In business, not the business would also have interest right from the first day of operations. But important questions that all businesses need to answer is: When is enough revenue to offset the cost and start profitable? The answer lies in analysis of the breakeven point – a financial instrument important to help businesses determine the minimum turnover to be achieved to avoid losses.
Understanding the breakeven point not only help business financial control, but also to support strategic decisions about price, production, costs and expand business. In particular, in the context of market competition is fierce, with the cost increasing day by day, businesses need modern approach than to analyze and optimize the breakeven point.
So how to accurately calculate the breakeven point? Business should avoid these mistakes when applying this tool in practice? And how to take advantage of AI technologies in financial analysis to optimize profit? Let's Lac Viet Computing learn all in the article below.
1. Learn about the breakeven point
1.1. The breakeven point is what?
The breakeven point (Break-even Point – BEP) is the level of sales or production at which the business does not suffer losses, but also have no interest. This is one of the financial indicators important to help businesses determine the minimum required gain to maintain operations.
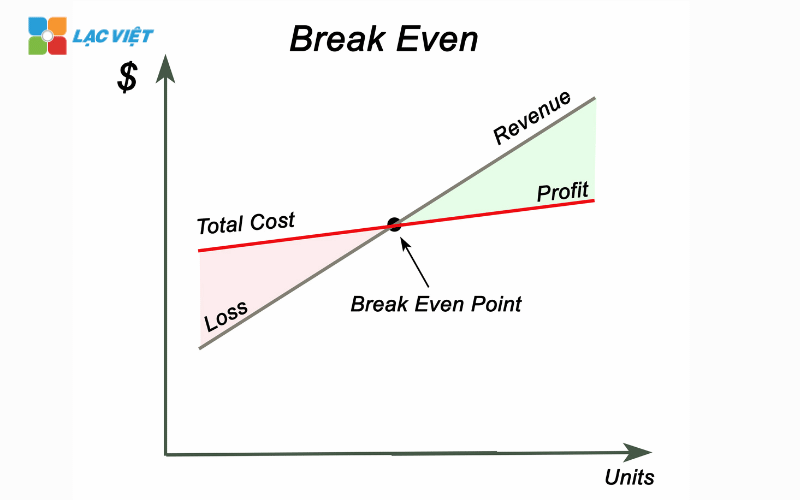
When businesses operate below the level of the breakeven point, which means total expenses are greater than revenue, business losses. Conversely, when sales surpassed the break-even point, the business began to take interest.
For example, If a company produces phones that total fixed cost is 1 billion/month, variable costs on each product is 3 million and the selling price per product is 5 million, then the company must sell at least 500 products per month to reach the breakeven point.
1.2. The factors that affect the breakeven point
The breakeven point is affected by financial factors, and activities such as:
- Fixed costs (Fixed Costs): Costs that do not vary according to production volume, such as rent, workshops, management staff salaries, the cost of machinery maintenance.
- Variable costs (Variable Costs): costs vary according to the number of products produced, like raw materials cost, direct labor shipping costs.
- Product sale price (Selling Price per Unit): The price that the business set out directly affect the time to reach the breakeven point.
- Output sales (Sales Volume): the Amount of product sold decide to speed business reach the level of breakeven.
If the business can reduce fixed costs or variable costs, or increase the reasonable price which does not affect sales, then the breakeven point will be lowered, help enterprises to quickly achieve profitability.

2. Break-even analysis help what is for business?
Break-even point analysis is not just an accounting, which is the strategy tool that helps business decisions business premises. Knowing the breakeven point – the point where total revenue sufficient to offset the total cost – businesses can actively control, profit, limited risk and optimize resources.
Here are the practical value to reply to the question of why businesses should care:
2.1. Help with the decision making reasonable selling price
The pricing of products is affected by many factors such as cost, market price, competitive... However, if not, determine the minimum sales to breakeven, business, easy to fall into a condition selling as much – hole as deep.
Through the break-even point, the business can determine is the minimum selling price should reach to no losses. From there, the business can adjust the pricing strategy more flexible, for example:
- Increase the product price when the profit margin is too low
- Cut costs to maintain competitive prices but still reach the breakeven point
2.2. Determine the minimum output for sale to non-hole
No little business to expand the business scale but didn't know what I have to sell, how much new product fully cover the cost. This is the cause of many plan to fail right from the start.
Help answer the core question: a Business must sell at least how many units of the product in the states to not anal?
For example, if each product word of 50,000 with a fixed cost is 500 million, the business needs to sell at least 10,000 products per month to reach breakeven.
This number is grounds to set business targets, track sales effectiveness and launched the early warning when output is lower than the minimum required.
2.3. Financial planning real more
Analysis of the breakeven point is important stepping stone in the process of financial planning, monthly, quarter, or year. By knowing in advance the breakeven point, businesses can:
- Planning to spend in accordance with resources and profitability
- Estimate the expected profit under each scenario business (for example selling 120%, 150% compared to production breakeven)
- Prepared the plans adjusted as increased cost or market fluctuations
This is especially important with the startup entrepreneurs or business is expanding production – where each financial decision has great influence on cash flow.
2.4. Control risks when expanding business scale
Expand business activities often entail fixed costs increase: rental of greater investment in new machinery, increase hr... If not analysis the breakeven point before expanding the business to fall into a state of imbalance cost – revenue.
Point acts as a “safety barrier”: help managers determine the level of sales growth, at minimum, have to ensure the extension is an investment reasonable, do not become a financial burden.
For example: if the business increases fixed costs add 300 million per month when opening more branches, it is necessary to predict whether branches that can contribute more how much output to reach back the breakeven point new.
As reported in Harvard Business Review 2024, the business often use break-even analysis in operations planning, business is likely to increase by 17% level to maintain stable profit in the first 2 years of operation, compared with the group not applicable or only once and then left open.
This suggests: not only know the “point” once is enough, which businesses need to constantly monitor and update this index according to the market movements in order to adjust timely.
3. 6 Models analyze the breakeven point STANDARD EFFICIENCY
3.1. Model analysis of the breakeven point in terms of output (Break-even by Units)
This model helps businesses determine the amount of product minimum required sold in a period of time (usually monthly or quarterly) to be able to harvest sufficient amount to offset the entire cost has dropped out, i.e. no holes also have no interest. This is one of the models of analysis, basic and easy to apply, especially for business only business with a product or product line-uniform.

Related components
- Fixed costs: Are the costs does not change in production or consumption, for example: rent, salary management, the cost of depreciation of assets.
- Variable cost: Is the cost varies according to the number of products produced, for example: raw material, the packing cost, shipping cost according to your order.
- Sale price unit Price: sell 1 product to market.
Formula
Output breakeven = fixed Costs / (selling Price – variable Costs unit)
The denominator of the above formula (selling Price – variable Costs), also known as gross profit, unit or contribution rates on a product, show the amount of money that each product sold will “contribute” to the offset of fixed costs.
Illustrative example: A manufacturing enterprise office chair:
- Price per seat: 100,000 VND
- Variable costs per seat: 60,000 VND
- Fixed costs each month: 400 million VND
Apply the formula:
Output breakeven = 400.000.000 / (100.000 – 60.000) = 10.000 product/month
=> If the business is sold under 10,000 products/month, they are still holes. Sold strictly 10,000 products is breakeven. Every product pass this number will start to generate real profits.
Practical value
- Production planning – sales basis: Know need to produce and consume, how many products to no holes.
- Control business performance: If the production of actual consumption is always lower than the breakeven, business need to review the strategy of sales or cost structure.
- Decision support when expansion of production: If the added investment machinery (increase fixed costs), the business must calculate the number of products increased need to sell in order to maintain the breakeven point new.
3.2. Model analysis of the breakeven point in revenues (Break-even by Revenue)
Different models under production, this model determines the revenue according to the monetary value that businesses need to achieve in order to not suffer losses. This method is effective for the business enterprise multiple product categories, each category, price and other expenses, making the calculation according to specific output becomes complex or inaccurate.
Related components
- Fixed costs: As explained above.
- Rate profit margin (Contribution Margin Ratio): Is the ratio of the percent is the revenue remaining after deducting variable costs, i.e., the revenue that can be used to offset fixed costs and make a profit.
The rate of profit margin = (selling Price – variable Costs) / selling Price
If the business has multiple products, this rate should be calculated on average, according to the revenue structure.
Formula
Revenue breakeven = fixed Cost / Rate profit margin
Illustrative example: A commercial business has a fixed cost per month is 500 million VND. Through analysis, the rate of profit margin average is 25% (which means after deducting the variable costs, the remaining 25% of revenues to cover fixed costs).
Apply the formula:
Revenue breakeven = 500.000.000 / 0,25 = 2,000,000,000 VND/month
=> If the business does not achieve the level of revenue of 2 billion VND per month, they are still active in the hole.
Practical value
- Overall, more flexibility: No need of specific interest, how many products, only need to specify the target of total revenue.
- Business suits are the list of goods diversity: this Model to avoid the calculation of sporadic according to each product which still ensure effective control of finance.
- Easy to integrate on the financial statements or KPI sales office: Because the system administrator often track turnover total, this is just some easy-to-follow and closely reflects the actual situation.
3.3. Model analysis of the breakeven point multi-product (Multi-product Break-even Model)
In fact, most of the business not only business, a single product, which is a diverse category including several product or service different. Every product has a price, the cost of production and the rate of profit separately. So, if you just use pattern point single product will no longer accurate.
Model analysis of the breakeven point multi-product allows businesses to calculate the breakeven point total by determining the proportion contributed an average of all the products, so you can estimate the level of sales or production should reach to no holes.
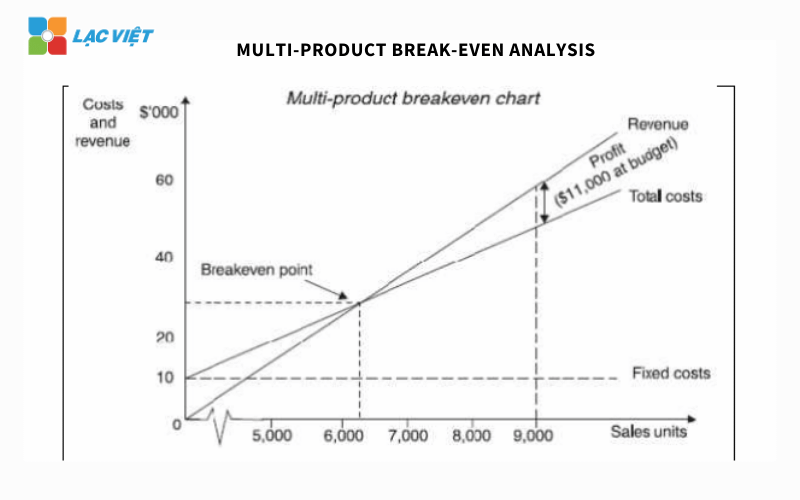
Ingredients and recipe
To calculate the breakeven point in the environment many products, businesses need to determine:
- Percentage of sales of each product in total sales structure
- Level of contribution per unit of product: sales Price – variable Costs
- The contribution of the average weighted: Is the average weighted of the contribution, calculated as the proportion of the revenue of each product.
Formula:
The breakeven point (sales) = fixed Cost / contribution Rate average
Or:
The breakeven point (output) = fixed Cost / contribution per unit of product
Illustrative example: A business company two types of products:
- Product A: accounting for 60% of revenue, profit on each unit is 30,000 VND
- Product B: accounting for 40% of revenue, profit on each unit is 20.000 VND
=> The contribution average = (0.6 × 30.000) + (0.4 × 20.000) = 26.000 VND
If fixed cost per month is 520 million:
Output breakeven = 520.000.000 / 26.000 = 20,000 units of product exchange
Business can be divided further to know how many units A and B according to the proportion of the corresponding (60 – 40%).
Practical value
- Control the entire product portfolio in a systematic way
- Assessing the impact of each product group to profitability
- Support strategic restructuring of the category of goods: Promote product groups with high rates of contributions, descending products have profit margins low in order to optimize revenues and reduce the pressure output breakeven.
3.4. Model analysis of the breakeven point on the basis of the capacity of the operation (Break-even by Capacity)
For the business activity based on fixed infrastructure have limited capacity – such as factory, hotel, airline transportation – the core question is no longer “how much product”, which is a must to use how much percent capacity for no holes.
Model analysis of the breakeven point under capacity activity that helps businesses answer: “I need to operate at a percentage of capacity to cover the cost?”
Ingredients and how to calculate
Suppose:
- The business has a capacity of a maximum of 100% (for example: 100 hotel rooms, 1,000 hours of machine per month)
- Business know fixed costs, variable costs, and income level unit (revenue per unit capacity)
General formula:
Capacity breakeven (%) = fixed Costs / (maximum capacity × the Level of contribution per unit of capacity)
In which:
- Level of contribution = revenue unit – variable Cost unit
Illustrative example: A hotel has 100 rooms, price to rent an average of 1 million vnd/night. Fixed cost: 900 million vnd/month. Variable costs (cleaning, water and electricity, reception...) average 300,000 vnd/room/night
=> Profit margin per night/room = 700,000 vnd
Gross profit margin maximum if reach 100% capacity:
= 100 × 30 days × 700.000 = 2,1 billion
Apply the formula:
Capacity breakeven = 900.000.000 / 2.100.000.000 = 42.86%
=> Hotels need to achieve a minimum of 43% room capacity to not suffer losses.
Practical value
- Match the business has assets fixed, big fixed costs high
- Help managers easily put only goal using the minimum capacity
- Early warning risk when the rate of use, low elongation, thereby making the marketing strategy, flexible discounts, seasonal or optimal re-scale operation.
3.5. Model analysis of the breakeven point can review to profit target (Target Profit Analysis)
If the breakeven point is the level at which the business “no holes – no interest”, then this model goes one step further: determine the yield or revenue to be achieved in order to create a level of profit expectations specific. This model is very useful for business has growth objectives clearly, the need to ensure a certain profit margin to:
- Return on investment
- Pay dividends to investors
- Re-investment extension
- Achieve the planned targets for the year
Other models breakeven traditional look only to the cost, this model combines both profit targets into the calculation, thereby creating the foundation set KPI and growth-oriented.
Ingredients need to determine
- Fixed costs: do Not change according to the production (lease, fixed salary, insurance, depreciation...)
- Variable costs: incurred by each unit of product
- Selling price per unit
- Target profit margin: the amount Of money the business expectations created after deducting all costs
Formula
Analysis according to the output:
Output should reach = (fixed Costs + profit target) / (selling Price – variable Costs)
Analysis according to revenue:
Revenue should reach = (fixed Costs + profit target) / Ratio profit margin
Illustrative example: A business has:
- Fixed cost: 500 million vnd/month
- Variable costs per product: 60,000 VND
- Selling price per product: 100,000 VND
- Target profit/month: 300 million VND
Calculating yield to be achieved:
= (500.000.000 + 300.000.000) / (100.000 – 60.000)
= 800.000.000 / 40.000 = 20,000 products/month
That is, businesses need to consume 20,000 products/month to not only capital, but also create 300 million profit.
Practical value
- Set up business plan have a clear goal: to Not only know his need “no hole”, but also identified specific steps to take interest.
- Leader board support building KPI sales, financial planning, with capacity: From target profit, the business can back out the targets to be achieved.
- Increase the autonomy in operating financial: When market volatility can adjust prices, yields, or costs to maintain profitability expectations.
3.6. Model analysis of the breakeven point according to the scenario (Scenario-based Break-even Analysis)
In the business environment more volatile as today, the calculation of the breakeven point only in a single script is not enough to reflect the comprehensive financial risks. This model allows businesses to build multiple scenarios, assumptions about:
- Sale price increase or decrease
- The cost of raw material fluctuations
- Output consumption lower than expectations
- Fixed costs increase when scaling
Since then, business will evaluate is:
- Point change in each situation
- Margin of financial safety
- The sensitivity of the profit for each element
Types of scripts can analyze
- Optimistic scenario: Price increase, cost, stable → point lower → increased profits fast
- Scenario average: Based on the data plan of the business
- Pessimistic scenario: Price decrease, rising input costs → point higher → risk of losses if not well controlled
Illustrative example
Business plan:
- Sell 10,000 products/month
- Selling price per product: 100,000 VND
- Variable costs: 60,000 VND
- Fixed cost: 400 million VND
Scenario 1 – normal:
- The breakeven point = 400.000.000 / (100.000 – 60.000) = 10.000 products
Scenario 2 – increased Cost of raw materials:
- Variable costs increase to 70,000 VND
- The breakeven point new = 400.000.000 / (100.000 – 70.000) = 13.333 products
→ Business to sell more 3.333 products just to keep the “no hole”
Scenario 3 – Price reduced:
- Sale price reduced 90.000 VNĐ, variable costs keep the
- The breakeven point = 400.000.000 / (90.000 – 60.000) = 13.333 products
→ Results like the case of increased costs
Practical value
- Understand the sensitivity of the breakeven point before the change factor
- Actively planning to respond in the worst situation
- A decision to invest, expand based on the level of acceptable risk
- Optimal pricing strategy and cost control when market volatility occurs
4. Application analysis the break-even point in business-to-business
Analysis of the breakeven point is not just a financial tool to help businesses determine the minimum turnover to be achieved in order to not suffer losses, but also plays an important role in the strategic decisions. When applied properly, it helps business optimal selling price, scaling, logical and control of financial risks more effectively.
4.1. Determine the minimum price to guarantee a profit
One of the most important applications of break-even analysis is to help the business determine the minimum selling price need to book to guarantee a profit. If the business is pricing the product too low, the revenue may not be enough to cover fixed costs, leading to losses. Conversely, if the price is too high, customers can leave and go to competitors.
The formula helps businesses determine the minimum selling price based on the breakeven point:
The minimum selling price = (fixed Costs + variable Costs) / Number of products is expected to sell
For example: A manufacturing enterprise bottled water has a total fixed cost every month is 500 million, the variable cost per bottle is $ 2,000. Business expected to sell 100,000 bottles per month. Then:
The minimum selling price = (500 million + 100.000 × 2.000) / 100.000 = 7.000 vnd/bottle
This means that if the business selling bottled water bottom prices 7.000 vnd/bottle, they will not be able to reach the breakeven point.
The influence of strategy discount, promotion to the breakeven point
The program discounts, promotions are often used to stimulate consumption, but if not carefully calculated, they can cause the business to fall into a state of loss.
For example:
- If the business sale discount 10%, they should calculate the amount of products sold be enough to offset the revenue lost due to discounts do not.
- If the cost of production does not change, but the selling price decreased, the breakeven point will increase, which means that businesses have to sell more to offset fixed costs.
Formula for calculating the number of products to be sold when the price reduction:
Output air new capital = Total fixed costs / (Price – variable Costs per unit)
This helps business decision whether to apply the program that promotion or not, and if there is need, how many products to ensure still achieve desired profit.
4.2. Strategic orientation of business scale
Businesses often expand production or enter new markets when they believe that the revenue can pass the breakeven point.
Break-even analysis help businesses answer the important questions such as:
- When the output current large enough to expand the plant, or buy more equipment?
- Whether the extension can help reduce variable costs per product and enhance profitability not?
- The market has enough potential to ensure revenue pass the level of new capital after the extension not?
For example: A manufacturing enterprise candies are sold 10.000 box cake per month and the revenue breakeven. When businesses want to double yields of up to 20,000 boxes, fixed costs also increased (due to hire more staff, buy more machinery). Businesses need to calculate whether the revenue expectations from the market are enough to offset the fixed costs new.
Application analysis of the breakeven point to calculate the increase in cost when production expansion
The expansion of production scale, usually pulled by an increase in fixed costs (for example, the rental cost, investment in new production line). To ensure the decision to expand is reasonable, businesses need to forecast the increase in revenue compared to the increase in fixed costs.
Formula to calculate the new revenue to be achieved when scaling:
The minimum revenue after expansion = (new fixed Costs + variable Costs new) / gross profit margin
For example:
A business, production of furniture are revenue of 10 billion/year, with fixed cost 3 billion and gross profit margin of 40%. If the business wants to expand production with fixed costs increased by 5 billion/year, the minimum revenue needed to achieve to not be the hole is:
The minimum revenue after expansion = (5 billion + variable Costs) / 40%
If the business is not sure that the increase in revenue after expansion can exceed this number, then decided to expand can be too risky.
4.3. Determine the point holes (Break-even Risk) to avoid financial risks
Break-even analysis helps to determine the level of revenue should reach to non-hole support companies to assess the financial risks.
One of the greatest risks for businesses is the breakeven point is too high, make business easily affected if market volatility or declining revenue.
Formula for calculating the minimum turnover to avoid heavy losses in the case of sales decline:
The minimum revenue to maintain operations = fixed Costs / (Rate of gross profit – Margin market risk)
For example:
If a business has a fixed cost is 2 billion/year, gross profit margin of 50%, but the market can drop in sales of 10%, the minimum turnover to avoid risk is:
The minimum revenue = 2 billion / (50% – 10%) = 5 billion
This helps businesses prepare a backup plan when the markets fluctuate unexpectedly.
Applications in financial forecasting, budget planning and cash flow management
The analysis also supports businesses in the financial forecast and budget planning by:
- Predict the revenue to be achieved under each scenario different business.
- Construction cost plan and cash flow in accordance with the financial situation real.
- Evaluate profitability while expanding product portfolio or test new business models.
5. Common mistakes in analysis, breakeven and how to fix
Break-even analysis is an important tool to help businesses make financial decisions and business strategy. However, many businesses suffer from these common mistake when calculating or apply the breakeven point in fact, lead to the financial decision is not correct. Here are three common mistakes and how to fix to help businesses manage finances more effectively.
5.1. Just focus on fixed costs that ignore market factors
Some businesses only focus on reducing fixed costs, which do not assess the influence of market and customer needs. They cut costs, rigid, such as reduction of personnel, the office rent cheaper or reduce budget marketing, which does not assess whether these changes can negatively affect the revenue or not.
How to fix
- Analyze the market before the cut fixed costs: Businesses need to perform research on customer behavior, market trends and customer feedback before you decide to reduce any fixed charges whatsoever.
- Optimal concentration instead of just cut: Instead of cutting budgets, marketing, business can move on to the methods of digital marketing to reach customers with lower cost but more effective.
- Combined analysis of competitors: Determine whether the business in the same industry have fixed costs and how material can maintain competitive advantage when adjustment costs are not.
5.2. Do not consider factors change of variable costs
Many businesses assume that variable costs are always fixed on each unit of product, when in fact, this cost may change according to the scale of production and market. When the scale of production increases, businesses can take advantage of economies of scale to reduce the cost per unit of product. Conversely, if the scale decreases, variable costs can increase due to not achieve the level of discount from the supplier.
For example: A business production food import raw material in bulk to get better prices. When production fell due to the market demand is low, businesses have to import raw materials, with orders more, causing the price of raw materials per unit of increase higher than originally expected. If the business doesn't update the data in the analysis of the breakeven point, they can take out sale price do not match.
How to fix
- Use dynamic analysis (Dynamic Break-even Analysis): Instead of using a level of variable costs fixed, businesses should analyze variable costs according to each level of output differences to determine the influence of the scale of production to the cost.
- Build script different cost: simulate the different situations when the price of raw materials increases, labor productivity changes or fluctuations in the supply chain.
- Leverage technology and AI to track expenses: Use the system analyze financial data to track variable costs in real time, and adjust the breakeven point in time.
5.3. Non-redundant elements of uncertainty in business
Analysis of the breakeven point is often made based on the assumption that the market and the cost does not change, when in fact, businesses can face more volatility as:
- The price of raw materials increases due to inflation or fracture of the supply chain.
- The interest on the loan changes, increases financial costs.
- Change tax policy, or regulatory laws affecting the cost of operation.
- The appearance of new competitors, causing revenue decreased in comparison with the original plan.
For example: A business automobile manufacturing planning breakeven based on the assumption that steel prices will remain stable. However, due to the crisis, supply chain, steel prices increased by 20%, making the cost of production increases sharply, causing the break-even point will also increase. If businesses do not have a backup plan, they may face financial risks serious.
How to fix
- Building financial scenario different: Instead of just calculating the breakeven point under one condition single business enterprise should set up different scenarios based on fluctuations in the market, including the script best, average and worst.
- Application AI to financial forecasting: tools such as Finance AI Agent can analyze historical data, trends, costs and forecast market movements, to help business owners adjust your financial plan.
- Establishment plan for cost and revenue: Enterprises should have a financial reserve fund or the alternatives to reduce the impact of fluctuations in surprise.
For example, A retail business can sign long-term contracts with suppliers to keep prices stable, avoid being affected by fluctuations in market prices. In addition, businesses can use the financial model forecasts to predict the impact of fluctuations in raw material prices up point in the next 6-12 months.
6. Finance AI Agent of Lac – support tool business break-even point analysis more accurate
The app artificial intelligence (AI) in financial analysis to help businesses improve efficiency, manage and optimize business strategy. Finance AI Agent of Vietnam is a smart solution to help businesses automate the process of analysis, breakeven, providing financial forecasts accurate, and proposed strategies to optimize costs.
Collect financial data from the accounting system and ERP
One of the biggest challenges when analyzing breakeven is the collection and processing financial data from various sources. Finance AI Agent can directly integrated with the accounting software and ERP system, to help automate the process of synthetic data, including:
- Fixed costs: office rent, staff costs, depreciation of assets.
- Variable costs: the Price of raw materials, production costs, operating costs.
- Revenue: sales Data according to each product, region, sales channel.
Instead of business to enter data manually, AI will automatically update data in real time, ensure accuracy, eliminating the risk of errors due to input by hand.
Automatically calculate the break-even point under each scenario financial
Different calculation methods traditionally Finance AI Agent can build many financial scenario different to help businesses assess the degree of influence of each variable to the breakeven point.
Enterprise alerts when cost or revenue have unusual fluctuations
One of the biggest risks in the analysis of the breakeven point is the sudden change of the cost or revenue that the business doesn't react. Finance AI Agent provides system alerts, auto business help early detection of problems such as:
- Production costs increased abnormal due to raw material scarcity.
- Revenue decreased suddenly due to market fluctuations or competitors launching new products.
- Operating costs exceeded the budget, the risk increases the breakeven point.
Besides, data analysis, Finance AI Agent also propose solutions to help businesses optimize the breakeven point, including:
- Reduce fixed costs: AI analyzes in detail each category of cost, determine what expenses are not effective can be cut without affecting business operations.
- Optimized price: AI proposed selling price reasonable to reach the breakeven point faster, while maintaining competitive advantage in the market.
- Adjust product strategy: If the business has many product lines, AI will calculate whether products have a high profit margin and proposed to focus resources on that product in order to reach the breakeven point faster.
Lac Viet Financial AI Agent to solve the “anxieties” of the business
For the accounting department:
- Reduce workload and handle end report states such as summarizing, tax settlement, budgeting.
- Automatically generate reports, cash flow, debt collection, financial statements, details in short time.
For leaders:
- Provide financial picture comprehensive, real-time, to help a decision quickly.
- Support troubleshooting instant on the financial indicators, providing forecast financial strategy without waiting from the related department.
- Warning of financial risks, suggesting solutions to optimize resources.
Financial AI Agent of Lac Viet is not only a tool of financial analysis that is also a smart assistant, help businesses understand management “health” finance in a comprehensive manner. With the possibility of automation, in-depth analysis, update real-time, this is the ideal solution to the Vietnam business process optimization, financial management, strengthen competitive advantage in the market.
SIGN UP CONSULTATION AND DEMO
Analysis of the breakeven point as a guideline to help businesses optimize business operations, pricing, products, accuracy and control costs effectively. A successful business not only understand clearly the minimum turnover to be achieved but also know how to adjust the strategy to quickly pass the breakeven point and increase profits.
Related questions
1. Phân tích điểm hòa vốn để làm gì?
Phân tích điểm hòa vốn là quá trình tính toán đánh giá để xác định tại mức sản lượng hoặc doanh thu nào thì doanh nghiệp không lãi, không lỗ – tức là tổng doanh thu bằng tổng chi phí.
Mục đích chính của phân tích điểm hòa vốn là để:
- Xác định mức doanh số tối thiểu cần đạt để không bị lỗ
- Giúp doanh nghiệp lập kế hoạch tài chính, sản xuất hợp lý
- Đánh giá độ an toàn cũng như rủi ro khi mở rộng quy mô, ra mắt sản phẩm mới hoặc tăng chi phí cố định
Hỗ trợ ra quyết định giá bán, khối lượng sản xuất hoặc chiến lược thị trường dựa trên dữ liệu thực
2. Công thức tính điểm hòa vốn là gì?
Có nhiều cách thể hiện điểm hòa vốn, nhưng phổ biến nhất là tính theo sản lượng hoặc doanh thu.
a) Tính theo sản lượng (số lượng sản phẩm)
Điểm hòa vốn (Q) = Chi phí cố định\(Giá bán mỗi đơn vị – Chi phí biến đổi mỗi đơn vị)
- Chi phí cố định: Là những chi phí không thay đổi theo sản lượng (ví dụ: thuê mặt bằng, lương cố định, khấu hao)
- Chi phí biến đổi: Là chi phí thay đổi theo sản lượng (nguyên vật liệu, nhân công theo ca sản xuất…)
- Giá bán: Giá bán mỗi đơn vị sản phẩm
b) Tính theo doanh thu (VND)
Doanh thu hòa vốn = Chi phí cố định\Tỷ lệ lợi nhuận biên đóng góp
Tỷ lệ lợi nhuận biên đóng góp = (Giá bán – Chi phí biến đổi) / Giá bán
3. Phân tích điểm hòa vốn giúp xác định điều gì?
Phân tích điểm hòa vốn không chỉ đơn thuần trả lời câu hỏi “bao nhiêu là đủ?”, mà còn mang lại nhiều giá trị quan trọng trong quản trị:
- Xác định ngưỡng an toàn của doanh nghiệp: Doanh nghiệp sẽ biết nếu doanh số thấp hơn điểm hòa vốn thì chắc chắn sẽ lỗ, từ đó có chiến lược kiểm soát chi phí hoặc gia tăng doanh thu.
- Đánh giá độ rủi ro trong kinh doanh: Nếu điểm hòa vốn quá cao so với sức mua của thị trường, doanh nghiệp cần xem xét lại kế hoạch sản xuất, định giá, hoặc kênh phân phối.
- Lập kế hoạch đầu tư, mở rộng quy mô: Khi tính toán thêm chi phí cố định mới, doanh nghiệp có thể dự đoán doanh số phải tăng bao nhiêu để vẫn duy trì lợi nhuận.
Ra quyết định định giá sản phẩm: Phân tích giúp xác định mức giá tối thiểu cần bán để có lãi, từ đó đưa ra chiến lược định giá phù hợp với chi phí và thị trường.














