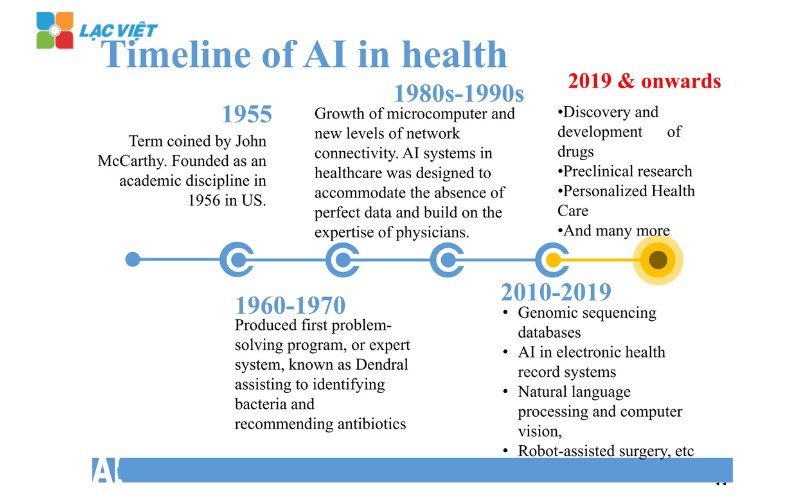
Artificial intelligence (AI) have and are making strides in many areas, in which, artificial intelligence in medical considered one of the applications most promising. A study from the Journal The Lancet Digital Health showed that AI can improve the accuracy in detection of breast cancer up to 94%, surpassing even the leading experts.
The application AI in the medical industry not only helps to improve operational efficiency, but also improve the quality of health care, bringing hope for millions of patients worldwide. So AI in what is health and why is it so important? Let's Lac Viet find out details in this article.
The same theme:- 4 Applications of AI in education reality
- Applications of AI in the financial sector is application how?
- 7 Application of AI in banking benefits superior
1. AI in healthcare is what?
AI or artificial intelligence in medical is using algorithms and machine learning models (machine learning) for processing, analysis, learning from medical data. AI has the ability to support the doctor given the clinical decision through big data analytics (big data), image recognition (image recognition), predict pathology. These tools not only reduce the time of diagnosis but also enhance accuracy, help save the lives of many patients.
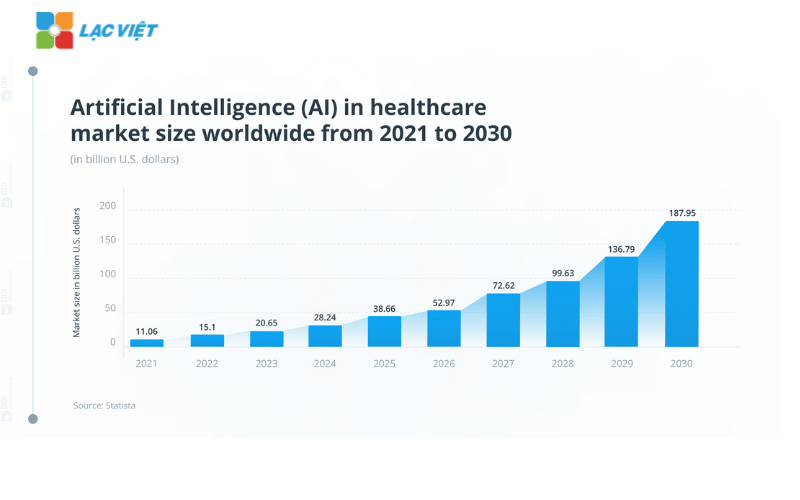
Artificial intelligence is no longer a strange concept that has become a strategic tool in the medical industry. The AI system supports not only data analysis but also plays a pivotal role in the diagnosis, pathology, treatment support, optimized operation. According to the report by MarketsandMarkets (2023), market AI in healthcare is expected to reach 187,95 billion in 2030, growing at a CAGR 37,6% from the year 2022. These numbers prove that the application of AI is no longer the trend that has become indispensable requirement in the medical industry.
2. The AI technology, artificial intelligence in medical
The AI technology used in medical:
- Machine Learning (machine Learning): popular application in predicting pathology and treatment support personalization. For example, AI can analyze data from millions of patients to predict the risk of diabetes.
- Natural Language Processing (Processing natural language): Help to analyze the information from the medical record electronic (EMR) or communication support with chatbot in health care.
- Computer Vision (computer vision): Applications to image analysis, X-ray, MRI, or other data complex medical, support diagnose the disease quickly and accurately.
- Reinforcement Learning help optimize the process of radiation therapy for cancer patients
- Generative AI to create fake photos establishment of cancer cells
2.1 Machine Learning (machine Learning)
Machine Learning (ML) is a branch of artificial intelligence, where AI systems learn and improve from data without the need for specific programming. In health, ML plays a key role in handling big data and detect patterns hidden from the patient information.
- Application in predicting pathology: ML analyze millions of patient records to predict the risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular, and cancer.
- Personalization of treatment: ML suggested treatment regimens based on personal data, such as genetics, medical history.
- Enhance the process of drug testing: ML analysis of the clinical response to shorten the duration of the test, specify group object matching. This is especially important in the development of vaccines and new drugs.
2.2 Natural Language Processing (Processing natural language – NLP)
Natural Language Processing is the technology to help AI understand, analyze and create natural language of humans. In the medical field, NLP plays an important role in the processing, information extraction from text or communicate.
- Analysis of medical records electronic (Electronic Medical Records – EMR): NLP to extract important information from medical records, medical reports, data tests.
- Chatbot and virtual assistant: NLP support chatbot to communicate with the patient, answer the basic questions, medical advice, preliminary.
- Research support: NLP analysis of thousands of scientific articles, research reports to find trends or new knowledge. This helps researchers save time, focus on important issues.

2.3 Computer Vision (computer vision)
Computer Vision is a different branch of AI that focuses on the “read” and analyze images, video, or image data, medicine such as X-rays, MRI, CT scan.
- Image analysis medicine: computer vision detection of abnormalities in medical images, support doctors diagnose diseases faster and more accurate.
- Support surgery: Computer Vision in conjunction with medical robot to perform complex surgeries with higher accuracy. Da Vinci robotic technology using computer vision to assist the surgeon in laparoscopic surgery, help minimize risk and recovery time of the patient.
- Monitor patients remotely: Computer Vision patient monitoring via camera or sensor to detect unusual signs such as falling, seizures, or deterioration of health.
2.4 Types AI else is used in medical
In addition to the main technology, a form of artificial intelligence in health are also widely applied as:
- Reinforcement Learning (Learning enhancement): Is used to optimize treatment regimens through the “learn” from actual results. Reinforcement Learning help optimize the process of radiation therapy for cancer patients by adjusting the parameter machinery to achieve the highest efficiency that still minimize the damage healthy tissue.
- Generative AI (AI creation): this AI has the ability to create image or data emulator service for medical research. Generative AI created images of cancer cells, help researchers understand more about the development and response of cells to the drug.
3. 5 Application of AI artificial intelligence in medical, the most prominent current
5 Application of AI in medical/health care:
3.1. Application of AI in diagnostic pathology
AI has opened a turning point in improving the accuracy and speed of diagnosis, pathology thanks to the ability to analyze huge data to identify unusual signs from a very early age.
- AI technology in the detection of skin cancer: A study at Stanford University (2023) has developed learning algorithm machine has the ability to analyze millions of skin images. The results showed that AI can diagnose skin cancer with an accuracy of 95%, equal or surpass the doctor specializing in dermatology.
- Detection of lung cancer: The AI system such as Google DeepMind has aided detection of pulmonary nodules in CT scans, to help increase the detection rate of lung cancer early stages added 11%.
- Cardiovascular: AI combined with wearables like the Apple Watch or Fitbit allows analysis of heart rate and give early warning about the risk of atrial fibrillation, stroke or cardiovascular disease danger. According to a study by Mayo Clinic (2022), the AI system remote support has decreased the mortality rate due to cardiovascular disease to 20%.
- Rare diseases: With data, genes and family medical history, AI as tools from company Face2Gene can accurately recognize the syndrome, rare genetic, shorten the time of diagnosis from a few years down the last few weeks.
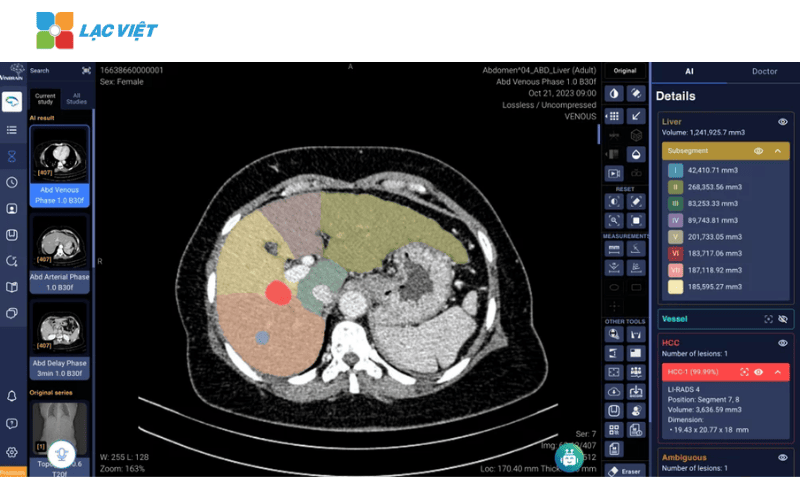
3.2. Application of AI in construction, development, treatment
Artificial intelligence in medical help build treatment regimens appropriate to each individual, based on data medicine, genetics, living habits of the patient.
- AI in genome analysis: The AI systems like IBM Watson for Genomics using genetic data to suggest therapy cancer treatment the most accurate. In the U.s., Watson has genetic analysis of a patient with breast cancer, suggested regimens of chemotherapy other than standard. Results, patients recover faster than 40% compared with conventional therapy.
- Treatment of chronic disease: The tool AI like CarePredict track and analyze routine activities of patients with diabetes or high blood pressure, suggesting lifestyle changes, reminders on medication right now.
- Pharmaceutical personalization: AI-assisted analysis of drug response for each patient, from which the proposed dosage compliance, reduce side effects, increase the therapeutic effect.
3.3. Application of AI in records management medical data
The health system is increasingly complex, with the volume of big data from medical records, treatment history, to the test results. AI has solved this problem by process automation, data management.
Added to that, blockchain technology helps encrypt data and AI ensure transparency in handling medical information. Estonia has deployed blockchain in storage, medical records, combined AI to analyze data, reduce 30% of the cost of storage, a 40% increase in effective access to information.
3.4.Application of AI support research, drug development
Artificial intelligence in medical're completely change the way pharmaceutical companies develop new drugs, helping save time, cost.
- Shorten the duration of the study: company Insilico Medicine uses AI to find the compound treatment of the disease arteriosclerosis in just 46 days, compared with the years of traditional methods. According to a report from Deloitte (2023), the application of AI in pharmaceutical research can reduce 60% of the cost of clinical research.
- Clinical trial intelligence: AI analysis of data from clinical trials to optimize the group of test subjects, increase the success rate of the drug. Pfizer has been using AI to increase the success rate of testing a vaccine COVID-19 in the stage of pandemic.
3.5. Application of AI in health care remote (Telehealth)
AI has become the foundation for the services of health care from a distance, especially in the context of the pandemic COVID-19 and the shortage of doctors in many countries. Help save travel time and cost for health care for patients. Increased accessibility health services for people in rural or remote areas.
- Chatbot and virtual assistant: Chatbot integrates AI as Babylon Health or Ada Health helps patient to check symptoms, preliminary advice, reduce the load to the doctor. In the Uk, Babylon Health has helped reduce 30% turn the patient to the clinic not necessary.
- Data analysis from AI receive data from medical devices such as blood glucose meter or blood pressure, analysis, send alerts to the doctor if it detects unusual.

4. Benefits of the application of AI in health
4.1 Increased operating efficiency and cost savings
According to a report by Accenture (2023), the application of artificial intelligence in healthcare can save more than $ 150 billion for global health sector by the year 2026, thanks to minimizing medical errors, optimize processes, improve operational efficiency.
AI is changing the way medical institutions operate, from patient management, optimization of personnel, to use health resources efficiently. The integration of AI into the process to help reduce tasks repeated, work automation, reducing waste.
Specifically, AI is used to process and analyze millions of health data from patient history, bills, to pharmaceutical management. The automated system helps to minimize errors in data entry and improve processing speed. For example: the Mount Sinai hospital (Usa) deploy AI system to analyze patient data, reducing the time to enter data from 4 hours down to 2 hours, at the same time save 30% on operating costs every year.
4.2 Improve the quality of health care
One of the most important benefits of AI is the ability to improve the quality of medical services. AI not only support doctors make clinical decisions, but also ensure that the treatment regimen is optimized for each patient.
- Minimize medical errors: The AI system can analyze patient data and suggested treatment regimens accurately, minimize the mistakes that humans are predisposed to be in a high pressure environment. According to research from the Medical Association of the United States, the percentage of errors in diagnosis was reduced to 85% thanks to the support of AI.
- Early disease detection: AI analyzes the initial signs that people can ignore, help detect the disease early. This is especially important with diseases such as cancer and cardiovascular disease. AI at the Mayo Clinic to help detect the risk of stroke before the patient shows symptoms, help to increase the 15% likelihood of survival.
- Personalized care: AI put out the course of therapy individually based on patient records, history, genetics, medical data worldwide. Johns Hopkins hospital has applied AI in personalized treatment regimens cancer, helps to increase the rate of recovery to 25%.
4.3 Reducing the load on medical staff
With the volume of work is increasing, medical staff often faced with a state of exhaustion. Artificial intelligence in medical support to automate administrative tasks and management, helping them to focus on more important tasks.
- Work automation repeated: AI undertake tasks such as data entry, invoice processing, management and schedule surgery. The AI system of the Japanese help plan surgery, arrange time schedule, reduce 40% of the volume of administrative work of the doctor.
- Support quick decision: AI provides the information detailed analysis in real time, help doctors make decisions quickly without having to search manually. A hospital in India to use AI to analyze the results of blood tests, warning danger signs within a few minutes.
- Increase the duration of patient care: With the support of AI, medical staff can spend more time to focus on the interactive, patient care, improving the experience of patients.
4.4 Expand the capabilities approach, health care
AI are open great opportunities for the rural and remote areas, where health services quality is still limited due to lack of doctors and infrastructure.
- Remote care: The application is integrated AI on smartphones allows patients to self-check symptoms, get preliminary advice from chatbot health. Babylon Health has provided care service, health free for millions of people in Africa, helps to reduce the pressure for health system, local time.
- Support in the case of an emergency: AI can analyze health data from remote and put out an immediate alert when it detects signs of danger, thereby increasing the opportunity to save patient's life. In Indonesia, AI helped detect dengue fever soon based on data from patients and weather, helping to reduce 30% of deaths.
- Discount medical gap between urban and rural areas: The device AI hand as ultrasound machine mobile are cheaper, easier to use, brings high quality service for those hard to reach areas.
5. Challenges faced when application artificial intelligence in medical
5.1 Problem of data security, privacy of patients
The handling of large amount of medical data is sensitive, including personal information, medical history, diagnostic results, which makes the system AI become the target of hackers and cyber attacks. This is one of the the biggest worry when the application is AI in the medical industry. Regulations such as GDPR (Europe), and HIPAA (U.s.) requires data security strictly medical, but not every country has a legal framework strong enough to protect the privacy of patients.
According to a report from IBM Security (2023), the medical industry is the top target of cyber attacks, with the average cost for each service data breach up to $ 10 million. The data leakage not only cause financial losses but also losing the trust of patients and medical institutions.
Current solution:
- Data encryption: The system AI need to use advanced encryption technology to protect data during storage and transmission.
- Blockchain: combining blockchain to ensure transparency and security of medical information, prevent the risk of edit, or delete data illegally.
- Access right management: application of AI to monitor and restrict data access, ensuring that only authorized users can access sensitive information.
5.2 Reliability and legal liability of AI
AI, though trained with large data volumes, the inevitable flaws. The minor errors in algorithms or data input not full can lead to serious consequences in the diagnosis, treatment.
Case AI take a wrong decision: AI can't completely replace the doctor, because the decisions of AI based on the input data, algorithm, can overlook these factors are not quantifiable as the context of medical or clinical experience. An AI system in the Uk has been misdiagnosed a patient does not have cancer, leading to missed opportunities timely treatment.
Liability: difficult question is raised as to when, AI make mistakes, who will be responsible? Technology providers AI, hospitals, or doctors use AI? The legal regulation is currently unclear, creating challenges when integrating AI into medical processes.
Solution:
- The role of the doctor: AI should only role was support tool, the doctor should check, is ultimately responsible in medical decisions.
- Clinical trial: booster inspection and testing AI in real-world environments before applying widely.
5.3 The Cost of implementing AI technology
Application to artificial intelligence in health requires a large investment in infrastructure, technology, software, training, human resources, this becomes a challenge especially with regard to the medical facility small and medium.
- Hard on costs: A system of AI in healthcare can spend millions of DOLLARS for the installation, maintenance and frequent updates. In addition to the cost of hardware and software, the training staff, medical use, AI is also a financial burden.
- Impact on base small: small hospitals or medical facilities in remote areas is often not enough budget to deploy AI, leading to inequalities in access to technology.
Solution:
- Financial support: The government and international organizations need to take out the program grants, preferential loans for medical facilities want to deploy AI.
- Public-private partnerships: collaboration with the technology company to provide solutions AI-based subscription or lower costs for the health organization, small.
5.4 Shortage of professionals in the field of AI medical
The rapid development of AI in health require human resources qualified in both the medical field and technology, but the distance between the actual demand current is still very big.
According to the report of AI (2023), global health sector, teen more than 6 million professionals medical technology, including expert on AI. Many doctors and medical staff is not trained enough to use the tool AI complicated, leading to the exploitation has not yet effective this technology.
The cause may be due to training programs on AI in healthcare is still limited and not enough to meet demand. The difference in medical expertise and technology, prompting the development in the industry becomes difficult.
Solution:
- Intensive training: Promote training programs, workshops combination between technology and health.
- Cooperation with educational institutions: hospitals and business technology should partner with universities to train human resources AI medical high quality.
- Application AI simplify: development tools AI easier to use, help medical staff fast access without the need for in-depth knowledge.
Artificial intelligence is opening a new chapter full of prospects in the medical industry, bringing tremendous benefits for organizations and businesses. However, to maximize the potential of AI in medicalthe need to overcome challenges of security, cost, human resources.
Medical institutions and businesses that need to quickly embark on the research, development artificial intelligence in medical not only to enhance operational efficiency, but also improve the quality of health care for the community. Be the pioneer in the application of AI technology to create positive changes for the future of the medical industry!
Do you know businesses are spending a lot of money to pay for staff looking for information?
- Of 1.8 hours per day employees spend out to search and collect information, the equivalent of 9.3 hours per week
- Business loss 500 hours per year for employees to perform searches for information for work
- 63% leadership said the sharing of knowledge and information internal trouble, reduce the productivity of the business
Lac Viet Chatbot AI assistant – Freeing up personnel to focus on creative work
- Virtual assistant process – approved LV Chatbot AI for Workflow: Access quick information, content summary, revise errors on file the signed
- Virtual assistant accountant LV Chatbot AI assistant for Finance: remove input crafts, bring the data to the correct input, automatically prompt-term LIABILITIES – PAYMENTS, cash flow forecasting, warning of financial risks
- Virtual assistant customer care LV CareBot AI assistant: Integrated Chat on multi-platform, feedback and customer requests quickly, consulting, flexible, not being constrained by fixed script
- Virtual assistant hr LV Chatbot AI for HXM: save 70% time for HR and leadership, extract the entire database of candidates any file format, faq auto welfare policies, rules, regulations 24/7, statistical, personnel, resources, business in few seconds.
CONTACT INFORMATION:
- Lac Viet Computing Corporation
- Hotline: 0901 555 063 | (+84.28) 3842 3333
- Email: info@lacviet.vn – Website: https://lacviet.vn
- Headquarters: 23 Nguyen Thi Huynh, P. 8, Q. Phu Nhuan, Ho Chi Minh city
1. Benefits of AI in healthcare is what?
AI brings many important benefits in health, helping to improve the quality of diagnosis and optimized treatment, improve health management. Specific:
- Diagnostic accuracy: AI analyze medical images (MRI, CT scan) to detect early disease, reduce errors in diagnosis.
- Support treatment personalization: Machine Learning analysis of patient data to suggest treatment regimen accordingly.
- Predict disease: AI big data analytics to forecast disease outbreaks, support prevention services effectively.
- Process automation medical: AI-assisted data entry, medical records, records management, electronic medical, reduce the load administrative work.
- Drug development, vaccines: AI helps shorten the duration of study drug testing, increased therapeutic effect.
2. Advantages of AI in medical?
- Precision: AI analyze medical data with higher accuracy than traditional methods.
- Save time: Reduce the time to diagnose, handle medical records.
- Decision support: Provides predictions, suggesting treatment based on medical data big.
- Enhanced accessibility health: Chatbot health, virtual assistants help patients receive counseling from a distance without having to hospital.
- Cost optimization: Reduce errors in treatment, optimal resource hospitals, performance improvement, health care.
3. Application AI in the medical field in Vietnam
AI is now being used increasingly widely in health in Vietnam, helping to improve quality of patient care, optimize processes and enhance the performance of treatment. Some typical applications include:
- Diagnostic medical images: AI-assisted analysis, X-ray, CT, MRI for early detection of pathologies such as cancer, brain damage, cardiovascular (application at Bach Mai hospital, Vinmec).
- Virtual assistant medical: System chatbot AI support health counseling, screening, initial symptoms, help reduce the load for the doctor (for example: DrAid of VinBrain).
- Support treatment personalization: AI analyzes patient data to given treatment regimen suitable for the optimal therapeutic effect.
- Forecast disease: AI helped track predicting trends in diseases such as COVID-19, dengue, support health authorities implement prevention measures in a timely manner.
Records management electronic medical: AI automatically processed, updates and analysis of patient data to help hospitals manage information more efficiently.
4. Why is artificial intelligence important in the development of modern medical?
Artificial intelligence plays an important role in modern medical because enhances accuracy, process optimization, improving the efficiency of treatment.
- Improve the quality of diagnosis: AI to help doctors detect diseases faster, more accurate, especially in incurable diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular.
- Personalize treatment regimens: AI big data analytics to give treatment to suit each patients, increase effectiveness, reduce side effects.
- Save time cost: AI, process automation, health, help reduce the load pressure for medical staff, optimize the resources of the hospital.
- Support research and drug development: AI helps shorten the duration of clinical trials, accelerate the process of developing new drugs.
Improve accessibility of health services: virtual Assistant AI helps people access medical information quickly, reducing the need for patient directly for the mild disease.