In business operations, financial statements, not merely as a mandatory procedure for filing for tax authorities or service audit. This is a documentation system fully reflects the “financial picture” of the business in a period of activity: business owns what, how much debt, business performance and cash flow are operating like.
However, in fact, many business owners, operating departments still not have a clear specific structure of financial statements, what to include, each part has meaning, the need to set up how to apply to internal management for efficiency. This leads to the condition reports only to “deal” that miss an opportunity to use financial statements as a tool to support executive decision-making strategy.
In this article Lac Viet will help you:
- Financial statements what is? Role in business operations
- Financial statements, what to include? Full structure according to current regulations
- Suggestion tool supported analysis report more effective
1. Financial statements what is? Role in business operations
1.1. Concept
Financial reporting is the overall picture of the financial situation and business results of the business during an accounting period, typically by a quarter or a year. Show the information about the assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, expenses, profit and cash flow.
Learn a simple way, if the business activity of the enterprise is a movie, the main financial statements that summarize the contents of the film it through the numbers to help managers, investors or tax authorities catch “what is happening” with the company – there is growth or risk, there is cash flow healthy or are losing control.
For example: A business has financial statements for the year 2023 recorded profit after tax 12 billion, but the net cash from business operations to 5 billion. This suggests the business may be of interest on papers but the problem really about cash flow, should be more in-depth analysis to have the solution.

1.2. Who uses financial statements?
Understand object used to help businesses identify what information to present clear, transparent, and valuable action:
- Tax authorities: used to determine tax obligations, review of compliance with regulations on accounting – tax.
- Business leaders: used to capture the entire financial situation, cost control, cash flow management to take strategic decisions or adjust the plan works.
- Banks and investors use to assess the likelihood of debt payment, the level of financial risk and potential profit before loan or pouring capital.
- Business partners: can refer to the financial statements, when should assess the level of financial credibility before you decide to sign contracts or long-term cooperation.
1.3. The role of financial reporting for business
- Manage cash flow, assets, liabilities: A business can be a large margin on the report business results, but it is “money” in fact. Financial statements, particularly statements of cash flows help the business early detection status imbalance the flow of money from that plan to manage debts and recover the money the sale and allocation of investment costs reasonable.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of business activities: Through indicators such as net revenue, gross profit, profit margin, net leaders can see the trading activity is operating effectively or are wastage because the price is high capital costs, management costs or increase revenue does not reach expectations.
For example, If the revenue increased, but net profit fell, can businesses are spending excessive for marketing or to reduce the selling price to compete from which to adjust product strategy.
- Base investment decisions, loan, distribute the profits: investment planning or expansion of production (if you see equity strong, stable cash flow); a decision on bank loans or call for investors (if liquidity ratios and profitability good enough); distribution of profits or retained for re-investment (based on profit after tax and cash flow remaining)
- [FULL] the Sample financial statements, financial situation excel file according to the circular, 200 and 133
- Financial statements consolidated what is? Instructions for setting up and reading effective for business
- Guide to writing a financial report according to circular 200 details for the business
- Guide how to read financial statements easy to understand for business want to manage financial efficiency
2. Financial statements, what to include? Full structure according to current regulations
A the model financial statements fully reflect the comprehensive financial status, business performance and cash flow of the business. According to current regulations (circular 133 and circular 200 of the Ministry of Finance), financial statement consists of 4 or 5 main ingredients, depending on the scale of business and accounting application.
2.1 the balance Sheet
Balance sheet (bcdkt) is a financial statement important subject is the entire property that the business owns, capital formation should that property be closed at a specific time (usually end of the month, quarter, or year).
Learn simply, this is the “financial picture taken at a time” to help businesses with stakeholders a clear view business are what (property), is how much debt (liabilities) and how much is the real owner of business owner (equity).
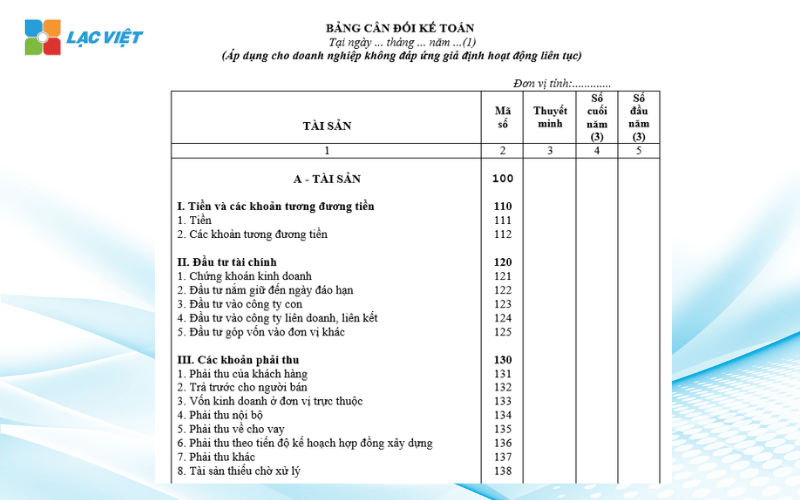
The balance sheet is divided into two big sections:
a. Property
Assets are what the business is holding to serve manufacturing business. Consists of two main groups:
Short-term assets: Are those assets that can be converted into cash or consumed within 12 months (or 1 business cycle). Includes:
- Cash and bank deposits
- Inventory
- Accounts receivable
- Prepaid expenses short-term
Long-term assets: these assets have the time used on the 12 months. Includes:
- Fixed assets (such as machinery, factories, trucks)
- The cost of unfinished construction
- The financial investments in the long term
- Prepaid expenses long-term
b. Capital (also called source assets)
Funds for know the business take money from where to forms of property are. Includes:
Liabilities: Is the property obtain from the borrower or unpaid. Includes:
- Short-term debt: loans, debts need to pay within 12 months
- Long-term debt: bank loans, issuance of bonds or debt finance lease long-term
Equity: Is the property really belongs to the business, including:
- Capital contributed by the owner (charter capital)
- Profits not distributed
- Investment and development fund
- Difference revaluation of assets
Recipe crux of the balance sheet always right is: Assets = Liabilities + Equity
Practical value the business receives:
- Understand the financial structure at present: Businesses are more dependent on debt or equity capital? Have enough assets to rotate capital or not?
- Decisions based on the basis of specific financial: There should invest more in fixed assets not? Need to cut property is not effective or renegotiate the loan?
- Enhance accessibility of capital: A balance sheet, clear healthy will help your business easily access financing from banks or investors.
2.2 report the results of business activities
Report results of business activities (referred to as reporting business results) is reported financial said in an accounting period, business profit or loss, interest and from where and for what. Other than the balance sheet showing the “snapshot finance at a time,” reported business results again reflect the “place of business” during a period (usually a month, quarter, or year). The main purpose of the report is to provide a comprehensive view of the ability to make a profit, based on the comparison between revenue – cost.
This report usually presented in order from the total revenue to profit eventually, including the following criteria:
Net revenue on sales – service provider
- Is the total revenue from sales minus the deductions such as trade discounts, sales returns, discounts sale.
- This is the number that reflects the true revenue that the business received from the main business activities.
Cost of goods sold
- The direct cost to create products/services sold, including the cost of materials, direct labour, cost of production,...
- The price of capital as low as compared to revenue, profit margin as high.
Gross profit on sales/service provider
- Is calculated by:
Gross profit = net Sales – cost of goods sold - This is the only important number to know the business generates how much value from sales activities.
Cost of sales and cost management business
- Cost of sales: this includes shipping costs, marketing, commissions, promotions,...
- Cost management business: includes salary, department, office, administrative costs, office supplies, depreciation of property, administrative...
Net profit from business operations
- Is gross profit after deducting the cost of sales, cost management.
- This is the only standard is the investors, the bank and executive business interest, because it is effective from core operations.
Other profit (if available)
- Is earnings not come from the main business activities, for example, proceeds from liquidation of assets, compensation, reimbursement enter the room,...
Profit before tax
- Total net profit from business plus profit other.
Profit after corporate income tax
- Is the profit remaining after payment of the tax to The state.
This is the amount of money the business can be retained for re-investment, dividend, or fund.
Practical value the business receives:
- Determine the effectiveness for each term business: There is profit or loss? Profits come from nowhere – main activities or other income?
- Cost analysis: items which are consuming the largest budget, there are optimal is not?
- Financial planning, growth-oriented: From this report, businesses can budgeting, forecasting, profit, identify development goals reality.
2.3 statements of cash flows
Reported cash flow is an important part of the financial statements indicates the line actual money was out on business during an accounting period. Other reports business results expressed profit accounting (can still “on paper”), the cash flow statement helps the reader see clearly:
- Business income is, how much real money
- The money was paid in.
- Have enough money to pay salaries, purchase, invest, or pay the debt or not
In other words, this is the record heart rate finance of the business. A business can now report interest, but if the line is money, pussy stretching, then the risk of insolvency is still very high.
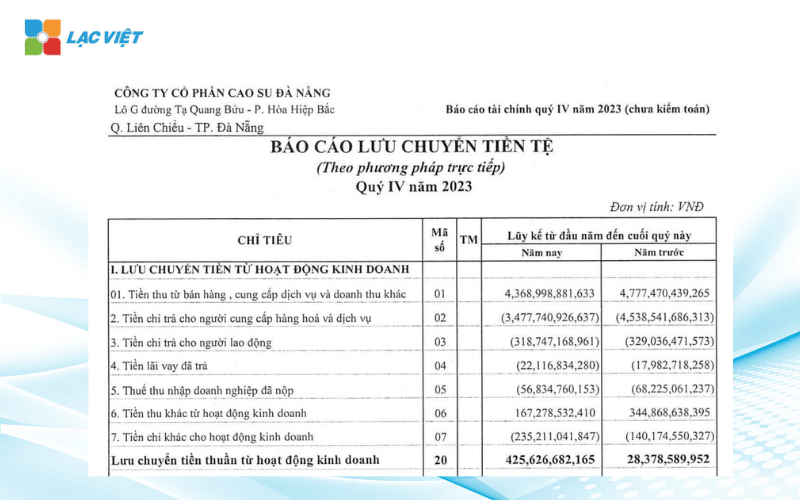
Structure report consists of 3 groups of main activities
a. Cash flow from business operations
This is the cash flow core, reflect the ability to generate cash from operations, sales, service providers, collect money from customers and spend the money to buy raw materials, pay wages, taxes, other expenses.
Significance:
- If cash flows from business operations and stable business platform financially healthy.
- If continuous sound indicates the business is to offset cash flow by borrowing or selling assets – potential risk of losing your balance.
For example: Business sales obtained 5 billion from guests, spend 3 billion for the supply of 1 billion paid → cash flow business net is +1 billion.
b. Cash flow from investing activities
Includes revenues and expenses related to long-term assets, such as:
- Shopping or liquidation of fixed assets (such as machinery, truck, workshop)
- Investment of capital contribution, purchase of shares other companies
- Income from investments, dividends received
Value identification:
- Great read for investment is a sign businesses are scaling
- Proceeds from liquidation of assets may indicate restructuring, capital recovery
Note: cash Flow investment pussy, not necessarily bad if it is offset by cash flow business ocean.
c. Cash flow from financing activities
Reflect the grants and financial obligations of the business:
- Receipt of capital contribution, loan, issuance of shares
- Repayment of the loan principal, pay dividends, buy back shares
For example: Borrow another 3 billion from the bank, repay 1 billion, dividend 0.5 billion → cash flow net financial is +1.5 billion.
Practical value the business receives:
- Early detection of risk cash flow: Whether the business can interest on the books, but if you do not have cash enough is used, all operations are stalled.
- Liquidity management better: active balance income and expenditure, avoid falling into the shortage of cash, especially at the time of payment of the debt due.
- Servicing loans efficiently: Bank special attention to the cash flow of the business when reviewing loan documents.
2.4 notes to financial statements
Notes to financial statements are an explanation, additional details for the numbers are presented in three main reports: balance sheet, report the results of business operations and statements of cash flows.
In other words, if the report there is the “combined data”, then notes is an explanation behind the numbers that help the reader understand the content, context, note-get the items accounting.
For example: balance Sheet recorded “fixed Assets tangible” is 25 billion, but explanations will let you know specifically what it is: 10 billion is a workshop, 8 billion is machinery, 7 billion is specialized vehicles, accompanied by information about the time depreciation, year put into use.
According to the accounting standards in Vietnam (VAS) and specified in the circular 200 or 133, the notes usually include the following contents:
a. Introduction about business and accounting policies applied
- Name, field of activity, scale, ownership forms
- Accounting period, the monetary unit used
- Accounting policies: the method of calculating the price of stock (FIFO, weighted average), the method of depreciation of fixed assets, exchange rates,...
Help the reader assess the level of compliance, consistency in recognition accounting.
b. Details each item in the financial statements
This section delve into structural details of the item itself, such as:
- Cash and cash equivalents: analysis of how much is cash, how much is a bank deposit, term or not
- Fixed assets: list each type of asset, cost, wear and tear accumulated value remaining usage time remaining
- Accounts receivable: the details by the customer, internal, advance, debt long day...
- Loan debt: classified as short-term/long-term debt bank loans, debt, bonds, interest rate, term, and collateral if there
- Revenues and expenses: divided according to each activity group, for example revenue, selling products, providing services, financial activities, other activities
For example: net revenue recorded as 150 billion. In theory I can only get: 120 billion from the array of retail, 25 billion from the distribution channel, 5 billion from contract maintenance services – thereby helping to assess the effectiveness each channel revenue.
c. The commitments and obligations implicit, events after the reporting date
- Committed to long-term contracts have not yet made
- The lawsuit is in the process of handling
- Large fluctuations after the end date of the accounting period as changing the shareholders, to issue additional shares, transfer of property,...
Meaning management: helping investors, banks, or the leader has sufficient information to predict risk, avoid looking only at short-term results.
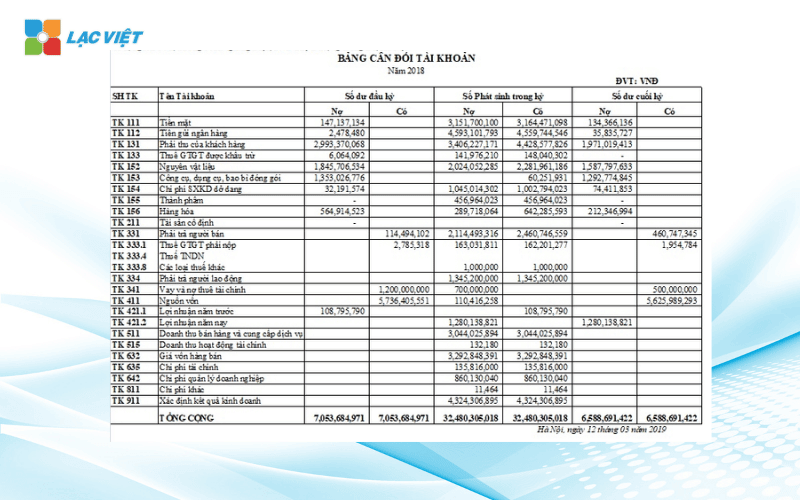
2.5 balance Sheet accounts
Balance sheet account is a report internal accounting reflects the balance of the first states arose in the period, ending balance of each account accounting. This is not a report presented to investors or the public, which mainly serves for the inspection, collated, complete bookkeeping.
As a rule, the balance sheet accounts only mandatory with the business applying circular 200, usually business to have large-scale public company, or the company has requested an independent audit.
The main structure of the balance sheet accounts:
- Account accounting: as 111 (cash), 131 (customer receivables), 331 (must be paid by the seller), 642 (cost management business)...
- Balance beginning of the period: the number exists at the time of the beginning of the period
- Arising in the states: show the recorded increase – decrease in each account
- Final balance: is the final result after subtraction between the beginning balance and incurred during the period.
Actual benefits businesses get:
- Collated data book easy: Help chief accountants detect deviations, accounting, teen or confusion before reporting financial official.
- Control transparency, internally: Is tool serves cross-check, to help minimize fraudulent or omission of the transaction.
- Prepare for audit or financial inspector: When auditors or tax authorities for screening each account, balance sheet account is clear evidence to prove the accuracy of the item.
3. Support tools set up and analyze financial statements effectively
3.1 Use accounting software for automatic synthesis report
Instead of preparing financial statements using Excel with many risks, errors, businesses today can apply the accounting software as AccNet or LV-DX Accounting to automate the process of reporting.
Benefits highlights:
- Data were aggregated automatically from the subsystem accounting (purchase, sales, stock, cash...).
- Report form is updated according to the standard circular 133 or 200.
- Reduce errors, save time, increase accuracy when filing a report to the tax authority or audit.
Values bring:
- Small and medium enterprises can standardize reporting system easily.
- Board of directors can fast track financial situation with just a few taps.
- Suit all industries, including business no accounting team strong.
3.2 application artificial intelligence with LV Financial AI Agent
LV Financial AI Agent is tools of financial analysis app AI (artificial intelligence) is developed to support the management, non-intensive financial can still understand, efficient use of financial statements.
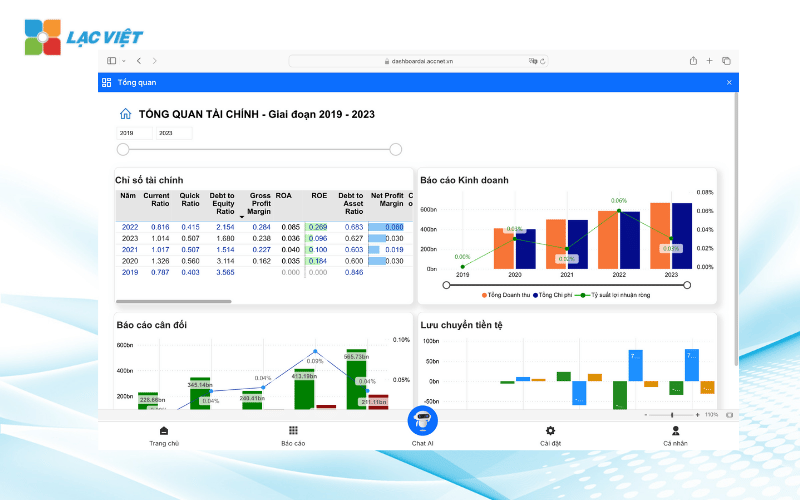
Feature highlights:
- Automatic calculation, analysis of financial indicators as important as ROA, ROE, payment rates, effective use of capital, profitability by product or unit.
- Warning indicators of anomalies: cash flow negative, debt increase high profit margin decreased...
- Hint strategic action: adjust the cost structure, cash flow, or orientation raising capital.
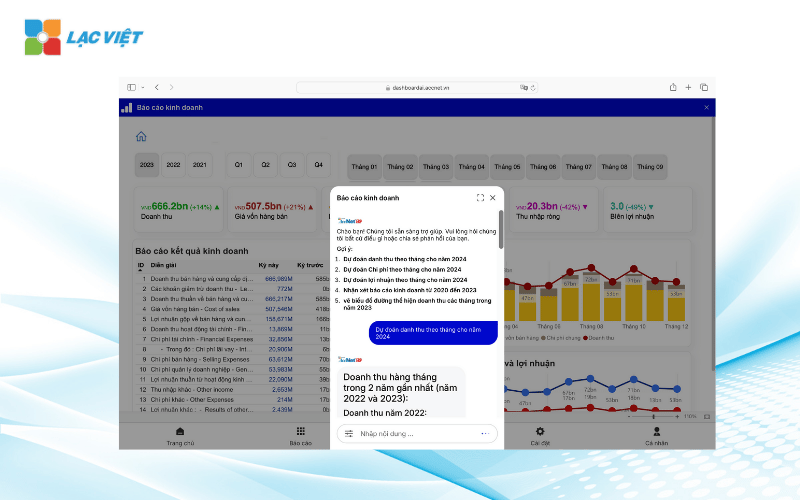
Lac Viet Financial AI Agent to solve the “anxieties” of the business
For the accounting department:
- Reduce workload and handle end report states such as summarizing, tax settlement, budgeting.
- Automatically generate reports, cash flow, debt collection, financial statements, details in short time.
For leaders:
- Provide financial picture comprehensive, real-time, to help a decision quickly.
- Support troubleshooting instant on the financial indicators, providing forecast financial strategy without waiting from the related department.
- Warning of financial risks, suggesting solutions to optimize resources.
Financial AI Agent of Lac Viet is not only a tool of financial analysis that is also a smart assistant, help businesses understand management “health” finance in a comprehensive manner. With the possibility of automation, in-depth analysis, update real-time, this is the ideal solution to the Vietnam business process optimization, financial management, strengthen competitive advantage in the market.
SIGN UP CONSULTATION AND DEMO
Understanding financial statements, what to include to help businesses comply with accounting regulations, open up opportunity management, business development in a scientific way. Each type of report – from the balance sheet, the statement of the business to cash flow was in the core information help managers see the financial situation, control the flow of money, make a decision at the right time. Business as using financial statements as a strategic tool, then as enhanced competitiveness, attract investment, sustainable growth.














