consume more electricity due to maintenance less
- Personnel working out of hours more but not effective
- Or simply the electricity price spike
The identification of early abnormalities will help businesses adjusted operating right in the next period, instead of waiting to the end of the year sums up just discovered “leaks budget”.
Enterprise value received:
- Track trends in costs over time to create a budget police practice
- Easily assess the effectiveness, cost savings of the initiative internal
- Detection of expenditures not reasonable to optimal right
4.2. Analysis of fluctuations in costs as inputs
This method delving into the specific causes that costs increase or decrease, to help the administrator does not stop at the level of “get to know have changed,” which progresses to “understand and control is reason to change”.
These factors often cause volatility:
- The price of raw material changes: directly affect production costs
- Production changes: Increase in output can cause increased costs, but the unit price reduction
- Performance using less Material wastage ratio, broken high, the working time is prolonged
- Fluctuations in cost from suppliers, partners
Practical example:
The cost of raw materials wheat flour of a manufacturing enterprise pastry increased from 150 million to 210 million in a month. In-depth analysis detection:
- The price of flour increased by 10% due to market fluctuations imported
- Business order fold, not to be discounted as before
- The rate of damage in the process of production increased due to the mixing machine at level
Results: There are 2/3 causes can completely internal control if recognized in a timely manner.
Enterprise value received:
- Analysis of police cause changes, which give accurate measures
- Actively renegotiate with suppliers, optimal performance machinery
- Avoid “cut the general”, which causes negative effects to the quality of products
4.3. Ratio analysis costs/revenue (Cost-to-Revenue Ratio)
This is a method of measuring financial performance is not based on absolute numbers, but on the relative proportions between cost and revenue. This ratio indicates the business is how much to spend to create 1 turnover.
Distance calculator:
Cost rate/revenue = Total cost / Total revenue
For example:
- Revenue: 2 billion
- Total cost: 1.5 billion
→ Rate = 75% → gross profit margin was 25%
Practical application:
- When revenues increase but profit does not increase proportionately, this is just some help detect problems.
- If the ratio of cost/revenue increasing, can business growth is not sustainable, the cost of “team up” 't control.
Illustrative examples:
Year 1:
- Revenue: 1.2 billion
- Cost: 960 million → Rate = 80%
Year 2:
- Revenue is still 1.2 billion
- Cost: 1,080 rate, → Rate = 90%
Increase revenue does not help increase profits if costs rise faster. This is the basis for tightening of the budget, the optimal hr or review sales strategy.
Enterprise value received:
- Measuring operational efficiency through each of the states
- Comparing performance between the branches, project or product line
- Create a premise to build KPI financial direction streamlined efficiency
4.4. Analysis of expenses by cost center (Cost Center Analysis)
This approach towards the allocation of cost control in detail according to each department or project. Each unit operation is seen as a “cost center” have the budget, responsibilities, and performance separately.
Benefits when analyzed according to the center:
- Detection parts are using the budget less effective, budget control in each unit, avoid losses, not control
- Delivery of financial autonomy comes responsibility, specific help to create a culture spend responsibly in each department
- Easily compare the results using cost between departments in the same function, thereby improving the effective use of cost across the organization
Practical example: The company has 3 departments: Marketing, business administration. The cost of 6 months:
- Marketing: 300 million → 1,200 potential customers
- Business: 450 million → just latch is 80 the contract
- Administrative: 250 million → increased by 20% compared with the previous month, with no major change in personnel
Through cost analysis according to the center, the executive board may:
- Reduced budget for business requirements improve conversion rate
- Review fixed costs of administration: have wasted no?
- Increased investment for Marketing – are bringing better efficiency
5. The pattern cost analysis business
Cost analysis business is one of the important tool to help businesses control the budget, the optimal profit, given the financial decisions correct. Below are the methods of cost analysis popular, from traditional to modern, help your business have the overall look in-depth about the cost structure.
The method of cost analysis traditionally focused on the calculation of the total cost based on the expenditure fixed – variable. This is a platform that helps businesses understand the cost structure before applying the model analysis enhancement.
5.1 Model cost analysis whole (Full Costing)
Cost model the whole, or also called the method of allocation of costs, fixed and variable, to help businesses determine the total cost of producing a product or service.
Distance calculator:
Total production costs = fixed Costs + variable Costs
Advantages:
- To help businesses determine the price of accuracy.
- Provide sufficient data to make financial decisions long term.
Cons:
- Not accurately reflect the impact of variable costs in profit.
- May increase the price of the product if fixed costs are too high.
For example, A manufacturing business are the cost of raw materials 100 million vnd/month (variable costs) and the cost of rent, workshops, staff salaries 200 million vnd/month (fixed costs). If the business is production of 1,000 products/month, then the total cost of each product is (100 million + 200 million) / 1.000 = 300,000/product.
5.2 analytical Model variable costs (Variable Costing)
This model only the costs directly related to production, excluding fixed costs.
Distance calculator:
Total production cost = variable Cost unit × Number of products
Advantages:
- Accurately reflect the cost varies with the volume of production.
- Business support break-even point analysis, and pricing strategy.
Cons:
- Can't is the whole costs the business incurs.
- Misleading, if not consider fixed costs.
For example: A business are the cost of raw materials is 100,000 vnd/product, cost of production is 50,000/product. If production of 1,000 products, the total variable cost will be (100.000 + 50.000) × 1.000 = 150 million.
5.3 Model analysis of the breakeven point (Break-even Analysis)
Break-even analysis help businesses determine the minimum sales needed to achieve to not be the hole.
Formula:
The break-even point = Total fixed costs / (selling Price – variable Costs per unit)
Meaning:
- Help the business know the number of products or revenue needed to achieve to be profitable.
- Support decisions about strategy, selling prices, costs and production.
For example, If a business has a fixed cost 500 million/year, the selling price per product is 200,000 and variable costs on each product is 100,000, then:
Point = 500 million / (200,000 and 100,000) = 5,000 products.
This means that businesses need to sell at least 5,000 products per month to not be the hole.
5.4 Model analysis of expenses by activity (Activity-Based Costing – ABC)
The ABC model helps to allocate the cost based on the specific activity instead of just using the traditional method.
How it works:
- Identify the main activities in the enterprise.
- Cost allocation based on the level of resources used by each activity.
Advantages:
- To help businesses understand the costs of each activity.
- Increase the accuracy in calculating the price of products/services.
For example, If a business has 3 products, but a product costs check out more quality, the ABC model will help determine the right cost for each product instead of divided equally.
5.5 Model cost analysis target (Target Costing)
This method helps the business determine the maximum cost may be acceptable to produce a product based on the selling price expectations.
Formula:
Target cost = selling Price expectations – desired profit
For example, If the market only accept selling price 500,000/products and businesses that want to profit by 20%, then the cost goal should be 500.000 – (500.000 × 20%) = 400.000 /products.
5.6 analysis Model, the cost according to the product life cycle (Life Cycle Costing)
This method helps enterprises calculate the total cost from the product development to when to stop trading.
The main stages include:
- Research and development
- Production distribution
- Sales marketing
- After sales support
For example, A business technology can accept the hole in the stage of research and development to optimize costs in the period the sales and after sales support.
6. Common mistakes in cost analysis and ways to overcome
Cost analysis is an important part in financial management business. However, many businesses suffer from these common mistakes made controlling costs, no optimal performance. Here are three common mistakes and how to fix it to ensure business strategy, financial sustainability.

5.1. Just focus on cost-cutting that ignores optimal performance
Why reduce excessive costs can reduce business performance
One of the biggest mistakes of business when cost analysis is focused only on the cut without assessing the impact on business performance.
The cost cuts can help your business save on the budget in the short term, but if there is no reasonable strategy, it can lead to:
- Deterioration in the quality of products/services, make customers leave.
- Reduce the motivation of staff due to cuts in personnel or reduce the remuneration.
- Reduced ability to expand and innovate, do business, loss of competitive advantage in the market.
How to fix: optimized instead of just cutting costs
Instead of just focusing on reducing costs, businesses should apply the approach to optimize the cost, that is:
- Focus on increasing operational efficiency instead of cutting personnel. For example, Use automated technology instead of reducing the number of employees.
- Optimal cost on each unit of product instead of cutting quality. For example: Purchase of raw materials with wholesale price, big order to reduce the price instead of choosing poor-quality raw materials.
- Investing in technology to reduce costs long-term. For example: Use the software cost analysis to control spend more effectively.
5.2. No cost analysis according to each business activity
Risks when not understood each account expense impact as to how revenue and profit
Many businesses consider only the overall costs without detailed analysis itemized costs according to each department or business activity specific. This leads to:
- Do not know the activity that is wasteful costs.
- Can't identify where the costs need to cut that does not affect performance.
- Product pricing mistake by not properly allocate costs for each product line.
Businesses can use the analysis of expenses by activity (Activity-Based Costing – ABC) to determine the actual cost of each activity and the optimal budget:
- Identify each of the processes in the enterprise: For example, production processes, shipping, marketing, sales.
- Assign costs to each activity: allocate correct shipping costs for each product line, instead of pooled into the overall cost.
- Performance analysis each activity: Determine which activities bring the highest value and the operation does need optimization.
5.3. Do not use technology to optimize cost management
Many businesses still manage costs by method or use Excel to keep track of the budget. However, this can lead to:
- The data are not exact, the lack of updates makes business decisions based on data obsolete.
- Difficult to detect trends in the cost increase unusual, doing business could not adjust the budget.
- Take a lot of time in the synthesis of data, reduce the working performance of the finance department.
How to fix: App technology to analyze the optimal cost
Businesses can take advantage of the tools of financial analysis to automate the process of expense management:
- Use accounting software, financial analysis as AccNet, Fast Accounting, QuickBooks to track expenses in real time.
- Application ANYONE in cost analysis to forecast future costs and to detect abnormalities in the cash flow.
- Use dashboard finance with tools such as Power BI, Tableau for visual display cost data to help managers make decisions quickly.
6. Finance AI Agent of Lac – support tool business analysis cost-effective
Finance AI Agent of Lac Viet is an advanced solution to help businesses automate the process of monitoring, analyzing, optimizing costs, help improve financial performance and make a decision more quickly.
Finance AI Agent provides system track expenses in real time to help businesses have a comprehensive view of every item of expenditure in each stage of operation. The system automatically collects data from sources such as:
- Accounting software finance management (as AccNet, Fast Accounting).
- System ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning).
- Reported cash flow from the accounting department of finance.
After collecting data, AI will analyze spending trends based on historical transactions and take out the intuitive reporting to help businesses answer the important questions such as:
- The account details are abnormal increase?
- Any costs tend to exceed the budget?
- Parts or activity that is costs the most?
Besides keeping track of the usual cost, Finance AI Agent also has the ability to detect abnormalities in the cost and risk warning.
The main features include:
- Discovered spend no reasonable: If a department spending exceeds normal levels, or there are unusual transactions, the system will immediately send a warning to the leader board.
- Analysis of hidden costs: AI can determine what payments are not effective or does not bring business value.
- Performance evaluation spending: Comparing the cost of the business with the standards in the industry to determine the level of efficiency.
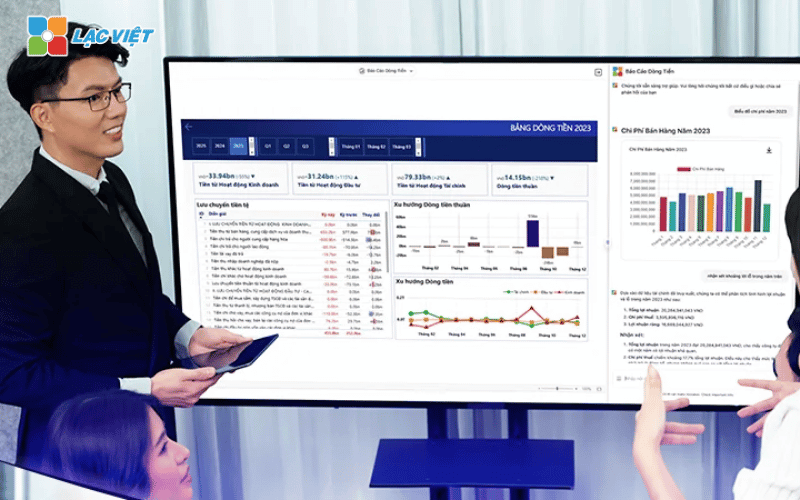
Lac Viet Financial AI Agent to solve the “anxieties” of the business
For the accounting department:
- Reduce workload and handle end report states such as summarizing, tax settlement, budgeting.
- Automatically generate reports, cash flow, debt collection, financial statements, details in short time.
For leaders:
- Provide financial picture comprehensive, real-time, to help a decision quickly.
- Support troubleshooting instant on the financial indicators, providing forecast financial strategy without waiting from the related department.
- Warning of financial risks, suggesting solutions to optimize resources.
Financial AI Agent of Lac Viet is not only a tool of financial analysis that is also a smart assistant, help businesses understand management “health” finance in a comprehensive manner. With the possibility of automation, in-depth analysis, update real-time, this is the ideal solution to the Vietnam business process optimization, financial management, strengthen competitive advantage in the market.
SIGN UP CONSULTATION AND DEMO
Cost management business doesn't just stop at the cut, which is also a strategic long-term financing to help businesses enhance performance, maintain sustainable growth. By applying the method cost analysis modern use data to optimize your budget and application technology, AI in financial management, the business can control spending in a smart way, at the same time to make decisions more strategic.