With the influence from economic fluctuations, businesses always face pressure to optimize operations, reduce costs to increase operating efficiency. One of the solutions advanced technology is attracting great interest is server virtualization Virtual Server. This is not just a progress in the management of IT infrastructure but also help business versatile application of modern technologies such as cloud, automation.
This article Lac Viet will help you to understand more about server virtualizationfrom the concept, the popular type, actual benefits to the deployment process. At the same time we will point out the challenges when applying this technology and development trend in the future for businesses to have a comprehensive view before making an investment decision.
1. Overview of server virtualization Virtual Server, what is?
1.1 What is Virtual Server?
Server virtualization is the process of using software to divide a physical server into multiple virtual servers, each server operates independently, have their own operating system to use resources in an efficient way. The virtual server is still made fully functional as a physical server often, but they are deployed on a common platform.
Ví dụ, nếu một máy chủ Dell poweredge vật lý có 32 lõi CPU, 128GB RAM có thể được ảo hóa để tạo ra 4 máy chủ ảo, mỗi máy sử dụng 8 lõi CPU, 32GB RAM.
1.2 The mechanism of action of the Virtual Server
Process virtualization is performed by a software intermediary, often called hypervisor. Hypervisor plays an important role in the management of allocated resources from physical server to each virtual server.
The type of hypervisor popular:
- Hypervisor type 1: Run directly on the hardware (for example: VMware ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-V).
- Hypervisor type 2: Running on the operating system (for example: Oracle VirtualBox, VMware Workstation).
The Hypervisor ensures that resources such as CPU, RAM, hard drive and the network is a reasonable allocation between the virtual server. At the same time, it creates the environment isolation to the virtual server does not affect each other.
- Price list host 2026 latest: comparison details according to your business needs
- Dell servers | Dell Poweredge Server genuine for the Titanium of Dell Technologies
- Advice configure server optimized for enterprise-scale, field
- Standard room temperature, server according to international regulations from ASHRAE
2. The importance of server virtualization Virtual Server in the modern enterprise
In the era of transformation of the enterprise increasingly depends on technology to operate efficiently. However, maintaining server infrastructure traditional physics often encounter problems such as:
- High cost: Include the cost of procurement of hardware, maintenance, power and installation space.
- Hard open wide: Demand rapid growth requires the ability to extend flexibility which servers physics hard to meet.
- Downtimes long: The process of troubleshooting usually takes a lot of time, interruption of business operations.
Technology server virtualization Virtual Server born to solve these challenges. Virtual Server not only help business resource optimization but also open up opportunities for the application of the model IT as advanced as hybrid cloud and multi-cloud.
Benefits of server virtualization for business
- Resource optimization: With virtualization, multiple virtual servers can be running on the same physical server, help optimize resources such as CPU, RAM, storage. The integration of multiple virtual servers help reduce the number of physical servers should operate, thereby reducing energy consumption. According to research from Gartner, the enterprise may be reduced to 70% of the cost of hardware thanks to deploy virtualization technology.
- Flexible easy to extend: Business can add virtual server or change the configuration in just a few minutes without the need for buying additional hardware. With Virtual Server, business easily test or deploy the new project without interrupting the current activity.
- Improve availability, reduce downtime: When a physical server having the problem, the virtual server can be moved to another server that does not cause service interruption. Virtual Server integrates the tools backup efficiency, ensure the safety data restored timely when there is a problem.
- Enhanced security, centralized management: The application on the virtual server is completely isolated, reducing the risk of spread security incidents. Hypervisor helps to manage the entire virtual servers from a single interface, save time, increase efficiency management.
- Support the transition to the cloud: Virtualization is the stepping stone ideal for business integrated solutions cloud (Cloud), help deploy hybrid cloud or multi-cloud easily.
3. The type of virtualization Virtual Server popular
Understand the types of server virtualization is a critical step for businesses to choose the solution that best suits the needs. Here are the types of virtualization downloads each type has advantages and disadvantages.
3.1. Virtualization-based software
Hypervisor Type 1 (Bare-Metal)
Hypervisor type 1 is installed directly on physical hardware, without operating system intermediate. Create a solid foundation for managing multiple virtual servers on the same physical server.
How it works: Hypervisor interacts directly with the CPU, RAM, hard drive of the physical server, to allocate this resource for the virtual server.
Advantages:
- High performance: Do not cross-class operating system, intermediate, virtual servers operate with the best performance.
- Stability, security: Suitable for the environment as important as the data center or large businesses.
Cons:
- High investment costs: Includes the cost of software, hypervisor, hardware configuration.
- Management complex: Requires a team of IT professionals to install, maintenance.
Hypervisor type 1 is often used in large businesses or organizations that have high demands on performance and security.
Example software: VMware ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-V, Citrix XenServer.
Hypervisor Type 2 (Hosted)
Hypervisor type 2 is installed on the operating system of the physical servers, works as a conventional application.
- How it works: Hypervisor running on an operating system (like Windows or Linux), then manage the virtual server is deployed.
- Advantages:
Easy to deploy: In accordance with the small business or the test environment.
Low cost: Does not require hardware specialized, take advantage of available operating systems.
- Cons:
Lower performance: Do not through the intermediate layer is the operating system, performance is affected.
Security capabilities inferior: Because depending on the operating system base, prone to attack than the Hypervisor type 1.
- Application: Hypervisor type 2 in accordance with small business development group or testing environment the application.
- Example software: Oracle VirtualBox, VMware Workstation, Parallels Desktop.
3.2. Virtualization based on the Container
Virtualization based on the Container is a modern technology, which stand out thanks to the ability to deploy quickly and save resources.
How it works: Containers share the operating system kernel of the physical server, but each container works as a standalone application with own environment.
Advantages:
- Rapid deployment: The Container can be started in a few seconds, faster virtual server traditional.
- Lighter: Container need only minimal resources to operate, save cost and resources.
- High mobility: Containers can easily move between the environment, such as physical server, cloud or device user.
Cons:
- Security restrictions: Containers share the operating system kernel, so the ability to quarantine security is not as high as virtual servers.
- Not completely replace virtualization traditional: For applications require high performance or the operating system separate virtual server is still the optimal choice.
Application: Suitable Container with the application deployed microservices, DevOps or systems that require high flexibility.
Common tools: Docker, Kubernetes.
3.3. Virtualization based on the operating system (OS-Level Virtualization)
Virtualization based on the operating system allows to create multiple virtual environments, all running on the same operating system facilities.
How it works: A physical server is divided into virtual space, each space is designed to run app or service different.
Advantages:
- High performance: Thanks for using common operating system, reducing the overhead.
- Rapid deployment: Virtual environment can be created and configured in minutes.
Cons:
- Restrictions on the operating system: All the virtual environment must use the same operating system, basis, not as flexible as virtual server traditional.
- Does not fit with the complex environment: Due to restrictions on the possibility of isolation, security, and diverse operating system.
Application: Suitable for running apps that need flexibility in the same ecosystem or in the development environment.
For example technology: OpenVZ, Virtuozzo.
Each type of virtual server both have advantages and disadvantages, to suit each use case. Businesses need to consider based on your needs, budget, deployment target to choose the right solution. Hypervisor type 1 is the top choice for data center, while the container is a flexible solution for modern applications.
4. Development system, server virtualization Virtual Server
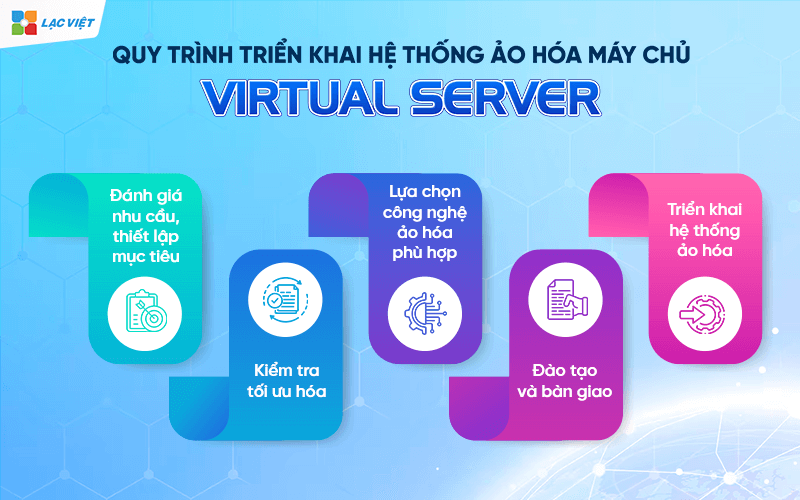
Step 1. Needs assessment, goal setting
- Analyze business requirements: Define specific goals such as reducing costs, increasing performance or expanded flexible.
- Assess infrastructure current: Check the hardware configuration, operating system, application to ensure compatibility with virtualization technology.
Step 2. Select virtualization technology fit
- Common tools: VMware, Hyper-V, KVM or Proxmox.
Selection criteria:
- Performance: In accordance with the volume of work, present, future.
- Scalability: Ensure that the system can grow with the business.
- Budget: Balance between the cost of software and hardware.
Step 3. System deployment, virtualization
- Install Hypervisor: Select and install the hypervisor directly on the server hardware physics.
- Create virtual servers (Virtual Machines): Configure resources such as CPU, RAM, of storage for each virtual server based on specific needs.
- Network configuration: Set up virtual networks (virtual network) to ensure that the virtual server can communicate and share resources.
Step 4. Test optimization
- Test performance: Ensure the server virtual stable operation, no conflict resources.
- Optimized configuration: Adjust resources according to actual needs, such as increase/decrease the CPU or RAM of each virtual server.
Step 5. Training and handover
- Manual: IT team of business should be trained to use, system management, virtualization.
- Policy maintenance: Set the maintenance process periodically to ensure performance, longevity system.
5. Challenges when deploying the system server virtualization Virtual Server
Requires initial investment high: Các doanh nghiệp cần đầu tư vào mua Server máy chủ vật lý có cấu hình mạnh để hỗ trợ nhiều máy chủ ảo. Các công cụ ảo hóa như VMware hoặc Hyper-V thường yêu cầu chi phí cấp phép sử dụng cao. Theo báo cáo từ Spiceworks, chi phí triển khai hệ thống ảo hóa có thể chiếm tới 20-30% of the budget IT original of small and medium enterprises.
Required expertise: Business needs a team of engineers knowledgeable about virtualization to deploy the operating system. The diversity of the virtualization platform makes managing or troubleshooting becomes more challenging, especially if businesses use many different suppliers.
Depends on hardware
- Risk score obstruction resources: A hardware error on the physical server can affect the whole virtual server is active on it.
- Fix: Enterprises need to deploy the solution redundancy (redundancy) as clustering or load balancing to minimize the risks.
Problem data security
- The risk from sharing environment: The sharing of resources between virtual servers can lead to security vulnerabilities, especially when the virtual machine running the application or different operating systems.
- Security measures: Use firewall for the virtual network; data encryption between the virtual server and storage systems.
Performance decrease if not managed well
- Resource management is not optimal: The allocation of resources not logical, can cause overload the CPU, RAM or memory, the full system.
- Solution: Use the monitoring tool dedicated performance; implement resource optimization routine.
6. The development trend of the system server virtualization Virtual Server
- Integrated cloud technology (Cloud Integration): The business is gradually converted to using models, Hybrid Cloud, Multi-Cloud combination between virtual servers and cloud services to increase scalability, cost savings. According to the report by Flexera in the year 2023, 87% of business have deployed or plan to use hybrid cloud with system virtualization.
- The development of container technologies: Integration with Docker and Kubernetes, the container technologies goods are complements virtualization traditions help optimize application deployment, resource management more effective. Compared with Virtual Server, container consumes less resources than appropriate for the application microservices.
- Network virtualization (Network Virtualization): Virtualization not only applied to server, but also expand into the field of network, creation of network virtualization to effectively strengthen the security. Typical technology: VMware NSX, Cisco ACI.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) supports virtualization: Các nền tảng ảo hóa Server AI đang tích hợp trí tuệ nhân tạo và Machine Learning để tự động phân bổ tài nguyên, dự đoán nhu cầu, tối ưu hóa hiệu năng hệ thống.Hệ thống AI có thể tự động phát hiện lỗi, điều chỉnh hoạt động máy ảo để tránh downtime.
- Strengthen security in virtualized environments: Security model “Zero Trust” is being applied strong in virtualized environments, helping to protect comprehensive data application. The technology support such as data encryption first, last, security monitoring, real-time.
Nếu Doanh nghiệp đang tìm kiếm giải pháp ảo hóa phù hợp:
- Please contact us Vietnam today to get advice, quotes, details, plans to deploy efficient, helping to save maximum cost and time.
- Support from the design, deployment, to maintenance of the system with the optimal solution for your business.
Server virtualization Virtual Server not only is the trend that has become indispensable solution in strategy development, technology infrastructure of the business. Despite facing a number of challenges when deployed, but the benefits of superior resource efficiency, security, scalability help virtualization become the top choice for businesses that want to optimize the cost, get ready for number conversion.
Xem thêm các công nghệ ảo hóa khác:
- Virtual desktop – ảo hóa máy tính
- Application virtualization – ảo hóa ứng dụng
CONTACT INFORMATION:
- Lac Viet Computing Corporation
- Hotline: 0901 555 063 | (+84.28) 3842 3333
- Email: info@lacviet.vn – Website: https://lacviet.vn
- Headquarters: 23 Nguyen Thi Huynh, P. 8, Q. Phu Nhuan, Ho Chi Minh city