The method of calculating the price of includes 6 main method as popular as: Simple (direct), norm (rate), number System, step Stool, exclusions, products and orders. Choosing the right method to help businesses properly reflect the actual cost control, cost effective as well as business decisions more accurate.
Many businesses today still troubled by the application of machinery a method of allocating the cost is not reasonable, or lack of tracking product orders. This makes the price not reflect the consumption of resources, which leads to deviations in pricing, profitability analysis and decision making management.
The article below Lac Viet will help the business understand 6 pricing methods of present common conditions apply and practical value of each method in production management.
1. The method of calculating the price is what?
The method of calculating the price is the accounting collection, classification and allocation of production costs to determine the price for each objects such as products, orders, works or stage. Each method is built according to the production characteristics as well as target cost management own, so there is no method suitable for all models. This is not only a tool of financial accounting, but also is an important basis for the management decisions.
The role of pricing methods in business
Choose, apply the correct method of price calculation requires not only accounting but also bring many practical value to management in the context of cost of production are coming under increasing pressure. Specific pricing methods to help business:
- Determine the price of accuracy & consistency: clarify which expenses are charged to the price, costs would need to allocate and allocate according to any criteria, from which ensure data stability to the basis between the states.
- Building foundation sale price & guaranteed profitto help businesses understand the cost structure of the product, properly calculate the profit margin, as well as actively adjust the selling price or cost structure.
- Support cost control & analysis production efficiency: product identification, stages or orders less effective to take measures to improve, remove, or re-structure.
- To meet the requirements management & regulatory compliance accounting: ensure the accounting of cost, pricing into line with current regulations, at the same time improve the quality of service information of internal administration.
In summary, the method of calculating prices not only serves financial reporting, but also the webmaster tools help business control costs, improve operational efficiency, as well as decisions based on reliable data.
2. Why business need understanding & choosing the right methods in the price?
Understand and select the right method of calculating price to help businesses control costs, pricing, accurate decision-making efficiency. Conversely, how do the estimate or apply machine easily lead to false data, risk in the operation.
Specifically, choosing the right method to help businesses:
- Avoid deviations prices lead to wrong price & weight gains: Price is base building price. If false, the business can sell below the cost price or overvalued compared to the market, reducing the profit or loss of the ability to compete.
- Advanced ability to control costs as products, orders, & stages: Suitable methods to help businesses clearly see the costs incurred where, every stage, wasting and products which are team cost. From that actively adjust production planning, purchase.
- Analyze profit and loss exactly according to each product, the contract: Businesses can determine which products make a profit, main product, any marginal, low, or potential risks hole, as the basis for the decision to continue, improve or remove.
- Meet compliance requirements as specified current accounting (Circular 99): Business organizations have accounting cost selection method, calculate the price of conformance to production, guarantee of data, consistency and possible explanations. Failure to comply may lead to the data, the lack of reliable, hard-settlement as well as the risk-adjusted, arrears.
3. The method of calculating the price of products in the production of today's popular
Every business has various peculiarities about the process, product, and organization costs, should be selected calculation method, reasonable price. Here are the pricing methods are commonly used in manufacturing enterprises in Vietnam.

3.1. How to calculate price according to the method of simple (direct)
Calculate the price according to the method of simply determine the price by taking the total manufacturing costs incurred in the period divided by the number of finished products, i.e. whole set cost and evenness for each product. This method does not require tracking of expenses according to the stages or under orders, should be relatively simple to apply.
Formula:
(Price unit = Total cost of the actual production during the period / Number of finished product)
In which:
- The total cost of the actual production in the states: cover the entire cost of direct material cost, direct labour and production overhead incurred in the period related to the finished product.
- Number of finished product: is the number of products has ended the production process, eligibility to enter the warehouse or delivered in the states.
Businesses should apply the method when:
- Business only produce a kind or very little product type
- Short production cycle, the finished product quickly
- Costs incurred between the product does not have a big difference
For the small business & medium, this method brings:
- How to calculate simple, easy to deploy
- Easy inspection and collation of data
- Suitable when resources accounting limited
However, this method is only effective when the product structure is simple. When the business expanded product portfolio, this method can no longer properly reflect actual costs.
Illustrative examples: In September, business of producing 1,000 products. The total cost of the actual production is 500 million.
The price of units is determined as follows:
500 million / 1,000 products = 500,000/product.
3.2. The method of calculating the price by a factor of
Method, system number is used when a production process produces many different products, but the cost incurred can't separate right from the start for each product.
Formula: Price of unit product i is determined by the formula
(Price unit of product i = [Total cost of production × coefficient of conversion of the products i] / Total output conversion)
In which:
- Total production cost: the Full cost incurred in the period of the production process joint (raw materials, labor, overheads...).
- The coefficient of conversion of the product i: coefficient reflects the level of consumption cost of each product compared to standard product.
- Total output conversion: the Total number of products of each type multiplied by the corresponding coefficients.
The main characteristics of this method are:
- Nature methods, the coefficient of: Business conversion different products on a standard product through the system specifications, then allocate costs according to the level of consumption relative of each type of product.
- How to determine the coefficient of conversion: Coefficient is constructed based on weight, volume, time, the technical levels or consumption of raw material of each product.
- In accordance with the business manufacturing many products of the same process: In accordance with enterprise producing many kinds of products on the same line, the same process technology, but there is consumption costs are different.
- Advantages in the allocation of general expenses: Help allocate common costs more reasonable compared to allocate, on average, reflect the level of use of resources of each product and limited product status this “burden cost” for other products.
In summary, how to calculate the price of products by a factor of helping businesses to allocate costs more accurately in the environment produce multi-products. At the same time improve the quality of information, price, service management, decision making.
Illustrative examples: A business, chemical production has a production process generally produces 2 types of products: product A (standard) – product B (technical requirements higher, consumption is much more cost). In January, the business has data as follows:
- The total cost of production incurred in the period, total cost: 300 million
- Actual output: product A: 1,000 units – product B: 500 units
- Number system conversion: product A: 1,0 (standard product) – product B: 1,5 (consumable costs 50% higher than A)
Step 1: convert the output of standard product
- Output conversion A = 1.000 × 1,0 = 1.000
- Output conversion B = 500 × 1,5 = 750
Total output conversion = 1.000 + 750 = 1.750 unit standard
Step 2: Determine the cost for 1 unit conversion
Cost for 1 unit conversion = 300.000.000 / 1.750 = 171.429 copper / units conversion
Step 3: Calculate the price of units of each product
- The price of product A = 171.429 × 1,0 = 171.429 copper / unit
- The price of product B = 171.429 × 1,5 = 257.144 copper / unit
3.3. The method of calculating the price in proportion
The method of calculating the cost of the rate is used to allocate common costs for many kinds of products have texture similar to each other, based on the ratio has been business established ago.
Formula for calculating price:
Step 1: Determine the total cost of the plan (or norm) of the product
[Total price of plan = Σ (Production of each product × Price plan/norm)]
Step 2: Determine the percentage allocation of costs
(Allocation rate = Total actual cost incurred / Total price of plan)
Step 3: Calculate the price of each product
(Price fact each product = Price of plan of product × Rate allocation)
The method of calculating the price in proportion to has the characteristics such as:
- Another method coefficients: The method of coefficients based on the consumption technique to exchange the product, while the method of proportional allocation of costs in proportion to the price of the plan or standard was build management plan and more.
- In accordance with the business manufacturing many of specification, sample different codes of the same type of products as well as have data about the price of the plan or the level is relatively stable.
- Help allocate costs fast, easy to control fluctuations in cost between the actual and planned. Convenient for analysis of variances, control production efficiency.
In summary, the method according to the matching rate of business product portfolio diversity, but the cost structure is relatively the same had planned system cost allocation base.
Illustrative examples: A business of producing plastic packaging there are 2 types of products with the same production process: product A – product B
Price city planning and production
| Products | Output | Price plan (copper/sp) | The total price of the plan |
| A | 1.000 | 80.000 | 80.000.000 |
| B | 500 | 120.000 | 60.000.000 |
| Total | 140.000.000 |
Total production costs actually incurred in the period: 154.000.000 dong
Step 1: Determine the ratio of cost allocation
Allocation rate = 154.000.000 / 140.000.000 = 1,1 → actual Costs higher than the planned 10%
Step 2: Calculate the price of reality each product
- The price of the actual product A = 80.000 × 1,1 = 88.000 vnd/sp
- The price of the actual product B = 120.000 × 1,1 = 132.000 copper/sp
3.4. The method of calculating the cost of orders
The method of calculating the cost of each order is applied when the product is produced according to individual requirements of each customer, as well as each order has the characteristics, different cost.
Formula:
(Price, order = CP NVL direct + CP NC direct + CP SXC allocation)
Or write full: (Zđơn rows = ∑CP NVLTT + ∑CP NCTT + ∑CP SXC)
In which:
- CP NVLTT: Raw material costs directly incurred for orders
- CP NCTT: Cost of direct orders
- CP SXC: Production overhead is allocated to orders according to the criteria match (man-hours, labor cost, machine running...)
This method has the main characteristics:
- Scope of application: In accordance with on-demand manufacturing, single or according to the contract, such as mechanics, construction, machining, design and manufacturing under the order.
- Aggregating cost: All cost of materials, labor and overheads are tracked separately for each order or contract; the price is determined only when the order finished.
- Help business control interest – hole detail to the contract early detection orders less effective as a basis for negotiating the price for the next orders.
In summary, the method according to the orders help businesses manage the cost efficiency at the level of detail high. Especially important for the manufacturing industry according to the contract, according to the individual requirements of the customer.
Illustrative examples: Business get Order A machining according to customer requirements.
The actual cost incurred for orders A:
CP NVL direct = 120.000.000 dong
CP NC direct = 60,000,000
CP SXC allocated = 30,000,000
- Price of order A is defined:
ZA = 120.000.000 + 60.000.000 + 30.000.000 = 210.000.000 dong
- If the sale price under the contract is 250.000.000 is:
Gross profit = 250.000.000 − 210.000.000 = vnd 40,000,000
3.5. The method of calculating the cost of each process in the production stage
The method of calculating the cost of each process is applied when manufacturing activity takes place continuously, the products have to go through the next stage, and the cost need to be followed in each stage.
Formula:
- For every stageprice is determined as follows
(Rates of stage i = CPDD early states i + CP arises stage i − CPDD end of period i)
Or sign: Zi = CPDDđk(i) + CPps(i) − CPDDck(i)
- The price of semi-finished products or finished products final:
(Z product = Z stage 1 + Z stage 2 + ... + Z stage n)
In which:
- CPDDđk: product Cost of uncompleted states
- CPps: Costs incurred in the states at stage
- CPDDck: the Cost of unfinished products end of the period (already calculated according to the level of completion)
This method has the main characteristics:
- Characteristics method: Production costs are set according to each stage or phase of production; the price is calculated sequentially from stage before moving on to the following stages.
- Processing cost of unfinished products: The accountant must determine the level of completion of the unfinished products at each stage to allocate a reasonable cost, avoid distorting prices.
- Scope of application: In accordance with the industry, continuous production, large volume, such as food, chemical, textile, cement, paper.
- Benefits administrationTo help businesses control costs, performance at each stage, early detection stitch arise waste or cost, unusual to make timely adjustments.
In summary, how to calculate the price of products according to the process help businesses manage costs international shipping practice, particularly effective in the production model, continuous and multi-stage.
Illustrative examples: The enterprise chemical production through 2 stages.
Stage 1:
- CPDD early states: 50,000,000
- CP arises in the states: 200,000,000
- CPDD end states: 30,000,000
Price of stage 1:
Z1 = 50.000.000 + 200.000.000 − 30.000.000 = 220.000.000 dong
Stage 2:
- CPDD early states (switch from stage 1): 220.000.000 dong
- CP arises in the states: 120.000.000 dong
- CPDD end states: 20,000,000
Price of finished products:
ZTP = 220.000.000 + 120.000.000 − 20.000.000 = 320,000,000 vnd
3.6. The method of calculating the price of the norm
The method of calculating the price of the norm is the administration tool to help businesses not only “calculated” cost, but also “managing” costs right from pre-production took place through the establishment of cost standards for each element.
Formula:
(Price, actual = Price of norm ± disparities than the norm)
In which:
Difference = actual Cost − the Cost norms
Details under each cost element:
- Difference NVL = CP NVL fact − CP NVL norm
- Spread the = CP NC reality − CP NC norm
- Difference general expenses = CP SXC fact − CP SXC norm
The method of calculating the price of this is expressed through the:
- Price norms: Is the cost of previously established for a unit of product, based on the consumption of raw materials, labor cost and overall production in the conditions of production normal.
- The role of norms in cost management: Norm is a standard of comparison for cost planning, construction, production budget, as well as control over the use of resources during operation.
- Compare actual costs & norm: Collation between the actual cost incurred and cost norms help business timely detection of deviations, waste, loss or points of congestion in the production process.
- Value management in modern production: This method supports the enterprise moved from management to administration actively advanced the discipline cost as well as promoting continuous improvement.
In summary, rating method, the norm to help businesses control costs in a standard clear, transparency, efficient use of resources to enhance the quality of management in the production environment of competition.
Illustrative examples:
Construction business price norms for product 1 as follows:
- Raw material norm: 300,000
- Workers norms: 120,000 vnd
- Production costs general norms: 80,000 vnd
Price norms: 300.000 + 120.000 + 80.000 = 500,000/products
In fact, the costs incurred:
- Material fact: 320.000 dong
- Employees fact: 115,000 vnd
- Cost general fact: 90,000 vnd
The price of reality: 320.000 + 115.000 + 90.000 = 525.000/products
The difference compared with the norm: 525.000 − 500.000 = +25,000/products
Business need analysis of causes beyond the level to adjust the process, control cost in the next period.
4. The criteria for selecting the right method
The choice of the method of calculating the price should not be based on habit, or apply according to the model of other business, which should be based on production characteristics and the capacity of management and actual value of each business.
The main criteria to consider include:
- Industry manufacturing: Production units, according to the order, mass production or continuous production will match with the various methods (order, process, system, number, rate,...).
- Enterprise scale: Small business is often preferred the simple method, easy to deploy; big business, multi-product need more detailed method to control the cost effectively.
- The level of complexity of the product: The product as a diverse range of ways, configuration, stages, it requires method of cost allocation as sophisticated correctly.
- Capacity accounting system: Personnel qualifications, accounting procedures and the level of support of the software decide on the possibility of applying the method has high levels of complexity.
In summary, the right method is the method reflects the true essence cost, to meet the requirements management can operate stable in real terms of business.
5. The note should hold when applying the method of calculating the price of
Choosing the right method of calculating prices is a necessary condition, but is correctly implemented in practically new condition is enough to prices reflect the cost to support decision governance. Businesses should especially note the following points:
- Does not apply machinery according to the book: The method of calculating the cost of books, because every business has the scale processes, as well as the degree of automation is different. If not, adjust accordingly with actual data rates of false, and a loss of value management. How to calculate the price of the products need to be tailored specifically for each model specific production.
- Updates as the production process changes: About technology, clips or norms, businesses need timely updates pricing methods and related data. If not, the material prices will quickly outdated, misleading analysis, cost – profit as well as the decisions of management. Meanwhile, the price may be right about accounting techniques, but no longer true about the actual operation.
- Ensure there is tool support fit: The price manually or with spreadsheets, discrete, easily cause delays, errors and difficult to control when data is growing. Accounting software or ERP to help automate the collection, as well as cost allocation, ensuring data consistency in real-time. Thanks to that, accounting, reduce work load to leadership with timely information and reliable for decision-making..
In summary, the method of calculating price only effective when be flexible and updated frequently have the support system fit. When that price is true not only in accounting but also the right of the administrator, became the basis of reliability for decisions about price, production plan and business strategy.
6. Accnet ERP – accounting solutions cost effective products for business
AccNet ERP is the solution accounting – admin is designed in accordance with special production enterprise in Vietnam, business support directly addressed the common problem in the calculated price. AccNet ERP helps businesses:
- Automatically set costs under each method, calculate the price of: The system of collecting data, the cost of raw materials, workers, as well as general expenses according to each stage of production, saving time synthesis and reduce errors.
- Calculate the price of fast – accurate according to the product – order – stage: In production, each batch of goods or products that constitute the different costs; AccNet ERP ensures flexibility in the application of the method as the cost of fixed rate or the actual cost to reflect the cost of production of each product.
- The data connection between accounting – inventory – production – sales on a single system: Data is shared constantly updated in real time between the parts, to help eliminate the status of discrete data, reduce deviations, as well as improve coordination internal.
- Provide reports, price analysis – service management – decision makingReport : be synthesized automatically, clearly presented under each scenario costs help managers timely recognition for extraordinary expenses, take strategic decisions more accurate.
ACCOUNTING SOLUTIONS ACCNET ERP INTEGRATED AI AUTOMATE ALL BUSINESS AccNet ERP is a software solution financial accounting integrated in the management system, comprehensive enterprise, which is developed by Lac Viet corporation. Difference highlights of AccNet ERP is the app artificial intelligence (AI) in many accounting process to help businesses: Thanks to that, AccNet ERP not only is support tool but also a “smart assistant” with the business in financial management transparent effect. Feature highlights: ✔️ Automatic accounting vouchers, collate public debt thanks to AI. TYPICAL CUSTOMERS ARE DEPLOYING ACCNET ERP SIGN UP TO RECEIVE DEMO NOW INTEGRATED AI ACCELERATION CONVERTER OF ACCOUNTING AI in AccNet ERP't just stop at automate data entry, but also: BUSINESS IS WHAT WHEN IMPLEMENTING ACCOUNTING SOFTWARE LAC VIET? See details, feature & get FREE Demo CONTACT INFORMATION:
✔️ Manage your finance – accounting multi-branch, multi-subsidiary.
✔️ Financial statements consolidated standards of Vietnam & international (VAS, IFRS).
✔️ Cash flow management, budgeting, forecasting the exact cost.
✔️ Connect with the manure management system, hr, production, sales to sync data.
✔️ Integration of AI in data analysis, risk warning and proposed optimal scheme.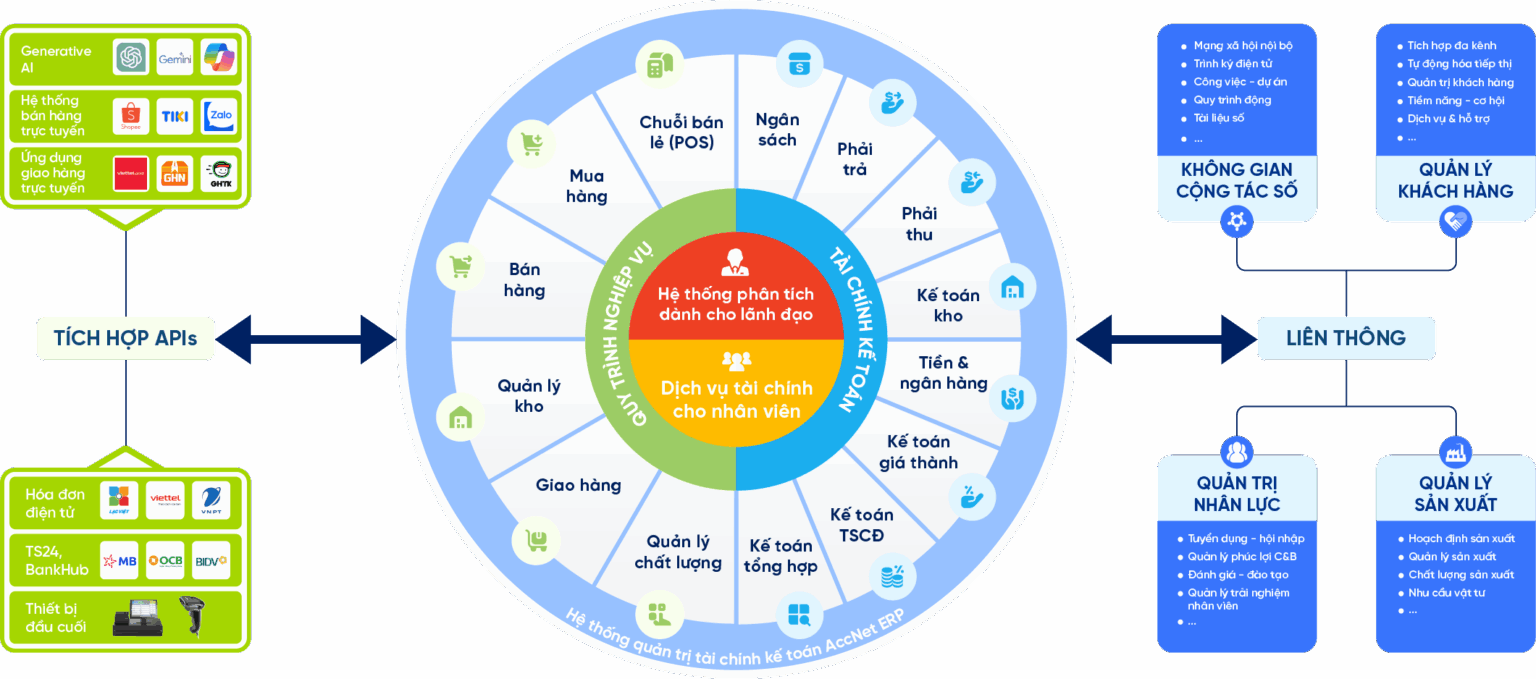
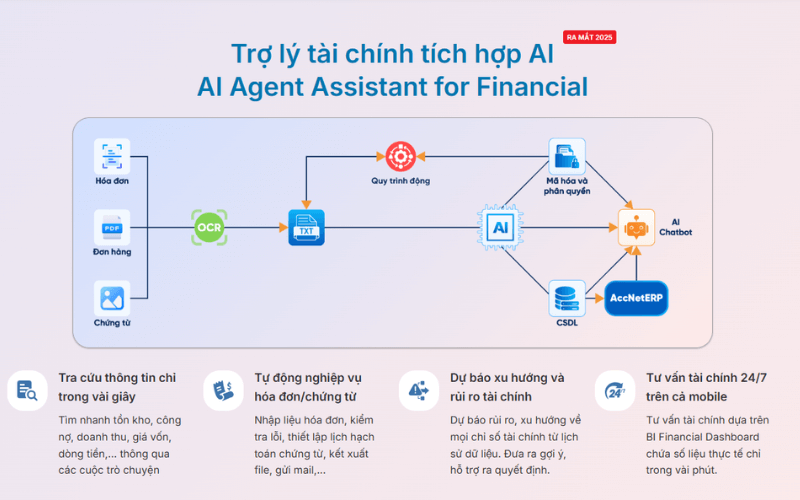
AccNet ERP not only help calculating the right price, but also bring greater value to business through shortening the synthesis time, cost transparency data rates of between the parts in order to improve the quality of decision management thanks to the metric system timely, consistent, reliable.
The method of calculating the price plays a pivotal role in helping businesses control costs, properly evaluate production efficiency in the construction business decisions based on real data. The selection as well as apply the right methods not only ensure the accuracy of product prices, but also support the management effectiveness analysis according to each product line, and each production stage. On that platform, enterprises can enhance financial transparency, optimize resources towards sustainable development in the long term.














