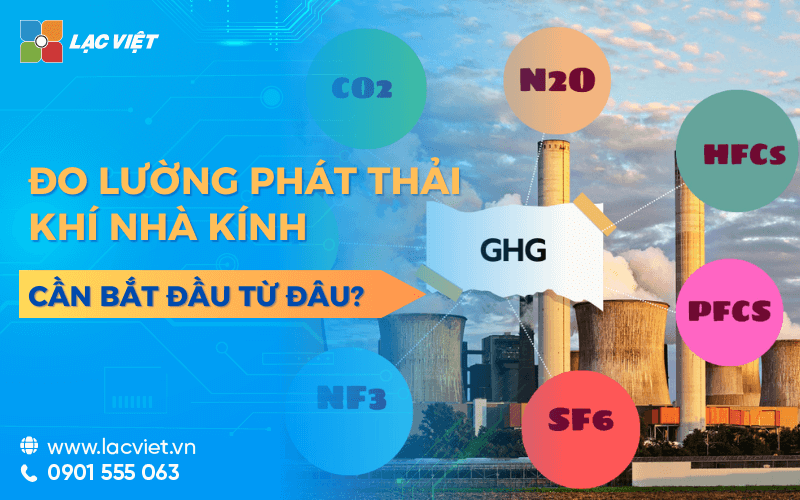
In the context of climate change are an increasing threat to the habitat Carbon Footprint (carbon footprint) become an important indicator to help the organizations and enterprises measurement management of greenhouse gas emissions into the environment, business support towards sustainable development, reducing environmental impact and meet international standards.
This article Lac Viet Computing will provide comprehensive information on the Carbon footprint: from concept, calculation, to the solution minimized. Through that, help businesses understand the role and how to apply carbon footprint in strategic sustainable development, meet international standard, positive contribution to the common goal.
1. Carbon Footprint is?
Carbon Footprintalso known as carbon footprint, is the total amount of CO2, a greenhouse gas, others (such as CH4, N2O) in which an individual, organization, or product emissions directly or indirectly into the environment during a certain period of time. This is an important indicator to help measure the environmental impact of economic activities, and production.

Carbon footprint is the basis to determine the amount of greenhouse gas emissions that businesses need to compensate through credits carbon. Credits carbon help organizations to manage and balance the emissions of himself on the international market.
How it works:
- Calculate emissions: Use Carbon Footprint to measure the total emissions of the business.
- Determine the number of credits required to buy or create: Number of credits carbon needed by total emissions minus the amount of CO2 reduced through measures internal.
Practical example: A business emissions 5,000 tons of CO2/yearafter reduction is 2,000 tons CO2 by measures of internal need offset 3,000 tons CO2 through credits carbon.
- Scope 3 Emission is? Comprehensive guide to measuring and managing emissions indirect
- CBAM is what? What should prepare to cope with adjustment mechanisms border carbon of the EU?
- What is CO2 offset Point? Explained in easy to understand and practical applications for business
- Carbon Neutral is what? Roadmap to help businesses achieve carbon neutral
2. The scope of application of Carbon Footprint
Carbon Footprint can be applied at many different levels, from individuals, businesses and to products. Applying the right range to help measure the exact amount of greenhouse gas emissions and build the strategy to reduce emissions effectively.
2.1 Personal
Carbon footprints personal measuring the amount of greenhouse gases generated from the daily activities of a person.
Source emission downloads:
- Travel by means of transport use fossil fuels (cars, motorcycles).
- Use electric, gas in the family.
- Consumption of food, especially foods that have emissions in the production process, such as beef, milk.
Practical example: A person travel by car, use 500 liters of gasoline/yearemissions is: 500 liters ×2,31 kg CO2/liter=1.155 kg CO2 (from 1.15 tonnes of CO2)
2.2 Business
Carbon Footprint business measure the amount of greenhouse gas emissions from the production process, operation and supply chain.
Source emission downloads:
- Energy consumption in the factory office.
- The process of shipping raw materials and products.
- Waste from production and waste water treatment.
Importance:
- Helps business identify the emission activity to optimize energy and reduce costs.
- Is facilities to meet international standards such as the GHG Protocol and ISO 14064.
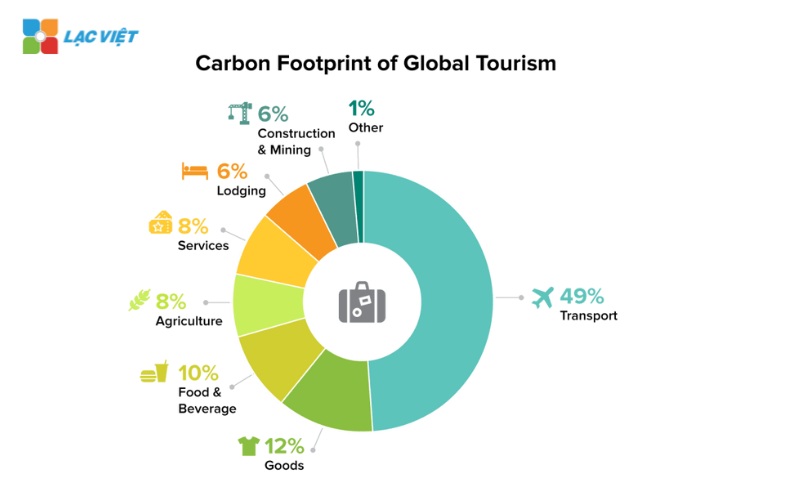
2.3 products
Carbon footprint of the product measurement of greenhouse gas emissions in the entire product lifecycle, from production, transport, use to handle after use.
Product life cycle:
- Manufacturer: Emissions from raw material extraction and processing.
- Shipping: Emissions from bringing products from factory to consumers.
- Use: Emissions in the process consumers use the product.
- Processor: Emissions from the process of recycling or destruction of the product.
Practical example: A plastic PET bottle 1 liter Carbon Footprint is the average 3.1 kg CO2including emissions from the production of plastic raw materials, transport, waste disposal.
3. Why measure Carbon footprint important?
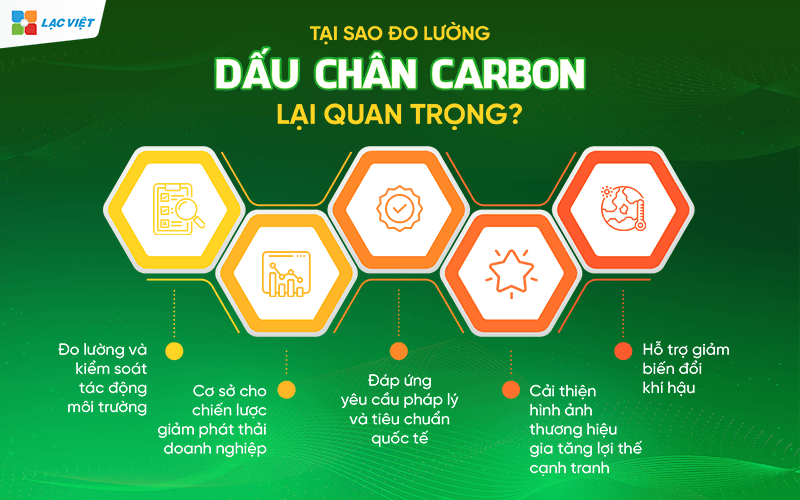
Carbon Footprint not just a measure but also a strategic tool that helps businesses and individuals accomplish the goals of sustainable development.
- Measurement and control environmental impact: To help businesses understand the amount of CO2, other greenhouse gases emissions in the production process, commissioning and providing services. Through it, businesses can identify activities have high emission, search for alternative solutions more efficiently.
- The basis for strategies to reduce emissions: When measuring the exact amount of gas emissions, businesses can set goals specific, feasible in order to minimize environmental impact.
- Meet legal requirements and international standards: The standard as GHG Protocol, ISO 14064the program credit global carbon require business calculations and reporting of greenhouse gas emissions. Understanding and managing Carbon Footprint is a prerequisite to participate in the market transaction credits carbon or certified sustainable.
- Increase competitive advantage: In an era where customers, investors increasingly prioritize the business sustainable, the measurement, reducing the Carbon Footprint to help businesses improve the brand image, to attract investors, meet the needs of customers are conscious about the environment.
- Support reduce climate change in the goal of reducing global emissions, as the target carbon neutral (net-zero) in the year 2050 of the united Nations.
4. The composition of the Carbon Footprint

4.1. Emission direct (Scope 1)
Emission direct (Scope 1) is the amount of greenhouse gas generated from the source that the business owns or controls directly. This is the most important component because it reflects the direct production activities and operation of the business.
Emission source key:
- Boiler and production equipment: The plant often used boilers burning fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) to produce heat or energy. This process is incurred large amount of CO2, greenhouse gases other.
- Means of transport: Vehicles owned by the business, such as trucks, cars, boats, cargo ships, is also a source of emissions privacy.
- Industrial processes: Industrial activities such as cement production, steel, chemicals often generate CO2 greenhouse gases such as CH4, N2O.
Practical example: A plant use coal boiler to produce energy. The amount of CO2 emissions from this process are: 500 tons of coal×2,86 tons CO2/ton of coal=1430 to tons CO2/year
4.2. Emissions indirectly from energy (Scope 2)
Emissions indirectly from energy (Scope 2) is the amount of greenhouse gases generated from the consumption of energy purchased from outside, such as electricity, heat or steam. Although businesses do not directly generate these emissions, but the use of energy still affect the overall Carbon Footprint of the business.
Emission source key:
- Power consumption: Electricity produced from fossil fuels such as coal, oil, or natural gas are often incurred large amount of CO2.
- Steam and heat: The manufacturing process steam or heat also arise greenhouse gases.
Practical example: A business consumption of 1,000,000 kWh of electricity from the national grid. If the emission of the grid is 0.5 kg CO2/kWh, the amount of emissions is: 1.000.000 kWh×0.5 kg CO2/kWh=500 tons of CO2/year
4.3. Emissions indirect (Scope 3)
Emissions indirect (Scope 3) include the amount of greenhouse gases generated from activities not under the direct control of the business, but related to supply chain and operations.
Emission source key:
- Shipping raw materials and products: Emissions from transport by road, rail, sea, or air.
- Waste disposal: The active garbage disposal, recycling, or destruction of products emit greenhouse gases.
- The operation of the offer: Emissions from raw material suppliers, service.
Practical example: A business use cargo by truck each year shipping 10,000 tons of cargo on the way average 500 kmwith the number of emissions is 0.25 kg CO2/ton/km. Emissions are: 10,000 tons×500 km×0.25 kg CO2/ton/km=1250 tons CO2/year
5. How to calculate Carbon Footprint
5.1. Basic recipe
Carbon Footprint is calculated by summing the amount of greenhouse gas emissions from specific activities, using the following formula:
Carbon Footprint = ∑(Activity×coefficient of emission)
Activity: Is the total volume or data related to operational emissions, such as:
- The amount of fuel consumption (in liters or kilograms).
- Number of kWh of electricity use.
- The volume of goods transported (metric tons) and road transport (km).
The coefficient of emission: Is the number expressing the amount of CO2 (or greenhouse gas equivalent) produced from each unit operation. The coefficient of emission is typically provided by international organizations such as the IPCC or standard measure country.
Examples of the emission:
- Diesel oil: 2,63 kg CO2/liter.
- Power from the grid: 0.5 kg CO2/kWh (depending on the structure energy source country).
- Transport by truck: 0.25 kg CO2/ton/km.

5.2. Process calculations
The calculation of the Carbon Footprint typically done through 4 main steps to ensure the accuracy and transparency:
Step 1: Determine the scope of emissions (Scope 1, 2, 3)
- Scope 1: The amount of greenhouse gas emissions directly from the source that the business owns or controls (boiler, vehicles).
- Scope 2: The amount of greenhouse gas emissions indirectly from the energy consumption of electricity, heat or steam.
- Scope 3: The amount of greenhouse gas emissions indirect, as transportation of raw materials, products, waste disposal activities in the supply chain.
Step 2: collect activity data
Required data:
- Fuel consumption (l, kg).
- Power consumption (kWh).
- The volume of goods transported and the distance moved.
Tool support: Using software inventory of greenhouse gases such as Carbon Trust Footprint Calculator or spreadsheet standard (GHG Protocol).
Step 3: Apply the emission
- Combining activity data with emission factors corresponding to calculate the amount of CO2 emissions for each activity.
- Formula applied to each source of emissions: CO2 emissions=activity Data×emission factors\text{CO2} = \text{activity Data} \times \text{coefficient of emission}CO2 emissions=activity Data×emission factors
Step 4: synthesis of emissions from the source
Summing up the results from Scope 1, Scope 2, Scope 3 to have Carbon footprints Footprint overall.
5.3. Illustrative example
Calculate the Carbon Footprint of the business use diesel:
- Activity information: Business use 1,000 liters of diesel in the year.
- The coefficient of emission: 2,63 kg CO2/liter (IPCC).
- Calculation: 1,000 liters×2,63 kg CO2/liter=2.630 kg CO2 (2,63 tons of CO2)
Calculate the Carbon Footprint from power consumption:
- Activity information: Business use 500.000 kWh of electricity from the national grid.
- The coefficient of emission: 0.5 kg CO2/kWh.
- Calculation: 500.000 kWh×0.5 kg CO2/kWh=250.000 kg CO2 (250 tons of CO2)
Calculate the Carbon Footprint from shipping goods:
- Activity information: Shipping 2,000 tons of cargo on the way 300 km.
- The coefficient of emission: 0.25 kg CO2/ton/km.
- Calculation: 2,000 tons×300 km×0.25 kg CO2/ton/km=150,000 kg CO2 (150 tons of CO2)
Summarizing Carbon Footprint:
Total amount of CO2 emissions from activities on is: 2,63 tons of CO2+250 tons of CO2+150 tons of CO2=402,63 tons CO2
- How to calculate credits carbon and the method applied to calculate credits carbon
- Business how to get credits carbon accordance with international standards?
- Coefficient of Co2 emissions according to the IPCC and any conversion of the form of energy
- Net Zero is what? Roadmap 2050 and solution goal commitment
6. Reducing the Carbon footprint for your business
6.1. Use renewable energy
Renewable energy is the effective solution to reduce the amount of CO2 emissions from fossil energy sources. Businesses can transition to using clean energy sources such as solar, wind, or biomass.
Benefits of renewable energy:
- Reduce emissions directly: Renewable energy does not generate CO2 in the process of operation.
- Reduce long term costs: After the initial investment, operating costs and maintenance systems renewable energy is usually lower than fossil fuels.
- Meet international standard: Many markets and partners requires the use of clean energy as a sustainable criteria.
Practical example:
- A manufacturing enterprise in Vietnam, system installation, solar power 1 MW, providing enough power for daily activities, reduce emissions 500 tons of CO2/year.
- The distribution center of IKEA switch to using 100% renewable energy, which helps reduce over 1 million tons of CO2 worldwide.
Solution deployment:
- Investment system installation, solar or wind at production facilities.
- Purchase electricity from the supplier of renewable energy (Green Energy Providers).
6.2. Optimized production processes
The production process is not effective is one of the main causes leading to CO2 emissions high. The process optimization not only help reduce emissions but also improve productivity and reduce production costs.
Benefits of optimization:
- Energy saving: Modern devices have performance, higher energy expended less energy.
- Reduced raw material: Process optimization helps to reduce the amount of raw materials used and limit waste.
- Increase productivity: Process optimization helps to increase production efficiency without increasing the consumption of resources.
Practical example:
- A paper factory upgrading the production line technology, save energy, reduce power consumption from Of 1,200 MWh at longer 1.000 MWhequivalent reduction 100 tons of CO2/year.
- A company produces steel replacement furnace the electric arc furnace, help reduce CO2 emissions up to 25% each year.
Solution deployment:
- Applied automation technologies and artificial intelligence (AI) to monitor, optimize the production process.
- Training employees about operating the equipment to save energy.
- Periodically check and maintain equipment to ensure operational performance optimization.
6.3. Join the project offset carbon
The project offset carbon (carbon offset) is the opportunity for businesses to reduce emissions indirectly by investing in the sustainability initiatives such as forest conservation, renewable energy or recycling.
Benefits of the project offset:
- Reduce the amount of greenhouse gases: The project forest conservation or renewable energy helps to absorb or reduce the amount of CO2 emissions.
- Increase brand reputation: Enterprises involved in the project offset carbon often be appreciated on social responsibility, the environment.
- Meet international standard: Credits carbon get from the project can be used to offset emissions and meet legal requirements.
Practical example:
- A business investment in the project REDD+ in Brazil, helping to preserve the 10,000 hectares of forest and offset 10,000 tons CO2 each year.
- Microsoft spent millions of DOLLARS each year to invest in projects in renewable energy, conservation, reach the target carbon emission pussy.
Solution deployment:
- Cooperation with international organizations such as the Gold Standard or Verra to invest in the project is certified.
- Selected project in accordance with industry and sustainability strategies of the business.
The measure and reduce Carbon Footprint not only helps business meet international standards to minimize risk, legal risk, but also enhance the brand image, attracting the interest of investors attach great importance to sustainability.
Journey to reduce greenhouse gas emissions requires commitment, investment and innovation, but the benefits are immense: from the optimization of the production process, saving operating costs, to contribute to the global goal of carbon neutral.
Let's start the action today by measurement Carbon Footprint of business, apply the solution to reduce emissions, to participate in the program credit carbon.